- Syneratio
advertisement
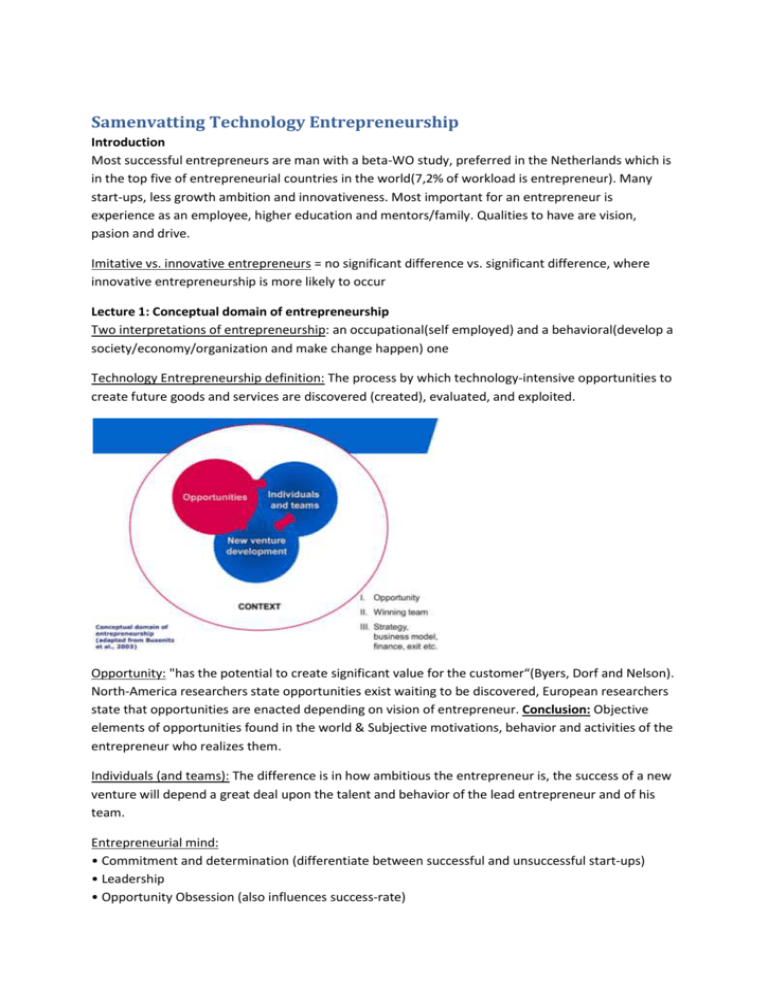
Samenvatting Technology Entrepreneurship Introduction Most successful entrepreneurs are man with a beta-WO study, preferred in the Netherlands which is in the top five of entrepreneurial countries in the world(7,2% of workload is entrepreneur). Many start-ups, less growth ambition and innovativeness. Most important for an entrepreneur is experience as an employee, higher education and mentors/family. Qualities to have are vision, pasion and drive. Imitative vs. innovative entrepreneurs = no significant difference vs. significant difference, where innovative entrepreneurship is more likely to occur Lecture 1: Conceptual domain of entrepreneurship Two interpretations of entrepreneurship: an occupational(self employed) and a behavioral(develop a society/economy/organization and make change happen) one Technology Entrepreneurship definition: The process by which technology-intensive opportunities to create future goods and services are discovered (created), evaluated, and exploited. Opportunity: "has the potential to create significant value for the customer“(Byers, Dorf and Nelson). North-America researchers state opportunities exist waiting to be discovered, European researchers state that opportunities are enacted depending on vision of entrepreneur. Conclusion: Objective elements of opportunities found in the world & Subjective motivations, behavior and activities of the entrepreneur who realizes them. Individuals (and teams): The difference is in how ambitious the entrepreneur is, the success of a new venture will depend a great deal upon the talent and behavior of the lead entrepreneur and of his team. Entrepreneurial mind: • Commitment and determination (differentiate between successful and unsuccessful start-ups) • Leadership • Opportunity Obsession (also influences success-rate) • Tolerance of risk, ambiguity, and uncertainty • Creativity, self-reliance (LOC) and not afraid of failing • Motivation to excel/Need for achievement (differentiate between successful and unsuccessful start-ups) • Energy, health and emotional stability • Intelligence 1. Abstract thinking or reasoning 2. Problem-solving capacity 3. Capacity to acquire knowledge 4. Memory 5. Adaption to one's environment Non-entrepreneurial Mind: •Invulnerability: nothing can happen to me, take unnecessary chances and unwise risks. •Machismo: impress others by taking large risks (adrenaline junkies), more than overconfidence, irrational. •Anti-authoritarion: no one can tell me what to do! In contrast with seeking and using feedback to attain goals, seeking team members and other necessary resources to execute an opportunity. •Impulsivity: fail to explore the implications of your actions and do not review alternatives before acting. •Outer control: opposite of internal locus of control. I cannot control what happens to me. •Know it all: entrepreneurs who think they have all the answers usually have very few. They fail to recognize what they not know. Lecture 2: Strategy NOT a good strategy: • Pretending there is no problem / challenge • When it only consists of goals (Strategy is how to get there!) • Vague concept / Misty Vision(official goal): An informed and forward-looking statement of purpose that defines the longterm destiny of the firm. •Clarity: Easily understood and focused • Consistency: Holds constant over a time period • Uniqueness: Special to this enterprise • Purposeful: Provides reason for being Mission(official goal): Description of the course of action to implement the vision (mission statement can contain: core values, customers/stakeholders, products, competitive advantage, values provided to customer and market/industry) Goals(operative goals): Desired results that are specific and measurable. Core competences: Unique skills and capabilities. Below a classification for starters by Hardjono (1995): Value proposition(Unique selling proposition=small version): States who the customer is and describes the values (the worth, importance, or usefulness) offered to this customer. This value proposition has five key values: product, price, access, service and experience. Strategy: Plan of action. How to achieve the desired results? What steps should we take? Strategy of a company: The specific pattern of decisions and actions that managers take to use core competences to achieve a sustainable competitive advantage and outperform competitors. Building blocks that determine the strength/superiority of the core competences: • Specialized resources (Functional and Organizational resources) • Coordination (result of the structure and culture) Strategy in an Entrepreneurial Context Start-ups: • Resource-starved • Financial limitations • Lack of experience • No (or limited) credibility in the market-place (liability of newness) • Startups generally have no existing products or services, and no existing customer base Three primary considerations for an early startup to demonstrate: • That products and services will sell • That the process for selling the products and services scales up • That a larger potential market exists for the products and services. • When these three have been demonstrated, investor confidence rises. The focus of the entrepreneur: • Attracting investors & sufficient resources • Attracting customers • When crafting a strategy for your startup, aim for returns that correspond to expectations of your investors, investors in startups are more tolerant of short-term losses and you can take advantage of this. • Address a major pain of the customer, and fully understand how you are going to find the target customer • Your strategy must take into account the necessity to focus during your early years. Established Company Perspective • CEOs must be concerned with the long-term viability • Market value of a firm is projected continuously • Senior managers must also constantly be aware of short-term market perceptions Strategic Planning Strategic Planning Model(in start-ups): • Vision and Mission Statement • Internal analysis -> Strengths and Weaknesses (A. Entrepreneurial Characteristics, B. Internal Resources and Abilities, C. Core Competences, D. Weaknesses) • External analysis -> Opportunities and Threaths (Macro Environment: PEST & Micro Environment: 6 Forces) PEST-factors: • Political and environmental forces • Economic forces • Social, demographic and cultural forces • Technological forces 6 forces model: Sources of uncertainty: • Complexity: strength, number and relationship between the environmental forces • Dynamic: number and speed of change • Richness: number of resources available SWOT-matrix: Outcome SWOT analysis: • S-O: Push the company forward • S-T: Startup can face the environmental challenges using core competences and entrepreneurial characteristics -> neutralize (some of) the threats. • W-O: Cover some of the internal weaknesses by external resources. • W-T: Don’t enter the market! Porter’s generic strategies: • Cost-leadership • Differentiation • Focus Four potential strategies: Black Hole Approach(Operational Excellence): Cost minimizing → Focus on Material assets(cost structure/cash flow/Revenue Streams Solar System Approach(Product Leadership): Uniqueness → Focus on intellectual assets Virus Approach(Customer Intimacy): spread virus to every potential customer → Focus on commercial assets Thunderstorm Approach(Resource Enrichment): Ideal Combination of Conditions Necessary → Focus on socialization assets(communication/flexibility) Lecture 3: Creating a Unique Business Model Business model definition: • Business model is a set of assumptions about how a firm will create and capture (appropriate) value for all its stakeholders – connecting technology to economic profits (Dorf and Byers, 2005). Rhineland vision • Business model is a representation of how an organization makes money and prevents others from making that money. Anglo Saxon vision BP levels: Anglo-Saxon vs. Rhineland Product uniqueness Value Pyramid: 3 layers: Purchase Conduct: Business Model CANVAS: 9 building blocks • Customer • Value Proposition • Distribution Channel • Customer relations • Revenue structure • Key resources • Key activities • Cost structure Lecture 4: Effectuation Two different ways of building a venture: • Textbook way(causal) • Expert entrepreneurial way(effectual) → begin doing → interact with potential stakeholders → let commitment of stakeholders reshape the goals → repeat process until new venture Effectual reasoning: the process: Different ways of thinking: • Managerial thinking → causal reasoning → selecting between given means to achieve a predetermined goal • Strategic thinking → creative causal reasoning → generating new means to achieve pre-determined goals • Entrepreneurial thinking → effectual reasoning → imagining possible new ends using a given set of means Effectual reasoning: the problem Causal vs. Effectuation: Framework f of prediction and control: Experience and firm lifecycle: Effectual reasoning: • No greater success-rate, but reduces cost of failure(less investment and earlier failure) • control of an unpredictable future Consequences for business plans: • business plan as an exercise • Slide deck instead of lengthy business plan • Stakeholder commitments! Lecture 5: The new venture team & Social Capital Management: A set of processes such as planning, budgeting, organizing, staffing and controlling that keep an organization running well. Leadership: The process of influencing and inspiring people to work together to achieve a common goal. Four styles of leadership: Seven traits of leaders: 1. Authenticity: consistent actions and words 2. Decisiveness: willing to act on limited, imperfect information 3. Focus: create a priority list and stick to it 4. Care: build relationships and social capital 5. People skills: offer helpful feedback and good coaching to all team members 6. Communication: stimulate conversation and communicate vision 7. Continuous improvement: keep learning and energy flowing in the firm, retain optimism Emotional intelligence (EI): most important act of the leader 1. Self-awareness 2. Self-management 3. Social awareness 4. Relationship management Entrepreneur ≠ manager / leader → entrepreneur who clings to the lead role too long will limit company growth Entrepreneur = manager / leader → shift from exploration/passionate commitment/direct personal control to exploitation/dispassionate objectivity/indirect personal control Truth is somewhere in between! Ventures go through stages of growth from start-up, through rapid growth, to maturity, to decline and renewal -> role of the entrepreneur changes. New venture team Description: 2-6 people with skills in finance/marketing/product development/production/human resource management selected on social/human capital. Effectiveness: all responsible/good communication/overall consensus/work together Collaboration: communication/cohesion/work norms/mutual support/coordination of tasks/balance Common pitfall: haste the formation process of the venture team Attracting/Retaining key employees depends on: Compensation systems, work design and training Main points: 1. A strong team usually makes the difference between a success and a marginal or failed venture 2. The fit concept (having a management team whose skills are complementary) is central in anticipating management gaps and building the team 3. Sharing the wealth and ownership with those who create it, are key to team building 4. Numerous pitfalls await the entrepreneur in team building and need to be avoided Social Capital/Social competence Social capital: consists of the accumulation of active connections among people in a network. Social competence: entrepreneurs' overall effectiveness in interacting with others 1.Social perception: accuracy in perceiving others (e.g. their traits, intentions, motivations). 2.Social adaptability: the ability to adapt to, or feel comfortable in a wide range of social situations. 3.Expresiveness: the ability to express one's emotions and feelings clearly to generate enthusiasm in others. Alliances: share knowledge/access new markets/efficiency/complement product/risk sharing Innovation: consists of an invention & market introduction of the invention. Innovation typologies: Value Chain: Networks: gives opportunities, extra resources and reduce liability of newness Venture Capital Private VC: (groups of) private investors investing VC in young start-up firms. Corporate VC: companies investing in VC funds → especially valuable in the first stages of technology development Corporate VC goals: • Financial returns • Strategic: learning new market developments and option building (portfolio of VC investments to create options) Why are some entrepreneurs more successful than others in exploiting opportunities? Many factors, interacting in complex ways, ultimately determine the success of individual entrepreneurs – being able to perform different roles (entrepreneur/manager/leader), their social capital, social competence, being a proper team builder, undertaking alliances etc. etc. Lecture 7: Financial Management Steps to Build A Financial Plan: 1. The Sales Forecast(assumptions on # customers/# sales p. customer/growth-rate sales)→ 2-3 years 2. The Costs Forecast(assumptions on the cost of doing business, cost associated with sales forecast) 3. The Income and Cash Flow Statement(summarizes revenues and expenses/summarizes the cash effects) 4. The Balance Sheet(summarizes the assets, liabilities and shareholders’ equity) 5. Break even analysis 6. Financial (performance) ratio’s(liquidity/investment/gearing/profitability/financial) → ROI = net income/ investment, ROA = net income/ total assets and Current ratio = current assets/ current liabilities 7. Stages of financing and financing sources: Always make 3 scenarios: a best case, a worst case and a realistic case. Five Methods of Harvesting The Wealth Created by a New Firm: • The Sale of the Firm to An Acquiring Firm • The Sale of the Firm's Stock on A Public Market through An Initial Public Offering • Issuance of Cash Dividends to the Owners and Investors • The Sale of the Firm to the Managers and Employees • Transfer the Firm through Gifts and Sales to Family Successors Risks and stages of funding: • R&D risks → Seed funding • Manufacturing risks →Seed / early stage funding • Marketing risks → early stage funding • Management risks → Growth / mezzanine funding Net Present Value (NPV): Real option analysis: Assesses the value of entrepreneurial decisions in response to new information “Bootstrap” Financing: depend solely on the resources available from oneself, family, and friends • Advantage: less pressure/easy terms/total control/no time spend on finding investors • Disadvantage: unable to fund growth stage/no funding commitment/loss of advice “Moonlighting”: slowly go from employed to self-employed Angel financing: One person investment(experienced entrepreneur) in promising start-up Venture Capital Financing: Investment professionals in high potential start-ups Bank Loans: Banks loan on assets but require demonstration of capacity to repay Government Financing: Government intervenes in the financing of new ventures to remedy market failure









