File
advertisement

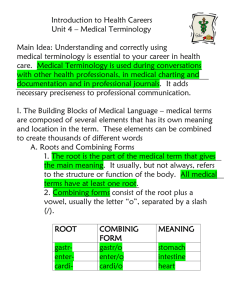
Medical Terminology Unit 1 1 Identify the three types of word parts found in medical terms Define the commonly used prefixes, word roots and suffixes Discuss the rules for combining medical terms Recognize the importance of correctly spelling medical terms Recognize how to change a medical term to its plural form. Recognize the importance of using correct abbreviations for medical terms Differentiate between terms and word parts that look-alike or sound-alike Acquire strategies for using a medical dictionary Define basic medical terms 2 Learning Medical Terminology is easy Know definitions of word roots (combining forms “/o”) Know definitions of prefixes Know definition of suffixes Understand how to put word parts together Know how to define medical terms 3 Word Roots Suffixes Prefixes 4 Also known as combining forms Foundation of most medical terms Contain basic meaning of the word Usually indicate body part involved Cannot stand alone Suffix must be added Some indicate color 5 Ot/o – Ear Hepat/o – Liver Rhin/o – Nose Oste/o - Bone Cardi/o – Heart My/o – Muscle Neur/o - Nerve 6 Must be added to all words Rules for using combining vowels apply Always added to end of word root Indicate Procedure Condition Disorder Disease 7 A prefix always comes before word Root Usually indicates Location Time Number Status Changes the meaning of the word 8 Added between root & suffix or between two word roots Make it easier to say medical term Most common vowel is “o” Combining Form Examples Cardi/o Leuk/o 9 Combining Vowel is NOT used when the suffix begins with vowel (a,e,i,o,u) Root Suffix Neur/o -itis = Neuritis itis begins with ‘i’ (vowel) Combining vowel not used – o is dropped 10 Combining vowel is used when the suffix begins with consonant Root Neur/o Suffix -plasty = Neuroplasty Combining Vowel ‘o’ is used 11 Combining vowel is always used when joining two or more roots Root Root Suffix gastr/o enter/o -itis = Gastroenteritis Roots gastr/o & enter/o are added together Combining vowel ‘o’ used Root enter/o & suffix -itis Combining vowel not needed-suffix starts with vowel 12 A prefix does not require the use of a combining vowel. The prefix is added to the front of the first word root Prefix word root suffix pericardi/o -centesis = pericardiocentesis No combining form is used after the prefix peri, but is used after the word root cardi/o, because the suffix –centesis starts with a consonant. 13 Completes term by changing root to an adjective form ac - al - ar - ary - eal - ical - ial ic - ine - ior - ory - ous - tic 14 Noun endings Completes term by changing root to noun form. a - e - um - us - y – ia – ism 15 -osis and -esis 16 Describes specific disease conditions algia - dynia - itis - malacia megaly - necrosis - sclerosis 17 Identify procedure performed on body part -centesis / -ectomy / -graphy -gram / -plasty / -scopy 18 -rrhage & -rrhagia A bursting forth, An abnormal excessive fluid discharge or bleeding Hemorrhage- Loss of large amount of blood in a short time -rrhea Abnormal flow or discharge of body fluids Diarrhea-abnormally frequent loose watery stool 19 -rrhaphy To suture or stitch Myorrhaphy- To suture a muscle wound -rrhexis Rupture Myorrhexis- Rupture of a muscle 20 Knowing meaning of WORD Parts helps in figuring out meaning of a term Separate term into word Parts Example: prenatal Prefix prebefore Root nat/o birth Suffix -al pertaining to Begin your definition with the suffix, follow with the prefix and then the word root. Definition: pertaining to the time before birth 21 otorhinolaryngology Root Root Root Suffix ot/o rhin/o laryng/o -ology ear nose throat study of Definition: study of the ears, nose & throat tonsillectomy Root Suffix tonsill/o -ectomy tonsil Surgical removal of Definition: surgical removal of tonsils Remember to start you definition first with the suffix, then the prefix (if one) and finally the word root. 22 Used to assist with term definition Helps to master correct use of terms Helps to determine correct meaning of word Helps to identify correct spelling of term 23 Write term down Could be alternate spelling for same sound Sounds Like May begin with EX F F flatus PH phlegm J G gingivitis J jaundice 24 Sounds Like K May begin with C CH K QU Example crepitus cholera kyphosis quadriplegia 25 Sounds Like S Z May begin with C PS S X Z Example cytology psychologist serology xeroderma zygote 26 Singular ending Plural ending example -a -ae Bursa Bursae -ex or –ix -ices Appendix Appendices -is -es Diagnosis Diagnoses -itis -itides Arthritis Arthritides -nx -nges Phalanx phalanges -on -a Ganglion Ganglia -us -I Alveolus Alveoli 27 Spell all Medical Terms accurately Changing just one letter can completely change meaning Could mean life or death to patient Example: ileum (part of small intestine) or ilium (part of pelvis) 28 Used as a medical shorthand Can lead to confusion & errors Caution when using or translating them BE Below elbow & Barium enema Be familiarwith institution guidelines “When it doubt…write it out. (write out the words if you think there could be any misinterpretation of an abbreviation. 29 Sign Evidence of disease - Fever, Cough Observed by Patient & Other Objective: Evaluated & Measured by others Symptom Felt by patient only - Headache / Pain Subjective: Evaluated by Patient only 30 Syndrome Set of Signs & Symptoms Occur together Part of a Specific Disease Examples Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Fatigue Syndrome 31 Diagnosis Identification of the disease Congested Heart Failure / Appendicitis Upper Respiratory Disease / Hepatitis B Differential Diagnosis Attempt to diagnosis which of several possible diseases all producing same symptoms Hepatitis A, B, or C Prognosis Prediction or Forecast of the probable course or outcome of disease 32 Acute Rapid Onset / Severe Course / Short Duration Appendicitis / Upper Respiratory Infection Chronic Long duration / Usually controlled Hypertension / Diabetes / Cardiac Disease 33 Remission Partial or Complete Disappearance of Symptoms of disease without a cure Usually Temporary Leukemia / Cancer 34 Named for Condition Chronic Fatigue Syndrome Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Eponym (EP-oh-nim) Named: Person who Discovered-Described it Ex: Alzheimer’s Disease: Neurologist Acronym Word formed by using initial letter(s) of compound term Ex: LASER Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation 35 Confusing Medical Terminology Arteri/o = Artery Ather/o = Plaque or Fatty Substance Arthr/o = Joint Ileum = Part of Small Intestine Ilium = Part of the Hip Bone 36 Infection = Invasion of body by pathogenic organism, local or systemic Inflammation = Local response to injury or destruction of tissue Laceration = Torn, Ragged wound Lesion = Pathological change of tissue due to injury or trauma 37 Mucous (adj.) = Specialized membranes that line body cavities Mucus (n.) = Substance secreted by the mucous membranes Myc/o = Fungus Myel/o = Bone Marrow or Spinal Cord My/o = Muscle 38 -ologist Radiologist-MD reads X-Rays Cardiologist- MD treats conditions of heart -ology = Specialist = Study of Radiology – Study of X-Ray therapy Cardiology – Study of the Heart conditions Neonatology – Study of newborn conditions 39 -ostomy Tracheostomy – Creating opening in Trachea Colostomy – Creating an opening in Colon -otomy = Creation of artificial opening = Surgical Incision Thoracotomy – Incision in Chest cavity Colotomy - Incision into Colon ***these two word parts are VERY commonly confused. Take extra time to memorize these 40 Palpation- to examine the patient with one’s hands Palpitation- a pounding or racing heart 41 Prostate = Male Gland under the urinary bladder Prostrate = To collapse or lying Flat Supination = Rotation of arm with palm of hand forward Suppuration = Formation or discharge of pus 42 Suturing = Act of closing a wound or incision by stitching Ligation = Act of binding or tying off blood vessels or ducts Triage = Medical Screening of patients to determine priority of need Trauma = Wound or Injury 43 Viral = Pertaining to a virus Virile = Possessing masculine traits 44 Hypotension: low blood pressure Hypertension: high blood pressure Addiction: a strong dependence on a drug or substance. Edema: Excessive build-up of fluid Intramuscular: within the muscle Phalanx: Finger or toe (plural phalanges) Gerontology: study of aging (old age) Gerontologist: specialist in the treatment of aging individuals. 45 The End There is no substitute for daily preparation! Review your flashcards every day. 46