The Great Depression - Wright State University
advertisement

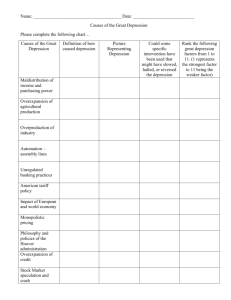
Resource Unit: The Great Depression PowerPoint by: Zachary Hyden Introduction General Theme – The Great Depression Subject – 10th grade American history Participants – Approximately 120, 10th grade American history students When – 2nd, 4th, 6th, and 7th periods between Thanksgiving and the Christmas breaks. Location – Fairborn High School – Fairborn, Ohio Duration – This is a ten day unit that will span the entire 46 minute class period for each of those ten days. Unit Objectives Students will know: – The causes of The Depression – How everyday life was affected by The Depression – The New Deal and pulling America out of the Depression – Impact of the New Deal – The beginning of World War II NCSS Standards I. Culture II. Time, Continuity, and Change III. People, Places, and Environments IV. Individual Development and Identity V. Individuals, Groups, and Institutions VI. Power, Authority, and Governance VII. Production, Distribution, and Consumption VIII. Science Technology and Society IX. Global Connections X. Civic Ideals and Practices Content – Industrial Causes of The Great Depression Industries in Trouble – Railroads – Textiles – Steel – Coal These once ultra-profitable industries were now facing hardships. Many of them barely made profits toward the end of the 1920’s Content – Industrial Causes of The Great Depression Farmers may have taken the worst hit of all. After World War I, demand fell but production didn’t. Farmers tried to produce more to re-gain their losses, but this only drove the prices farther down. As farmers defaulted on their loans, local banks failed Economic Reasons for the Great Depression People have less money Buying on Credit Uneven Distribution of Income Stock Market Crashes Economic Reasons for the Great Depression People Have Less Money Rising Prices v. dormant wages The rich are getting richer and the poor are getting poorer Over-reliance on credit Economic Reasons for the Great Depression Buying on Credit Buy now pay later mentality Credit easily available – People went into massive debt Businesses encouraged credit so they could sell more goods and make more profit. – These were not “real profits” though since no money had actually changed hands People then stopped spending as much money when they realized that they were in so deep of debt. Economic Reasons for the Great Depression Distribution of Money The rich got richer and the poor got poorer A family needed $2,500 to live comfortably in the 1920’s. – Less than 30% of people made $2,500 Money became centralized at the top echelon of society Economic Reasons for the Great Depression Stock Market Crashes In early September, the market peaked. Black Thursday – The market dropped dramatically Black Tuesday – 16.4 million shares were dumped off by investors trying to save what little money they could. Economic Reasons for the Great Depression Reasons for the Crash Speculation – High risk, High reward investing Buying on Margin – Buying a small percentage of a stock and putting the rest on credit – People hoped to hit it big on the market – People had no way to pay back the money for the stocks that they bought on credit. Economic Reasons for the Great Depression Ramifications of the Crash General Panic People lost trust in the banks – pulled all their money. – Not everyone could get their money back Banks had invested in the market Banks were not insured by the federal government The crash did not cause the depression, just sped the process up. The World Wide Depression The depression did not just hit the United States, but affected the World as a whole Causes Reviewed Vocabulary Credit Speculation Buying on Margin Black Tuesday Black Thursday Great Depression Life During the Depression Life in the Cities Life in the Country Family Life Life During the Depression Life in the Cities Shantytowns – People built shacks for shelter when they lost their homes – Also known as Hoovervilles Many people placed direct blame on President Hoover for the economic hardships that they were facing. Soup Kitchens & Bread Lines – Free or low cost foods – Came from charitable organizations Life During the Depression Life in the Country Banks foreclosed – If the farmer could not make the payment, banks would take the farmers land and all the equity that the farmer had built. Life During the Depression Country Continued Tenant Farming – “an agricultural system in which landowners contribute their land and a measure of operating capital and management while tenants contribute their labour with various amounts of capital and management, the returns being shared in a variety of ways.” http://www.britannica.com/eb/article9071664/tenant-farming Life During the Depression Country Continued Dust Bowl – “The most visible evidence of how dry the 1930s became was the dust storm. Tons of topsoil were blown off barren fields and carried in storm clouds for hundreds of miles. Technically, the driest region of the Plains – southeastern Colorado, southwest Kansas and the panhandles of Oklahoma and Texas – became known as the Dust Bowl, and many dust storms started there. But the entire region, and eventually the entire country, was affected.” http://livinghistoryfarm.org/farminginthe30s/water_02. html – Dustbowl Video Life During the Depression Family Life Men – Were used to going to work and supporting a family – Many left home to find work – Term “hobo” originated during this time, describing men that would roam from town to town looking for work Life During the Depression Family Life Women – Women kept the family together – Faced resentment for working outside of the home Children – Poor diets, lack of medical attention, disease. – Schools closed – Young children left home to find work and to take the burden off of their family Vocabulary Shantytown/ Hooverville Soup Kitchen Bread Lines Foreclosed Tenant Farming Dust Bowl Hobo The New Deal Franklin Delano Roosevelt – The New Deal – Alphabet Soup Fireside Chats Problems with the New Deal – Deficit Spending The New Deal F.D.R. – Elected President in 1932 – Began working on his “New Deal” before he took office in 1933 100 Days – Refers to the time period between March 9th and June 16th – Congress passed 15 pieces of new legislation The New Deal Alphabet Soup This term was given to F.D.R.’s programs due to their acronyms. FDIC – Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation SEC – Securities and Exchange Commission AAA – Agricultural Adjustment Act TVA – Tennessee Valley Authority CCC – Civilian Conservation Corps PWA – Public Works Administration NIRA – National Industrial Recovery Act CWA – Civil Works Administration NRA – National Recovery Administration HOLC –Home Owners Loan Coporartion FHA – Federal Housing Act The New Deal Fireside Chats F.D.R. would give speeches that were broadcasted over the radio and were known as Fireside Chats These chats were aimed to ease the mind of the American Public and to let them know the progress that has been made and the future plans that would be implemented Fireside Chat with F.D.R. The New Deal Problems with the New Deal Deficit Spending – The national government was spending more money than they were making Critics – Said that the new deal gave too much authority to the national government – Took away individual rights – Impeded Capitalism Vocabulary F.D.R. 100 Days New Deal Alphabet Soup Deficit Spending Impact of the New Deal “The New Deal created jobs that provided the necessary encouragement, hope, value and self-esteem to assist the American people to recapture their economic values. It was the solution to the problems everyone was facing: widespread unemployment, homelessness, and farmers losing their land and livestock.” http://www.nps.gov/fdrm/generation/newdeal.htm World War II The United States enters the War December 7th, 1941 – A date which will live in infamy F.D.R's Pearl Harbor Speech Vocabulary New Deal December 7, 1941 Pearl Harbor Speech Lesson 1 and 2 A pre-activity: “Quiz Run” – Students will be given a pre-test the day before the unit starts over the Great Depression – The grades for these tests will not be recorded because they are a tool for the next days simulation – The next day I will re-distribute the “graded” tests and inform the students that I have lost over half the tests that were taken. – I will tell the students that they can not re-take the test since they already know the answers and those tests which I lost will go in the grade book as a zero. – Hopefully this will get an emotional reaction out of the students. – From there I will describe the concepts of “bank-runs” during the Great Depression From here, the students should realize the concept that is being described. NCSS Standards – I, V, VI, VII Activity 3 Web Quest Students will be taken to the media center and given two days to finish the Web Quest that is provided with this link Depression Web Quest NCSS Standards – I, II, III, V, VI, VII, VIII, IX, X Lesson 4 Buy Me On Credit – I will make up 30 credit cards and distribute them to the class – I will give the students $300 Monopoly Money – I will give the students a list of goods that they can purchase with their credit cards which they will pay me for at a later date. – I will have the students write down all the goods they want and have them turn them in to me – These goods will range from a $25 toaster to a $400 new Model T-Ford. Lesson 4 continued – As the class progresses, I will slowly call in small amounts of money to simulate paying off the credit card on a monthly payment. – All at once, I will call in all the debt that the class has accumulated. – This should simulate the beginning of the economic crisis – This will also work in describing how buying on margin facilitated to crash of the stock market. NCSS Standards – I, II, IV, V, VIII Lesson 5 The students will analyze this picture through the classroom smart board and write emotions that it evokes. NCSS Standards – I, III, IV, VII Lesson 6 My family – The students will break off into “families” of three. – Each student will be designated a role with-in the family (Father, Mother, Child) – They will collaborate as a group and talk about the hardships that they face as individuals – From this collaboration, each member will write a one page paper describing his/her hardships and how the rest of the family is dealing with these hardships as a whole. – A rubric will be provided for this assignment NCSS Standards – I, II, III, IV, V, VII Lesson 7 Listen To Me Closely – Students will listen to a fireside chat orated by F.D.R. two times The first time just to hear his message The second time to analyze his message – They will take this fireside chat and will write down what they believe he was trying to convey in his speech. – The students will also describe how this would have made them feel if they would have been alive during this time period. – The students will take their written responses and use them as a guided facilitator in a classroom discussion. NCSS Standards – I, II, III, VI, VIII Lesson 8 Soups On!!! – Students will be asked to make a poster with as many acronyms as they can find from the New Deal. – The poster should contain between 8 and 10 acronyms from the New Deal They should write the entire name of the group next to the corresponding letters Students should find pictures of the organization or something that they accomplished Students will present their posters and they will be displayed around the classroom NCSS Standards – I, II, IV, V, VII, VIII, X Lesson 9 Poetry/Music from the time – Primary literature… Students will choose two of the three poems/songs below to read and analyze. They will be expected to use the S.O.A.P. model to dissect the poems and will turn their diagrams in for a grade. NCSS Standards – I, II, III, IV, VIII Brother can you Spare a Dime? Brother, Can You Spare a Dime," lyrics by Yip Harburg, music by Jay Gorney (1931) They used to tell me I was building a dream, and so I followed the mob, – When there was earth to plow, or guns to bear, I was always there right on the job. – They used to tell me I was building a dream, with peace and glory ahead, – Why should I be standing in line, just waiting for bread? – – – – Once I built a railroad, I made it run, made it race against time. Once I built a railroad; now it's done. Brother, can you spare a dime? Once I built a tower, up to the sun, brick, and rivet, and lime; Once I built a tower, now it's done. Brother, can you spare a dime? – – – – Once in khaki suits, gee we looked swell, Full of that Yankee Doodly Dum, Half a million boots went slogging through Hell, And I was the kid with the drum! Say, don't you remember, they called me Al; it was Al all the time. Why don't you remember, I'm your pal? Buddy, can you spare a dime? Once in khaki suits, gee we looked swell, Full of that Yankee Doodly Dum, Half a million boots went slogging through Hell, And I was the kid with the drum! Say, don't you remember, they called me Al; it was Al all the time. Say, don't you remember, I'm your pal? Buddy, can you spare a dime? Bowl of Cherries "Life is Just a Bowl of Cherries," lyrics by Lew Brown, music by Ray Henderson (1931) – – – – – – – – People are queer, they're always crowing, scrambling and rushing about; Why don't they stop someday, address themselves this way? Why are we here? Where are we going? It's time that we found out. We're not here to stay; we're on a short holiday. Life is just a bowl of cherries. Don't take it serious; it's too mysterious. You work, you save, you worry so, But you can't take your dough when you go, go, go. – – So keep repeating it's the berries, The strongest oak must fall, The sweet things in life, to you were just loaned So how can you lose what you've never owned? – – Life is just a bowl of cherries, So live and laugh at it all. Life is just a bowl of cherries. – – – – – Don't take it serious; it's too mysterious. At eight each morning I have got a date, To take my plunge 'round the Empire State. You'll admit it's not the berries, In a building that's so tall; There's a guy in the show, the girls love to kiss; Get thousands a week just for crooning like this: – – Life is just a bowl of . . . aw, nuts! So live and laugh at it all! We’re in the Money We're in the Money," lyrics by Al Dubin, music by Harry Warren (from the film Gold Diggers of 1933, 1933) – – – – – – – – – – We're in the money, we're in the money; We've got a lot of what it takes to get along! We're in the money, that sky is sunny, Old Man Depression you are through, you done us wrong. We never see a headline about breadlines today. And when we see the landlord we can look that guy right in the eye We're in the money, come on, my honey, Let's lend it, spend it, send it rolling along! Oh, yes we're in the money, you bet we're in the money, We've got a lot of what it takes to get along! Let's go we're in the money, Look up the skies are sunny, Old Man Depression you are through, you done us wrong. We never see a headline about breadlines today. And when we see the landlord we can look that guy right in the eye – – – – – – – – We're in the money, come on, my honey, Let's lend it, spend it, send it rolling along! Oh, yes we're in the money, you bet we're in the money, We've got a lot of what it takes to get along! Let's go we're in the money, Look up the skies are sunny, Old Man Depression you are through, you done us wrong. We never see a headline about breadlines today. And when we see the landlord we can look that guy right in the eye We're in the money, come on, my honey, Let's lend it, spend it, send it rolling along! Lesson 10 Grapes of Wrath – The students will watch the Grapes of Wrath “Oklahoma in the Thirties is a dustbowl and dispossessed farmers migrate westward to California. After terrible trials en route they become little more than slave labor. Among the throng are the Joads who refuse to knuckle under.” http://imdb.com/title/tt0032551/plotsummar y Written by Ed Stephan Grapes continued – After watching the movie, students need to draw a picture, with color, depicting a scene in the movie they feel accurately represents this period in time. Supplies will be provided for the students NCSS Standards – I, II, III, V, VI, VII Lesson 11 Opponents to Roosevelt – Many people felt that F.D.R. was trying to circumvent the power of the Supreme Court – This political cartoon depicts some of the feeling towards Roosevelt at this time – Students will be instructed to analyze this cartoon, which will be shown on the class room smart board and write bulleted responses about it. After they have turned in their responses, they will be instructed to create their own political cartoon in opposition to the New Deal/F.D.R. NCSS Standards – I, V, VI Lesson 11 continued Lesson 12 Video Clips – Students will watch a variety of video clips from the internet that will be provided for them through the teachers projector monitor. The students will watch the clips and write a brief summary of what they saw, heard, and felt and how those emotions translate to the Great Depression Depression 1 Depression 2 F.D.R.'s recovery plan NCSS Standards – I, II, III, IV, V Instructional Resources Teacher References Class Notes. American history 10. Rob Banks. Fairborn High School, Fall 2007. Class Notes. History 212. Dr. Jacob Dorn. Wright State University, Winter 2005. Danzer, G., Klor de Alve, J., Krieger, L., Wilson, L., Woloch, N. (2007). The Americans: Reconstruction to the 21st century. Evanston, IL: McDougal Littell. Cassutto's, G. (2007). The alphabet soup of new deal agencies. Retrieved November 3, 2007 from http://www.cyberlearningworld.com/lessons/ushistory/newdealagencies.htm Pojer, S. (2007). The Great Depression begins: (1929 – 1933). Retrieved November 7, 2007 from http://historyteacher.net/AmericanHistoryAndGovernment/Topics/Ch apter22-TheGreatDepressionBegins.htm Instructional Resources Class Notes. American history 10. Rob Banks. Fairborn High School, Fall 2007. – These are notes that my cooperating teacher at Fairborn High School has provided me with. These resources included worksheets, PowerPoint presentations, chapter overviews, and assessment tools. Instructional Resources Class Notes. History 212. Dr. Jacob Dorn. Wright State University, Winter 2005. – This class gave a thematic survey of events, forces, groups, and individuals that contributed to and helped to shape an American civilization on the North American continent. It spanned the time period of 1877 to the present. These notes gave good background and in depth knowledge on the Great Depression. Instructional Resources Danzer, G., Klor de Alve, J., Krieger, L., Wilson, L., Woloch, N. (2007). The Americans: Reconstruction to the 21st century. Evanston, IL: McDougal Littell. – This is the text book that is used for this particular history class. It covers American history from the end of the American Civil War through the beginning of the 21st century. The book is broken down into seven units and consists of twenty six chapters. The chapters used for this resource unit included the end of chapter 13 (The Roaring Life of the 1920’s) most of chapter 14 (The Great Depression Begins), most of chapter 15 (The New Deal), and the beginning of chapter 16 (World War Looms). This tool provided very good background and activity ideas. It also gave ideas for assessment opportunities. Instructional Resources Cassutto's, G. (2007). The alphabet soup of New Deal agencies. Retrieved November 3, 2007 from http://www.cyberlearningworld.com/lessons/ushistory/newdealagencies.htm – This resource was pulled from the web and gave the idea for the “Alphabet Soup of the New Deal” game. The project listed in this resource unit is an adaptation that uses a more student centered style of learning. – Students will make a poster board depicting between 8 and 10 acronyms from the New Deal era. The students will tell what the acronym stands for, give a brief synopsis of what the group accomplished, and a draw/copy a picture of the group or an accurate representation of the group. Instructional Resources Pojer, S. (2007). The Great Depression begins: (1929 – 1933). Retrieved November 7, 2007 from http://historyteacher.net/AmericanHistoryAndGovernmen t/Topics/Chapter22-TheGreatDepressionBegins.htm – This website was rich with information, assessment ideas, and teaching tools. The website had a wide spectrum of history knowledge that spanned from American History, to European History, to Global Studies, to Advanced Placement European History. Each sub-category had syllabi, assignments, quizzes, web links, and review questions. – The link that I used was located under American History & Government – Main Page – Chapter 22 (The Great Depression Begins, [1929-1933]) – This site gave sources, questions, terms, and quiz questions Instructional Resources Delong, J. (1997). Slouching towards utopia?: The economic history of the twentieth centuryXIV. The great crash and the great slump. Retrieved October 28, 2007 from http://econ161.berkeley.edu/TCEH/Slouch_Cras h14.html – This site gives an immense amount of information and resources. It provides graphs as well as world background to the Great Depression. This site was developed by a professor at the University of California, Berkeley and has many different chapters at a persons disposal, not just material on the Great Depression. Instructional Resources Student References Danzer, G., Klor de Alve, J., Krieger, L., Wilson, L., Woloch, N. (2007). The Americans: Reconstruction to the 21st century. Evanston, IL: McDougal Littell. – This is the text book that is used for this particular history class. It covers American history from the end of the American Civil War through the beginning of the 21st century. The book is broken down into seven units and consists of twenty six chapters. The chapters used for this resource unit included the end of chapter 13 (The Roaring Life of the 1920’s) most of chapter 14 (The Great Depression Begins), most of chapter 15 (The New Deal), and the beginning of chapter 16 (World War Looms). This tool provided very good background and activity ideas. It also gave ideas for assessment opportunities. Instructional Resources Kirk, K. (2005). The Great Depression treasure hunt. Retrieved November 7, 2007 from http://web.dps.k12.va.us/gibson/7th%20Grade% 20Webpage%20by%20Kirk/Depression_Thunt.h tm – This activity will get the students involved with the Great Depression through technology. The web quest has many links and educational tools that the students will benefit from. There are interactive questions as well as a work sheet that the students will use to guide their endeavors during the activity. Instructional Resources Gibson, K. Causes of the Great Depression. Retrieved November 7, 2007 from http://web.dps.k12.va.us/gibson/7th%20Grade% 20Webpage%20by%20Kirk/Causes%20of%20th e%20Great%20Depression_GO.gif – This is a very simple diagram that uses main ideas to help break down the causes of the Great Depression in a visual manner. Students could use this as a starting point and as time went on they could fill in details under each category. Students learn in many different ways, and the more diverse learning techniques that are implemented in the classroom the more students will benefit. Instructional Resources Delong, J. (1997). Slouching towards utopia?: The economic history of the twentieth centuryXIV. The great crash and the great slump. Retrieved October 28, 2007 from http://econ161.berkeley.edu/TCEH/Slouch_Cras h14.html – This site gave a very informative graph that the students will use and analyze to show the effects of the Great Depression, not only in America but on a World Wide scale. Although this unit is geared toward an American history course, world wide context is always pertinent information. Instructional Resources Encyclopedia Britannica. (2007). Tenant farming. Retrieved November 3, 2007 from Encyclopedia Britannica Online: http://www.britannica.com/eb/article-9071664 – This gives students definitions that are more complete and easy to understand in a real world context compared to text-book definitions. This particular definition gave students insight into tenant farming and its impact in the 1930’s. Instructional Resources Ganzel, B. Farming in the 1930’s:The dust bowl. Retrieved November 2, 2007 from http://livinghistoryfarm.org/farminginthe30s /water_02.html – This website gives definitions and first hand video account of people who lived through the dust bowl and the experiences that they took from this time period. Instructional Resources Ibis Communications. (2007). History in motion: The dust bowl 1936. Retrieved November 8, 2007 from http://www.eyewitnesstohistory.com/himdu stbowl.htm – This website gives first hand historical accounts. This particular video gives a good representation of what someone living through the dust bowl would have seen during one of the storms. Instructional Resources F.D.R. Memorial. (2004). A new deal. Retrieved November 8, 2007 from http://www.nps.gov/fdrm/generation/newde al.htm – This website gives a very good overview of what the new deal was trying to accomplish and the goals that F.D.R. set out to accomplish. It is short but very concise. Students can read this and use it as a cheat sheet for quick reference. Instructional Resources Peters, G. (1999). Franklin D. Roosevelt: First fireside chat (banking). Retrieved November 5, 2007 from http://www.presidency.ucsb.edu/mediaplay.php?i d=14540&admin=32 – This is a clip of F.D.R.’s first fireside chat where he addressed the nation about banking. This resources allows the students not only to hear the words of F.D.R. but allows them to see the person as well. It is a first hand account and is a very good educational tool. Instructional Resources Eidenmuller, M. (2001). Franklin Delano Roosevelt: Pearl Harbor address to the nation. Retrieved October 30, 2007 from http://www.americanrhetoric.com/speeche s/fdrpearlharbor.htm – This website gives a first hand account of F.D.R.’s speech to the nation. In addition to giving the audio, this website has a transcript of his speech so students can read along as F.D.R. is speaking. Instructional Resources Lavender, C. Songs of the Great Depression. Retrieved November 8, 2007 from http://www.library.csi.cuny.edu/dept/history/laven der/cherries.html – This website gives three examples of songs/poems that were written at this time. Although there is no audio streaming from this website, it would not be very difficult to find a copy of one of the songs for the students to listen to. Music often reflects the culture of a time period and I feel that these are three good reflections of the Great Depression. Instructional Resources Ford, J. (1940). The grapes of wrath (movie). Retrieved November 2, 2007 from http://imdb.com/title/tt0032551/ – Oklahoma in the Thirties is a dustbowl and dispossessed farmers migrate westward to California. After terrible trials en route they become little more than slave labor. Among the throng are the Joads who refuse to knuckle under. ~ plot summary – This movie will give students a different form of exposure to the hardships that people faced in the 1930’s Instructional Resources Cassutto's, G. (2007). The alphabet soup of New Deal agencies. Retrieved November 3, 2007 from http://www.cyberlearningworld.com/lessons/ushistory/newdealagencies.htm – This resource was pulled from the web and gave the idea for the “Alphabet Soup of the New Deal” game. The project listed in this resource unit is an adaptation that uses a more student centered style of learning. – Students will make a poster board depicting between 8 and 10 acronyms from the New Deal era. The students will tell what the acronym stands for, give a brief synopsis of what the group accomplished, and a draw/copy a picture of the group or an accurate representation of the group. Instructional Resources What the president wants. This is a political cartoon that was pulled from the internet on November 4, 2007 from http://www.nisk.k12.ny.us/fdr/1937/37_scgifs/sm all/37021601.gif – This cartoon depicts Roosevelt trying to squash the Supreme Court with his New Deal. This cartoon shows the opposite side of what many students are taught about F.D.R. For most students F.D.R is portrayed as a knight in shining armor that rescued America from the Great Depression. This cartoon, and the activity that goes along with it, gives perspective to other points of view. Instructional Resources Library of Congress. (2007). Scenes from the Great Depression: 1935-1945. Retrieved November 5, 2007 from http://youtube.com/watch?v=pgR2Buke5M Q – This gives a great picture show and has music from the time period in the background. This should get an emotional response from students. Instructional Resources (2007).The Great Depression: (Britannica.com). Retrieved November 5, 2007 from http://youtube.com/watch?v=TCNKq09p3w – This video shows the panic of the Stock Market crash in 1929. It gives first hand video of the panic in the streets as well as the ramifications felt worldwide. Instructional Resources (2007). U.S. thrilled as FDR outlines recovery,1933/10/23 (1933). Retrieved November 5, 2007 from http://youtube.com/watch?v=PXY7TkrPPzI – This is the actual video of a F.D.R. speech to the nation. He speaks about farm recovery, money security, and home foreclosure. Assessments “Web Quest”-20 points Paragraph from picture10 points “My Family” Assignment20 points “Fireside Chat” Notes and Class Discussion -15 points “Alphabet Soup” Poster20points Poetry/Music – S.O.A.P. – 15 points “Grapes of Wrath” Poster20 points F.D.R. Political Cartoon – 10 points for analysis – 10 points for creating a new picture Response to Video Clips – 5 points for each video clip response (15 points total) Unit Test – 50 points Unit Test Questions 1. Multiple Choice Questions The strongest opposition to F.D.R.’s New Deal came from? 1. 2. 3. 4. 2. Migrant Workers Business Leaders Factory Workers Recent immigrants In the 1930’s, which geographic change most influenced the westward migration of thousands of people from the Southern Great Plains? 1. 2. 3. 4. Extended drought in farming areas Excessive flooding of the Mississippi Earthquakes in Pacific coastal regions Destructive hurricanes in the Gulf of Mexico Unit Test Questions Multiple Choice Questions 3. What event most closely associates with the end of the Great Depression? Passage of the Social Security Act Beginning of WWII Re-election of F.D.R. in 1940 Announcement of the Marshall Plan 4. The Dust Bowl experiences of the Oklahoma farmers during the Great Depression demonstrated? The effect of geography on peoples’ lives The success of government farm subsidies The limitation of civil liberties during times of crisis The result of the Indian Removal Act Unit Test Questions Short Answer 1. Give 3 examples of Alphabet Soup agencies. Give the acronym, the actual name, and something that the agency accomplished 2. How did the Dust Bowl impact farmers in Oklahoma? Unit Test Questions Extended Response 1. In four to six sentences, explain how the prosperity of the 1920’s facilitated the economic collapse of the 1930’s. Intervention and Adaptation Any student that needs interventions or adaptations will be accommodated. The student can sit closer to the front of the room to see the PowerPoint presentation more clearly. The student can be provided with audio equipment to hear lectures/audio clips more efficiently. Extra time will be granted for tests if need be. When needed, an intervention specialist will be provided. Extra time, or alternate assignments, will also be provided for reading and writing assignments for students who need it. Reflection Since I have been unable to implement this resource unit, I have no reflection at this time. In the future I hope to use this as an educational tool that facilitates learning in my classroom.