Final Review Part 1 KEY
advertisement

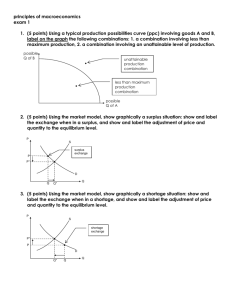
Final Review Part 1: (Ch. 1-3) Chapter 1: Positive Statement: Don’t have to be correct but can be Proved or disproved; fact based 1. 2. 3. 4. Normative Statement: Can not be tested or proven; opinion based The government should provide basic healthcare to all citizens. N The government-provided healthcare increases public expenditures. P Japan has the most passionate tennis team. N The ocean is purple. P Chapter 2: Opportunity Cost vs. Direct Costs Opportunity Cost: Measures the benefits that will be lost if One option is chosen over another Direct Cost: what is actually spent in monetary value 1. Assume that a storeowner has a vacant rack in front of the counter that he wants to fill with merchandise. He found out that if he filled the rack with apples, his estimated sales for one week would be $100, but if he filled the rack with candies he would expect to sell $190 worth of candy. He chooses to fill the rack with apples. What is his opportunity cost? Opportunity cost = $190 2. David has $20. He doesn’t know whether to buy 2 movies for $10 each or 1 video game for $20. If he chooses to buy the video game what is his direct cost and what is his opportunity cost? Direct: $20 Opportunity: 2 movies Possibility Frontier Diagram is attainable and efficient or not? Discuss attainability and efficiency of each: 1. 2. 3. 4. Point C Point X Point Y Point B Yes A and E Yes A, No E No A or E Yes A and E Absolute Advantage vs. Comparative Advantage Absolute Advantage: Comparative Advantage: When one country is able to use its When, during a trade, it would be Resources to produce more of a product more efficient to produce this good Than another country while the other country produces The other good Chapter 3: Variables that shift demand and supply: Demand: 1. Changes in Prices of Related Goods and Services 2. Changes in Income 3. Changes in Taste 4. Changes in Expectation 5. Changes in Number of Consumers Supply: 1. Changes in Input Price 2. Changes in Prices of Related Goods and Services 3. Changes in Technology 4. Changes in Expectation 5. Changes in Number of Producers Reference “All About Demand” and “All About Supply” to see how they shift and to look at examples. Surplus vs. Shortage Surplus There is excess surplus; Supply > Demand Y Shortage There is excess demand; Demand > Supply If there is no shift in supply or demand, the Price at ______ will create a ________. 1. Price at Y, will create surplus 2. Price at P, will create equilibrium 3. Price at X, will create shortage X Substitute vs. Complementary Goods Substitute: Complementary: two goods that can be used for a good that is usually bought along the same purpose. If price of one with another good. If the price of increases, than demand for sub rises one increases, the demand for the other decreases.