Analgesics - Dr. More Chemistry
advertisement

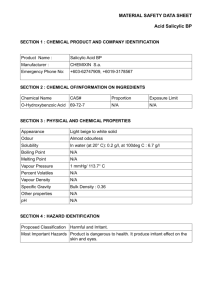
12.3 Analgesics http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlinepl us/druginformation.html Describe and Explain the different ways in which analgesics prevent pain Pain Receptor • Nerves that transmit the pain • Free nerve endings that transmit the pain based on thermal/ mechanical/ chemical stimuli • Pain receptor generate an impulse • Pain results from interaction between various impulses arriving at the spinal cord and the brain Prostaglandins • Injures tissues release prostaglandin and leukotriene • Make the pain receptors more sensitive Prostoglandin • Prostaglandins have an extraordinarily wide range of biological effects • controlling blood pressure and controlling inflammation. • blood clotting, kidney function and the reproductive system • and are the subject of a great deal of research to produce new drugs. Analgesics • Understanding how neurons work comes from study of membrane potential • (i.e. the difference in electrical charge between inside and outside of the neuron); • To record a membrane potential two electrodes are needed: intracellular and extracellular • Aspirin Analgesics: relives pain Mild : aspirin, acetaminophen( metabolic byproduct of phenacetin) -same as Tylenol, Paracetamol, ibuprofen ( sold as Actiprofen, Advil, MortrinIB, Medipren) NSAIDS ( non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) Mild analgesics : non addictive Mild Analgesics • Block the enzyme –cyclooxygenase / controlled synthesis of prostaglandins • responsible for constricting of blood vessels • increase the body temperature • Direct effect on hypothalamus / body’s heat regulating center / produces fever • Cause swelling and pain / increase the permeability of capillaries, allowing water to pass out into nearby tissues Mild Analgesics • Lower the concentration of prostaglandins • Reduce fever • And inflammation Endorphins and enkephalin Enkaphalin Endorphin • Endorphin comes from the words endogenous morphine. • Endogenous means developing from within. • Endorphins are similar to the narcotic morphine in their functions,. • They occur naturally in the brain and bloodstream. Endorphin • a group of peptide hormones that bind to opiate receptors • and are found mainly in the brain. • Endorphins reduce the sensation of pain and affect emotions. Endorphin • Russian scientists claim a beating on the buttocks with a strong cane is the perfect way to cure everything from depression to alcoholism by releasing the body's natural "happy chemicals" known as endorphins. B3.2 Salicylic acid • Describe the uses of derivatives of salicylic acid as mild analgesics and • compare the advantages and disadvantages of using • aspirin and paracetamol • acetaminophen) Salicylic acid /Acetyl salicylic acid Salicylic Acid • Antipyretic / fever reducer • Mild analgesic / pain killer • Strong/ damages the membrane lining the mouth, esophagus and stomach • Chemically modified to sodium salt of acid • Less unpleasant, but turn to acid in the stomach • acetyl salicylic acid / reduce acidity/ non irritating /taken orally Synthesis Hydrolysis + H2O CH3COOH ASA • Prodrug :less active form of drug that is converted to the active form of drug after administration • Sometimes sold as sodium salt of ASA / Alka Seltzer. / ionic bonding / dissolves in water ASA • The presence of OH and COOH group on benzene ring makes salicylic acid as strong acid • Other derivatives are insoluble due the presence of aromatic ring Uses of the Derivatives of salicylic acid ( Miracle drug) • Antipyretic: reduces fever • Anti-inflammatory • Anti-platelet agent / prevent abnormal blood clotting , anti clotting agent • (inhibits the production of prostaglandins) • Mild analgesic – minor aches/pains, headaches, sunburn, arthritis Disadvantages of ASA • Stomach upset due to acidity in aq. Solution • Gastrointestinal bleeding following use of alcohol • 0.5% who take ASA (and 3-5% asthmatic) are allergic to ASA leading to skin rashes, respiratory difficulty • Accidental poisoning in infants • Development of Reye’s syndrome/ liver and brain disorder can result in coma, brain damage and death ( children who took ASA for chicken pox symptoms) Base hydrolysis Pain reliever Aspirin Substitute • • • • • • Paracetomol Active ingredient in many OTC USES: Anti –pyretic / reduces fever Analgesics reduce pain Does not upset stomach Acetaminophen • NOT an anti-inflammatory • Can cause blood disorder and kidney damage • Over dose can cause liver damage, brain damage, coma and even death Acetaminophen Phenacetin Ibuprofen • (2-[4-(2-Methylpropyl)phenyl]propanoic Acid, Isobutylphenylpropionic Acid) • Same as ASA but fewer stomach problems • Anti-inflammatory • Wide margin of safety, • Lower effective dose • Large doses /kidney problems www.wcer.wisc.edu/.../Spr2000/esselman/IBU b.html 2-(4-Isobutyl-phenyl)-propionic acid • ibuprofen Opium Strong Analgesics • Relief of very severe pain, • include narcotics : heroin, codeine, morphine • Addictive • Controlled substances Heroin Strong Analgesics Local anesthetics • Pain killers in localizes areas • Lidocaine and procaine (Novocaine) • Used in dentistry Novocaine • t is the first injectable local anesthetic to be synthesized, • commonly known as Novocain. • The German Chemist, Alfred Einhorn, developed it in 1904. • Procaine is the precursor to cocaine. • Procaine works to anesthetize a patient for about 15 minutes. To prolong anesthesia epinephrine is added as a vasoconstrictor. Procaine/Cocaine • Cocaine blocks Na+ passage through the axon cell membrane and • inhibits the reuptake of Dopamine and Serotonin • resulting in psycho-stimulation. Procaine • Procaine blocks nerve conductance via inhibiting Na+ at the membrane, • thus no psycho-stimulation. • Both reactions are brief. • Drug Interactions? • Procaine is thought to reduce the effects of sulfonamide antibiotics. • How is this medication administered? • Oral injection. Lidocaine General Anesthetics B9-447 SEROTONIN, happy neurotransmitter. • 5-hydoxytryptamine, is naturally produced in the pineal gland, which lies at the centre of our brain. • “It is essential to numerous body function including appetite control, sleep, memory and learning, temperature regulation, mood, behavior, cardiovascular function, muscle contraction, endocrine regulation and depression. DOPAMINE, • 4-(2-aminoethyl)benzene-1,2-idol, is produced in several areas of the brain including the substantia nigra. • It is central to movement coordination, cognitive functions (by mediating signal transduction in the frontal lobe thus affecting memory, attention, and problemsolving in particular), latent inhibition and creative drive. Dopamine • Its release is stimulated by naturally rewarding experiences • such as happy foods (bananas!), drugs,