Input , output and memory devices
advertisement

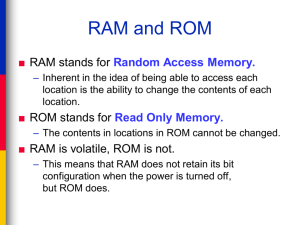
INPUT , OUTPUT AND MEMORY DEVICES Notes Input devices: Input devices The input unit is responsible for accepting input i.e. data &instructions from the user. The work is accomplished with the help of input devices like :- OUTPUT DEVICES: OUTPUT DEVICES The output unit is responsible for producing the output in user readable form. Various output devices like monitor (also called VDU i.e. visual display unit) , printer, plotter etc. makes the output unit of computer. monitors: monitors Monitor or screen is the most common form of output from a computer . It displays information in a similar way to that shown on a television screen. The picture on the monitor is made up of thousands of tiny colored dots called pixels. CATHODE RAY TUBE(CRT):- it works in the same way as a television – it contains an electron gun at the back of the glass tube which fires electrons to make the screen glow. LIQUID CRYSTAL DISPLAY(LCD):- liquid crystal is the material used to create each pixel on the screen. Each tiny cell of liquid is a pixel. printers: printers A most convenient and useful method by which the computer can deliver information is by means of printed characters. Printers can be divided in two distinct categories. Impact printers : In this printers, there is mechanical contact between the printer head and paper. Non impact printers : In this printers, there is no mechanical contact between the printer head and paper. Impact printers: Impact printers Dot matrix printer : A dot matrix printer (DMP) is the most popular serial printer i.e. it points one character at a time. In DMPS, the printing head contains a vertical array of pins. as the head moves across the paper, selected pins fire against an ink ribbon to form a pattern of dots on the paper. There are 80 columns DMPs and 132 columns DMPs available ion the market. Non impact printers : Non impact printers 1.Electromagnetic printers : By using magnetic recording techniques, a magnetic image what is to be printed can be written on as drum surface. 2.Thermal printers : An electric pulse can be converted to heat on selected sections of a printing head or on wires or nibs. When this heat is applied to heat sensitive paper, a character is printed. 3.Electrostatic printers : For electrostatic printers the paper is coated with a non conducting dielectric material which hold charges when voltages are applied with writing “nibs” (heads). This heads write dots on paper as it passes. 4.Inkjet printer : Printers direct a high-velocity stream of ink toward the paper. The ink stream is broken into droplets by an ultrasonic transducers. 5.Laser printer : This printers make use of office copier technologies. The desired output image is written on a copier drum with the help of a light beam controlled by a computer. These laser printers are quite and are capable of producing very high point quality. The speed of laser printers can be upto10-15 pages per minute ( ppm ). Speakers : : Speakers : Speakers receives the sounds in form of electric current from the sound card and then convert it to sound format. RANDOM ACCESS MEMORY(RAM): RANDOM ACCESS MEMORY(RAM) In the ram the memory cells can be accessed for information transfer from any desired random location i.e. the process of locating a word in memory is the same and requires an equal amt. of memory ,thus the name “random access”. DRAM(DYNAMIC RAM): DRAM(DYNAMIC RAM) It consists of a transistor and capacitor that’s capable of storing an electric charge . Depending on the switching action of the transistor the capacitor either contains no charge(0) or does hold a charge(1). DRAM STORAGE Density Since a DRAM cell consists of one transistor and capacitor per bit, it allows a DRAM chip to pack a large number of cells within the chip compared to SRAM. Generally a DRAM chips are available with 128 bit or 256 bits densities or even more. DRAM refreshing The problem of a capacitor is they it starts loosing the charge over a period of time, & can retain data for barely a thousandth of a second. So, the memory controller needs to refresh the memory contents as many as thousand times a second, which is called memory refreshing. Types of DRAM: Types of DRAM EDO DRAM : An EDO RAM cell keeps its data valid until it receives a additional signal. It has a duel-pipeline architecture, which allows the memory controller simultaneously read new data while discharge the old. Synchronous DRAM (SDRAM) : With the arrival of higher speed processors, designers of system soon felt the need to run memory bus faster than 66 MHz This was made possible by redesigning the basic memory chip interface. These improved memory chips were called SDRAM. Rambus dram (RDRAM) : the Rambus protocol creates an independent control and address bus and data is transmitted across a16 bit wide data bus. Double data rate (DDR) SDRAM : Unlike SDRAM memory the support one operation in each clock, DDR SDRAM memory can do two operation per clock,threby double memory bandwidth over single data rate SDRAM. Static RAM:- Static RAM consists eventually of internal flip-flops that store the binary information. The stored information remains valid as long as power is applied to the unit. Read Only Memory (ROM):Read Only Memory (ROM) is a memory unit that performs the read operation only; it does not have a write capability. This implies that the binary information stored ROM is made permanent during the hardware production of the unit and cannot be altered by writing different words into it (non-volatile). A ROM is restricted to reading words that are permanently stored within the unit. Programmable Read Only Memory (PROM) is a ROM that can be programmed to record information using a facility known as PROM- Programmer. Once the Chip has been programmed, the recorded information cannot be changed i.e. prom becomes same as ROM. Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EPROM) is another type of ROM that can be erased and chop can be re programmed to record different information using a special PROM- programme facility. Electrically erasable PROM (EEPROM) of ROM can be programmed and erasable by electric signal. It does not require expose to ultraviolet light erase its contents as EROM memory does, and provides an easy means to load the stored temporary or permanent information in a form of ROM memory. Cache Memory: Cache Memory The Cache Memory is a high speed memory available inside CPU in order to speed up access to data and instructions stored in RAM memory. A memory cache, some times called cache store or RAM cache , is a portion of memory made of high speed static RAM (SRAM) instead of the slower and cheaper dynamic RAM(DRAM) used for memory main memory. Memory caching is effective because most programs access the same data or instructions over and over. By keeping as much of this information as possible in SRAM, the computer avoids accessing the slower DRAM. The Secondary Memory Device: The Secondary Memory Device Since primary memory has a limited storage capacity and is not permanent, secondary storage devices are v used to store large amount of data permanently. The following secondary devices available these days. ( i ) Magnetic Media :-Hard disks, Floppy Disks. (II) Optical Media :- CD ROMs, DVDs. kilo bytes (KBs),megabytes (MBs), giga bytes (GBs), and tera bytes (TBs)as we do for main memory. Floppy Disks: Floppy Disks The floppy disks are one of the portable storage device still in use. The floppy disks enable one to transfer small files between computers and also to store data/information as back up. The floppy disk is made of a flexible substances called Mylar. They have a magnetic surface which allows the recording of data. a standard floppy disk can store upto 1.44MB of data equivalent to 300A4 size paper. However graphics/picture can stoe in it as graphics/picture . Hard Disks: Hard Disks The hard disk memories store information on one or more circulars platters (or disks) which are continually spinning. This rotation disks are coated with magnetic material and stacked with spaces between them. Information is recorded on the surface of the rotating disks. By magnetic tapes as tiny magnetic spots. These heads are mounted on access arms. Information is recorded in bands. Each band of information on a given disk is called a track. Storage capacity of hard disk is measured by gigabytes in today, most common being 80 GB to 300 GB. Compact Disks(CD): Compact Disks(CD) The CDs are optical media. the CDs are relatively chip & have a storage capacity of up to 700 Mb. There are 3 main types of CDs. CD-ROM (Compact Disk-read Only Memory): This is used only to store information & cannot be used for store data. CDROM comes with a reported speed of 48x to 75x. CD-R (Compact Disk-recordable) : Data can be recorded on those disk only once on one part of the disk and another part at later time onetime each. This disk cannot be erased. CD-RW (Compact DiskRewritable) : CD-RW is an erasable disk, one can write multiple times. It overcomes the difficulty of writing once on CDs.CD-RW disks are more like floppy/hard disks as data are erasable and rewritable . DVDs: DVDs DVD is an optical storage device that looks the same as a CD but storage capacity 15 times more than CD and transfer data to computer 20 times faster than CD-ROM. DVDs also come in three verities. DVD-ROM Digital Video Disk – Read Only Memory . DVD-ROM is high capacity optical disk capable of storing 4.7 GB to 17 GB. Huge capacity makes them attractive for storing large amounts of data. DVD-R (DVD-Recordable). DVD-R similar to CD-R’s allow users to write once and in multiple times but read it many times. DVD-RW (DVD-Rewritable). Most rewritable DVD drives are DVD-RW. One can erase and read many times on them. Because of there enormous capacity they are replacing CD technology. CD/DVD DRIVE: Pen/Thumb Drives – Flash Memories: Pen/Thumb Drives – Flash Memories Another kind of storage device has recently emerged. It is called Flash memory , USB memory,. The thumb drives/pen drives and cell phones today use flash memories. Flush is a ‘solid state’ memory i.e. it has no moving parts unlike magnetic storage devices. Nor does it make USE of lasers- unlike optical drives. Data is retained in flash memory even when power is switched off.