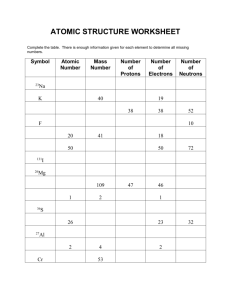
File - Mr. Astor's Chemillionaires
advertisement

100 Fermium Fm Fermium Name: Fermium Symbol: Fm Atomic Number: 100 Atomic Mass: (257.0) amu Melting Point: Unknown Boiling Point: Unknown What is Fermium? Radioactive metallic transuranic element, belongs to the actinoids. Ten known isotopes, most stable is Fm257 with a half-life of 10 days. First identified by Albert Ghiorso and associates in the debris of the first hydrogen-bomb explosion in 1952. 101 Mendelevium Md Mendelevium Name: Mendelevium Symbol: Md Atomic Number: 101 Atomic Mass: (258.0) amu Melting Point: Unknown Boiling Point: Unknown What is Mendelevium? Radioactive metallic transuranic element. Belongs to the actinoid series. Only known isotope, Md-256 has a half-life of 1.3 hours. First identified by Glenn T. Seaborg, Albert Ghiorso and associates in 1955. Alternative name unnilunium has been proposed. Named after the 'inventor' of the periodic table, Dmitri Mendeleev. 102 Nobelium No Nobelium Name: Nobelium Symbol: No Atomic Number: 102 Atomic Mass: (259.0) amu Melting Point: Unknown Boiling Point: Unknown Link What is Nobelium? Radioactive metallic transuranic element, belongs to the actinoids. Seven known isotopes exist, the most stable being No-254 with a half-life of 255 seconds. First identified with certainty by Albert Ghiorso and Glenn T. Seaborg in 1966. Unnilbium has been proposed as an alternative name. 103 Lawrencium Lr Lawrencium Name: Lawrencium Symbol: Lr Atomic Number: 103 Atomic Mass: (262.0) amu Melting Point: Unknown Boiling Point: Unknown What is Lawrencium? Appearance unknown, however it is most likely silvery-white or grey and metallic. Lawrencium is a synthetic rare-earth metal. There are eight known radioisotopes, the most stable being Lr-262 with a half-life of 3.6 hours. Due to the short half-life of lawrencium, and its radioactivity, there are no known uses for it. Identified by Albert Ghiorso in 1961 at Berkeley. It was produced by bombarding californium with boron ions. The name is temporary IUPAC nomenclature, the origin of the name comes from Ernest O. Lawrence, the inventor of the cyclotron. If sufficient amounts of lawrencium were produced, it would pose a radiation hazard. 104 Rutherfordium Rf Rutherfordium Name: Rutherfordium Symbol: Rf Atomic Number: 104 Atomic Mass: (261.0) amu Melting Point: Unknown Boiling Point: Unknown What is Rutherfordium (Unnilquadium)? Radioactive transactinide element. Expected to have similar chemical properties to those displayed by hafnium. Rf-260 was discovered by the Joint Nuclear Research Institute at Dubna (U.S.S.R.) in 1964. Researchers at Berkeley discovered Unq-257 and Unq-258 in 1964. 105 Dubnium Db Dubnium Name: Dubnium Symbol: Db Atomic Number: 105 Atomic Mass: (262.0) amu Melting Point: Unknown Boiling Point: Unknown What is Dubnium (Unnilpentium)? Radioactive transactinide element. Half-life of 1.6s. Discovered in 1970 by Berkeley researchers. So far, seven isotopes have been discovered. 106 Seaborgium Sg Seaborgium Name: Seaborgium Symbol: Sg Atomic Number: 106 Atomic Mass: (263.0) amu Melting Point: Unknown Boiling Point: Unknown Link What is Seaborgium (Unnilhexium)? Half-life of 0.9 +/- 0.2 s. Discovered by the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research at Dubna (U.S.S.R.) in June of 1974. Its existence was confirmed by the Lawrence Berkeley Laboratory and Livermore National Laboratory in September of 1974. 107 Bohrium Bh Bohrium Name: Bohrium Symbol: Bh Atomic Number: 107 Atomic Mass: (262.0) amu Melting Point: Unknown Boiling Point: Unknown What is Bohrium (Unnilseptium)? Radioactive transition metal. Half-life of approximately 1/500 s. Discovered by the Joint Institute for Nuclear Research at Dubna (U.S.S.R.) in 1976. Confirmed by West German physicists at the Heavy Ion Research Laboratory at Darmstadt. 108 Hs Hassium Name: Hassium Symbol: Hs Atomic Number: 108 Atomic Mass: (265.0) amu Melting Point: Unknown Boiling Point: Unknown Hassium 109 Mt Meitnerium Name: Meitnerium Symbol: Mt Atomic Number: 109 Atomic Mass: (266.0) amu Melting Point: Unknown Boiling Point: Unknown Meitnerium Einsteinium (Es) Albert Einstein – Relativity – E = mc2 – Offered Presidency of Israel – Element 99 – Photoelectric effect • Solar calculator Curium (Cm) • Madame Curie – Pioneer in radioactivity • (Ra = radium) – 25 pounds of pitchblende ore yields 1/1000 of a gram of radium – Emits 2 millions times as much radiation as uranium • (Rn = radon gas) – Discovered 5 elements – Nobel Prize (5 in Curie family) – Born in Poland • (Po = polonium) Marie Curie (1876–1934) Radium (Ra) Radium was used as a fluorescent paint on watch dials. It was applied with thin brushes that workers would lick to keep a fine tip. Many people died from the exposure to radium. Radon Gas Radon gas occurs naturally from the radioactive decay of radium. Radium is found in small amounts in rock. Ra Rn + radiation Predicted fraction of homes over 4 picocuries/liter radon Nobelium (No) Element 102 Inventor: dynamite (TNT) blasting gelatin Nobel Prize NO2 O2N NO2 CH3 Trinitrotoluene Alfred Nobel “Merchant of Death” Seaborgium (Sg) Glenn Seaborg – Separated f-block from rest of periodic table – Worked on Manhattan Project (Atomic bomb) – Classified until after WW II – Element 106 • Only living person to have an element named for them Silicon vs. Silicone • Silicon (Si) element • Silicone (…Si – O – Si…) polymer – Sealant (caulk) prevents leaks – Breast augmentation No cause-and-effect relationship exists between breast enlargement and breast cancer. Only one researcher found a causal link. 12 Mg Magnesium Atomic Mass 24 amu melting point = silver gray metal used in flash bulbs, bombs,and flares 8th most abundant element (2.2% of Earth’s crust) lack of Mg produces same biological effect as alcoholism (delirium tremens) 24.305 Potassium Metal in Water Newmark, CHEMISTRY, 1993, page 25 e Ir O N Mn 77 1 8 7 25 H H He 1 2 1 2 3 Li Be B C N O F Ne 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Al Si P S Cl Ar 13 14 15 16 17 18 Na Mg 11 4 K 19 5 7 Ca Sc Ti V Cr Mn Fe Co Ni Cu Zn Ga Ge As Se Br Kr 23 24 35 36 I Xe 53 54 20 21 22 Rb Sr Y Zr Nb Mo Tc Ru Rh Pd Ag Cd In 39 40 41 42 49 Hf Ta W 72 73 74 37 6 12 38 Cs Ba 55 56 Fr Ra 87 88 * W 25 43 26 44 Re Os 75 76 27 28 29 47 30 45 46 Ir Pt Au Hg Tl 77 78 81 79 48 31 80 32 33 34 Sn Sb Te 50 51 Pb Bi 82 83 52 Po At Rn 84 85 86 Rf Db Sg Bh Hs Mt 104 105 106 107 108 109 La Ce Pr Nd Pm Sm Eu Gd Tb Dy Ho Er Tm Yb Lu 57 58 59 Ac Th Pa 89 90 91 60 U 92 61 62 63 64 65 66 Np Pu Am Cm Bk Cf 93 94 95 96 97 98 67 68 69 70 71 Es Fm Md No Lr 99 100 101 102 103 Printable Periodic Table Elements Database Elements listed Alphabetically Actinium Aluminum Americium Antimony Argon Arsenic Astatine Barium Berkelium Beryllium Bismuth Boron Bromine Cadmium Cesium Calcium Californium Carbon Cerium Chlorine Chromium Cobalt Copper Curium Dysprosium Einsteinium Erbium Europium Fermium Fluorine Francium Gadolinium Gallium Germanium Gold Hafnium Helium Holmium Hydrogen Indium Iodine Iridium Iron Krypton Lanthanum Lawrencium Lead Lithium Lutetium Magnesium Manganese Meitnerium Mendelevium Mercury Molybdenum Neodymium Neon Neptunium Nickel Niobium Nitrogen Nobelium Osmium Oxygen Palladium Phosphorus Platinum Plutonium Polonium Potassium Praseodymium Promethium Protactinium Radium Radon Rhenium Rhodium Rubidium Ruthenium Samarium Scandium Selenium Silicon Silver Sodium Strontium Sulfur Tantalum Technetium Tellurium Terbium Thallium Thorium Thulium Tin Titanium Tungsten Unnilhexium Unniloctium Unnilpentium Unnilquadium Unnilseptium Uranium Vanadium Xenon Ytterbium Yttrium Zinc Zirconium Get free Chemistry and Physics images for your school projects and/or research work. Feel free to use the periodic table images below in your school projects and/or research work. Periodic Table of the Elements Images from: http://www.chemsoc.org/viselements/pages/pertable_j.htm Data from: http://www.chemicalelements.com/ http://www.elementsdatabase.com/ Periodic Table of the Elements http://www.periodictable.com Written by: Bill Byles - bylesb@internet4classrooms.com & Jeff Christopherson – unit5.org/chemistry