Word Root
advertisement

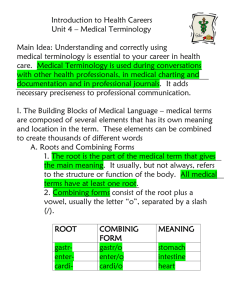
醫用流體力學 Medical Terminology Reference Cohen, B. J. (1998). Medical terminology; An illustrated guide. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven Publishers. Gyls, B.A. & Wedding, M.E. (1983). Medical Terminology: A Systems Approach. Philadelphia: F.A. Davis Basic Elements of a Medical Word 1. 2. 3. 4. Word Root Combining Form Suffix Prefix These four parts of a word are known as ELEMENTS. Dr. Joel Gluck Word Root Main part or foundation of a word. All words have at least one word root. A word root may be used alone or combined with other elements to form a complete word. i.e., SPEAK (word root) + ER (suffix) = SPEAKER (complete word) The word root usually refers to a body part. Some root words are derived from the Latin or Greek language. Word Root Examples “dent” means tooth “dermat” means skin “cardi” means heart “gastr” means stomach “pancreat” means pancreas Combining Forms Correct pronunciation of medical words is important. In order to make the pronunciation of word roots easier, sometimes it is necessary to insert a vowel after the root. The combination of a word root and a vowel is known as a COMBINING FORM. Combining forms consist of a combining vowel. The combining vowel is usually an “o”, but others may be used. IE: gastr / o Word root pronounced GASTRO. Combining vowel When a word has more than one root, a combining vowel is used to link the root to each other. Slashes separate elements IE: osteoarthritis oste/ o / arthr/ itis Word root suffix Combining vowel Word root Word-Building System By understanding the meanings of word roots, one can determine the meaning of complex medical terms by putting together the smaller parts. Leukocytopenia Word Roots: Leuk / (white) cyt / (cell) Combining Vowel /o/ Suffix: / penia (decrease) Suffixes A suffix is added to the END of a word root or combining form to modify its meaning. By adding a suffix to the end of a word root, we create a noun or adjective with a different meaning. A combining vowel is used between a word root and a suffix that begins with a consonant (not a vowel). This is to make pronunciation easier. Word root: scler / (hardening) Suffix: / derma (skin) Term: Scler / o / derma Combining vowel (hardening of the skin) Meanings of certain suffixes -al -er -able pertaining to dent/al (pertaining to teeth) one who speak/er (one who speaks) capable of being playable (capable of being played) -oma (tumor) hematoma (blood tumor) NOTE: The element that comes before a suffix can either be a word root or combining form. The suffixes -scope (instrument to view) -rrhexis (rupture) -rrhea (flow or discharge) all begin with a consonant, therefore a combining vowel must be used between the word root and the suffix. The suffixes -algia (pain) -edema (swelling) -uria (urine, urination) These suffixes begin with a vowel, therefore a combining vowel is NOT used between the word root and the suffix. REVIEW A combining vowel IS used to link one root to another root, and before a suffix that begins with a consonant. A combining vowel IS NOT used before a suffix that begins with a vowel. Prefixes A prefix is a syllable or syllables placed BEFORE a word or word root to alter its meaning or create a new word. Some prefixes: Hyper- (excessive) Pre(before) Post(after) Homo- (same) Hypo(under) Hypoinsulinemia Hypo / insulin / emia Prefix LOW Word root INSULIN suffix BLOOD Notice that there is no combining vowel in this word because the prefix ends with a vowel and the suffix begins with a vowel. Plurality To make a medical word plural (more than one), first look at the suffix. Then, choose the rule that changes the singular form to the plural form. The rules appear on page 18 of the text. Chart of Prefixes aabadananteanteroantobibradydiadys- without or not away from to, toward absence of before in front against two slow through difficult, painful malmediomesmetamicroorthoparapathoperipolypseudo- bad middle middle beyond, over small straight, correct beside disease outside, around many false Chart of Prefixes endoepieuexexohyperhypoinfraintra- within upon well, good away from outside over under or less below within quadriretrosubsupratachytranstriultrauni- fourfold backward beneath above fast across three beyond single, one Chart of Roots aden arteria arthros auris brachion bronchus cardium cephalos cholecyst colon costa cranium derma gland artery joint ear arm windpipe heart brain gallbladder intestine rib head skin gaster haemo, hemo hepar hydro hystera kystis, cysto larynx myelos nasus nephros neuron odons odynia stomach blood liver water womb bladder throat marrow nose kidney neuron tooth pain Chart of Roots enteron epithelium esophaqus ostium otis pes pharynx phlebos pleura pneumones psyche pulmones pyelos pyon intestine skin gullet mouth, orifice ear foot throat vein chest lungs mind lungs pelvis pus optikas os osteon pyretos ren rhin rhythmos spondylos stoma thorax trachea trophe vene vesica eye bone bone fever kidney nose rhythm vertebra mouth chest windpipe nutrition vein bladder Chart of Suffixes -algia -centeses -clasia -ectasis -ectomy -edema pain puncture remedy dilatation cut swelling -emia -iasis -itis -oma -sclerosis blood a process inflammation swelling, tumor hardening Relative position in medical usage • Anterior • Distal • Dorsal situated in front of; forward part of away from the center of the body a position more toward the back of an object of reference • Frontal situated at the front • Inferior situated or directed below • Lateral a position more toward the side of flank • Proximal toward the center of the body • Sagital relating to the median plane of the body or parallel to it • Superior situated or directed above • Anatomy refers to the internal and external structures of human body and their physical relationships. Anatomical terms Word Amylolysis Glucogenesis Hydrocephalus Kalemia Lactosuria Lipoma Lithotrite Natriuresis Stearate Definition digestion of starch production of glucose excess of fluid inside the skull presence of potassium in the blood lactose in the urine benign tumor containing fatty tissue instrument for crushing a stone in the urinary bladder abnormal amounts of sodium in the urine a type of fat Word Aboral Adduction Adoral Alloantigen Allopathy Antebrachium Antepartum Antitoxic Apophysis Contraception Dextrogastria Diapedesis Definition away from the mouth movement of a limb toward a median line near or directed toward the mouth (or) occurs in some but not others of same species second disease, condition that is incompatible with first forearm before childbirth neutralizing the action of a poison an outgrowth or projection, especially from a bone prevention of conception or pregnancy displacement of the stomach to the right the passage of blood through the walls of blood vessels Dissect to cut apart or separate the tissue of a body for study Dorsocephalad toward the back of the head Word Ecchondroma Encephalopathy Endoderm Epicranium Excementosis Heterocellular Heterotypic Homeostasis Homomorphic Infusion Inhale Laterotorsion Levorotation Opisthotonos Definition outgrowth from cartilage, mass protruding from bone any disease of the brain innermost of the primary layers of the embryo the muscle, aponeurosis, and skin covering the cranium outgrowth of root surface of a tooth occurs in some but not others of the same species different or unusual type state of equilibrium in the body two or more structures of similar size steeping a substance in water to draw in breath twisting to one side turning or twisting to the left a spasm in which the spine and extremities are bent Word Perinatal Periodontal Peroral Postanaesthetic Postnasal Precapillary Predentin Procephalic Prochondral Recuperate Rehydration Retrogression Schizonychia Schizophrenia Transfusion Definition time period before, during or after the time of birth around a mouth through the mouth after anaesthetic posterior of the nasal cavity preceding a capillary organic fiber of dentin before its calcification relationing to the anterior part of the head developmental stage prior to formation of cartilage to recover, to regain health and strength return of water to a system after its loss previous, less complex conditions splitting of the nails personality disorder, withdrawal from outside world transfer of blood Word Ankylosis Brachygnathia Bradypnea Chloroma Cirrhosis Cyanopsia Erythrocyte Glaucoma Kyphoscoliosis Leukomyelitis Melanin Orthodontist Stenothorax Tachycardia Definition immobility of a joint due to a disease abnormal shortness of the lower jaw abnormal slowness of breathing greenish-yellow tumour arising from myeloid tissue hardening of an organ, especially the liver defect of vision in which objects appear tinged with blue red blood cell group of eye diseases backward and lateral curvature of the spinal column inflammation of the white substance of the spinal chord dark pigment of the skin, hair, choroid coat of the eyes and various tumours. a dentist who specialists in the branch of dentistry concerned with irregularities of teeth and malocclusion abnormal narrowness of the chest abnormally rapid heart rate Word Acardia Ambilateral Amphibolic Anisotropic Diplopia Hypodermic Hyperthermia Macrocephaly Megakaryocyte multi-infection Oligotrophy Inert Isoenergetic Pananxiety Polyplegia Primigravida Protoneuron Definition congential absence of the heart pertaining to or affecting both sides having both an anabolic and catabolic function. having unlike properties in different directions perception of two images of a singie object applied below the skin very high body temperature excessive size of the head the giant cell of bone marrow containing a greatly lobulated nucleus, from which mature blood platelets orginate many infections insufficient nutrition lacking the power to move exhibiting equal energy a diffuse, all pervading anxiety paralysis of several muscles a woman pregnant for the first time the first neuron in a peripheral reflex arc