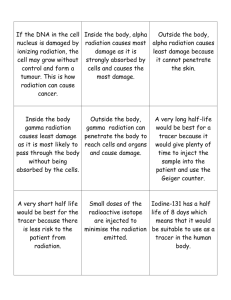
half life
advertisement

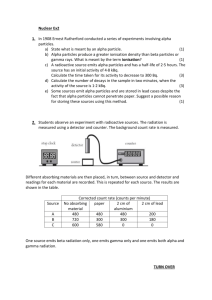
Properties of radiation 1 1. What does alpha radiation consist of? Two protons and two neutrons One electron Electromagnetic radiation 2 2. Which type of radiation is the least penetrating? Gamma Alpha Beta 3 3. Which type of radiation travels the furthest in air? Alpha Beta Gamma 4 4. Which of these is the correct definition of half-life? The time it takes for the number of protons to halve The distance it takes for the number of nuclei to halve The time it takes for the number of nuclei to halve 5 5. What shape is the line on a decay curve for a radioactive substance? Straight line upwards Curve downwards Curve upwards 6 6. What charge is alpha radiation? Negative Neutral Positive 7 7. Which type of radiation will be attracted to a positively charged plate? Beta Alpha Gamma 8 8. What colour will photographic film turn when it absorbs radiation? Stay the same Darker Lighter 9 9. What tube detects radiation? Fluorescent Geiger-Muller Glass 10 10. Which of these is an artificial source of background radiation? Cosmic rays Rocks and soil Radioactive waste 11. What are the (possible) three particles found inside an atom? Protons, neutrons and positrons Positrons, neutrons and electrons Protons, neutrons and electrons 2 12. What is the electrical charge found on a proton? Positive Neutral - no charge Negative 3 13. What particles are found inside the nucleus of an atom? Protons and electrons Protons and neutrinos Protons and neutrons 4 14. What is ionisation? Ionisation is the loss or gain of protons to create a charged particle called an ion Ionisation is the loss or gain of neutrons to create a charged particle called an ion Ionisation is the loss or gain of electrons to create a charged particle called an ion 5 15. An unknown source of radiation is blocked by 5 mm of aluminium but not blocked by paper. What kind of radiation is present? Alpha Beta Gamma 6 16. A student in a classroom measures 450 counts on a Geiger-Muller tube in 5 minutes. What is the background radiation in the classroom? 90 Bq 2250 Bq 1.5 Bq 7 17. What steps should be taken when dealing with radioactive sources? Maintain a safe distance and store the material in an appropriate lead lined container Wear appropriate footwear so that you don’t slip Make sure that you are wearing a hard hat at all times 8 18. What is the absorbed dose of a 2 kg piece of tissue exposed to 500 mJ of energy? 0.25 Gy 0.5 Gy 1 Gy 9 19. A substance has a half life of 60 seconds. How long will it take for its activity to decrease from 20 kBq to 2.5 kBq? 120 seconds 180 seconds 240 seconds 10 20. What type of energy is released by the reactions inside a nuclear reactor? Heat energy Light energy Electrical energy 21. A radioactive source has a half-life of 15 minutes. At a particular time the activity of the source is 16 kBq. What is the activity of the source one hour later? 22.