SWOT ANALYSIS
advertisement

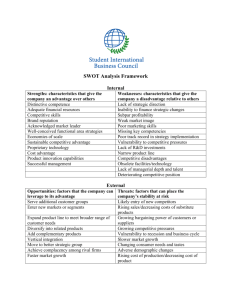
Strategic Planning and Visioning: SWOT Technique Strategic Planning and Visioning Group process centered on four key core processes in information-gathering phase of strategic planning. Each designed with a different purpose and together they create most of the essential knowledge base for strategic planning. (2) 1. Identify Core Values Purpose: To identify core values of the program; determine how and to what extent these core values are currently expressed in the actions of the program community and identify potential misalignments. We can prompt our thinking with phrases like we believe…, we believe in…, we value…, we care about…: (2) 2. Review or Develop a Mission Mission is the purpose, the reason the program exists. Develop or review and validate a mission statement that answers “Why do we exist?” http://cid.vcc.ca (2) 3. Review or Develop a Vision Develop a shared vision of a future state. Consider “Vision” as you plan…what the program wants to look like in the future? If we could have the program of our dreams and the impact we most desire, what will our program look like in the year 2010 and beyond? (2) SWOT: Description A SWOT analysis generates information that is helpful in matching an organization or group’s goals, programs, and capacities to the social environment in which it operates. It is an instrument within strategic planning. When combined with dialogue it is a participatory process (1) SWOT/OTSW Strategic Planning Process (1) Factors Internal to program Strengths Factors External to program Weakness Opportunities Threats Brainstorming Questions What opportunities exist in our external environment? What threats to the institution exist in our external environment? What are the strengths of our institution? What are the weaknesses of our institution? Facilitator polls, synthesizes and storyboards the top 5 findings in each area (2) SWOT Facilitator One who contributes structure and process to interactions so groups are able to function effectively and make highquality decisions. A helper and enabler whose goal is to support others as they achieve exceptional performance" – Bens (3) The Facilitator's Role Supports everyone to do their best thinking. Encourages full participation, promotes mutual understanding and cultivates shared responsibility. This enables group members to search for inclusive solutions and build sustainable agreements. Kaner-(3) SWOT Analysis S – Strengths W – Weaknesses O – Opportunities T – Threats SWOT: Internal Factors Strengths Positive tangible and intangible attributes, internal to an organization. They are within the organization’s control. Strengths What do you do particularly well? What do you do that is unique in the “marketplace?” What do your customers/clients/patrons ask for you to do over and over again? What do you have the right tools/resources to accomplish? (1) Weaknesses Weaknesses Factors that are within an organization’s control that detract from its ability to attain the core goal. Which areas might the organization improve? SWOT: External Factors Opportunities External attractive factors that represent the reason for an organization to exist and develop. What opportunities exist in the environment, which will propel the organization? Identify them by their “time frames” (1) Opportunities Are there new situations coming down the road that you can take advantage of (new programs being offered, new faculty joining the department, new tools available to you)? Are there gaps in the “market” that you can fill? Are there partnerships that might be fruitful? (1) SWOT: External Factors Threats External factors, beyond an organization’s control, which could place the organization mission or operation at risk. The organization may benefit by having contingency plans to address them if they should occur. Classify them by their “seriousness” and “probability of occurrence”. (1) Threats Who is your competition and what do they offer that you can’t do as well or at all? Are there “environmental” changes or situations that could cause problems for you and your programs? What other roadblocks are being thrown in your path? Simple Rules SWOT Analysis Be realistic about the strengths and weaknesses of your organization or group Distinguish between where your organization is today, and where it could be in the future Be specific: Avoid gray areas. (1) Simple Rules SWOT Analysis Always analyze in relation to your core values, mission, mandate, goals, vision. Keep your SWOT short and simple. Avoid complexity and over analysis Empower SWOT with a logical conceptual framework. (1) SWOT (OTSW) MATRIX Opportunities-external Threats-external 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Strengths-Internal 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Weaknesses-Internal 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Create a Plan of Action Set goals and objectives, like with any other plan. Limit 3-5 What steps can you take to: Capitalize on your strengths Overcome or minimize your weaknesses Take advantage of some new opportunities Respond to the threat (1) Goals from SWOT Create a 1 page summary for the department to laminate and post Ensure priorities for action/goals are addressed on meeting agendas throughout the year Note progress on an ongoing basis. (2) References 1. 2. 3. Benito CA. (2001) S.W.O.T. Analysis PPT cited 23 March 2009 at: www.sonoma.edu/users/b/benito/swot.ppt Drouin, C. (2007) Strategic Planning SWOT. Cited Feb 15th 2009 at http://www.planonline.org/ Justice, T, Jamieson, D. (2006) The Facilitator’s Fieldbook (2nd ed). AMACOM/American Management Association.