Group B PROTEIN SYNTHESIS
advertisement

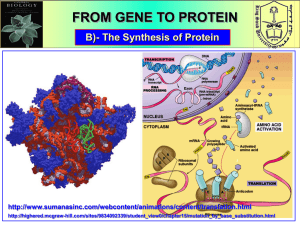
PROTEIN SYNTHESIS In this experiment we modeled the structure of DNA and the processes involved in protein synthesis DNA Structure DNA is a double stranded helix molecule made of subunits called nucleotides. Each nucleotide contains a sugar (deoxyribose), a phosphate, and a base. There are four bases (adenosine, thymine, cytosine and guanine). Alternate sugar and phosphates form the sides with bases connected to the sugars making “rungs” like a ladder. The chemical structure of the bases allow them each to pair up with only one other base, thus they form complementary pairs. Protein Synthesis Information about the number, type and sequence of amino acids necessary to make a protein molecule, is found as a code in the DNA. This code is in the sequence of bases. One gene sequence codes for one polypeptide. A set of 3 bases (a codon) codes for one amino acid of a polypeptide. A protein is made of one or a small number of polypeptides. Equipment • 42 tooth picks representing the bonds between the chemicals • 18 milk bottle lollies cut in half (36 halves) representing sugar • 18 raspberry lollies (36 halves) representing phosphate units • 25 jelly beans halved (5 each of 5 colours) representing bases • 4 different jelly snakes 6cm long representing amino acids • • A4 white paper representing a • cell • • Coloured paper circle, 6cm • diameter, representing a • ribosome • Clean sharp knife Cutting board Gloves Scissors Marking pen Heinemann Biology textbook Transcription A gene length of DNA unwinds in the nucleus. RNA polymerase enzyme moves along the exposed single DNA strand linking complementary RNA nucleotides together to form a messenger RNA strand. RNA contains the base uracil where thymine is found in DNA. The start codon (AUG) and a stop codon control the length of the mRNA strand. The mRNA strand is then modified to remove non-coding regions called introns. Protein coding regions, exons, are spliced together. In the cytoplasm, an enzyme attaches amino acids to tRNA molecules. Each type of amino acid is attached to its specific tRNA. The modified mRNA moves out of the nucleus into the cytoplasm. Translation The start codon (AUG) end of the mRNA strand binds onto a ribosome. A tRNA carrying the amino acid methionine and anticodon (UAC) binds to the mRNA start codon within the ribosome. A second tRNA binds to the next codon. Its amino acid links with a polypeptide bond to the first amino acid. The first tRNA is released from the ribosome. The ribosome moves along the mRNA strand one codon at a time. Two tRNAs at a time are temporarily bound within the ribosome and their amino acids linked together. A polypeptide chain forms. When a stop codon is reached the polypeptide chain is released into the cytoplasm. The chain folds on itself and may join other polypeptides to form a protein. Its specific shape is vital for its particular function.