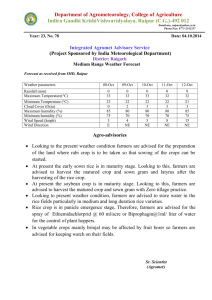
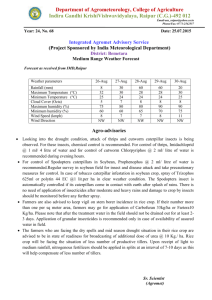
ANNUAL REPORT KVK SAGROLI - 2013
advertisement

REVISED PROFORMA FOR ANNUAL REPORT – 2013-2014 1. GENERAL INFORMATION ABOUT THE KVK 1.1. Name and address of KVK with phone, fax and e-mail Address Telephone Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Sharda nagar, Office FAX 02465 At. Post. Sagroli, Tq. Biloli Dist. 02465 - 227757 227757 Nanded - 431731 1.2 .Name and address of host organization with phone, fax and e-mail Address Telephone Office FAX 02465-227843, 02465-227848 Sanskriti Samvardhan Mandals, Sharda nagar, At. Post. Sagroli, Tq. 227848 Biloli Dist. Nanded - 431731 E mail kvksagroli@gmail.com E mail deshpramod@gmail.com 1.3. Name of the Programme Coordinator with phone and mobile No Name Telephone / Contact Residence Mobile Email 09890382130 Suresh12.kvksagroli@gmail.com Dr. Suresh D. Kulkarni Sharda nagar, Sagroli 1.4. Year of sanction: Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Sagroli, is established in October 2011 (Vide Sanction Letter No. F.N0. 5-2/2009-AE II, dated 4/10/2011, ICAR, New Delhi-12), 1.5. Staff Position (as on 31st March, 2014) Sr. No . Sancti oned post Name of the incumbent Desig natio n Discipl ine Pay Scale (Rs.) Present basic (Rs.) Date of joining 1 Dr. Suresh Dhondopant Kulkarni Mr. Kapil Shivajirao Ingle Prog. Coor. SMS 3 SMS Dr. Datta Ashok Mhetre SMS 4 SMS Mr. Pravin Purushottam Deshpande SMS 22320+RGP 8000 15600 – 39100 GP 5400 15600 – 39100 GP 5400 15600 – 39100 GP 5400 5 SMS Mrs. Madhuri Sudhakarraro Revanwar SMS 6 SMS SMS 7 SMS 8 Prog. Assis. Comp . Prog. Farm Mana Dr. Gajanan Pandurang Dhage Mr. Vaijanath Tukaram Bombale Mr. Vyankat Pandharinath Shinde Mr. Suprabandh Babanrao Bhavsar Agri. Extn. Agron omy Hortic ulture Plant Protect ion Home Scienc e Vet.. Scie. Agri. Eng. 31230 2 Prog. Coor. SMS Prog. Assis. Prog. Assis Mr. Vivek Subhashrao Patange Farm Mana 9 10 SMS 14/07/12 Perma nent /Temp orary -- Category (SC/ST/ OBC/ Others) Open 21630 19/06/12 -- Open 21630 02/07/12 -- OBC 21630 30/06/12 -- Open 15600 – 39100 GP 5400 21630 30/06/12 -- Open 21630 02/07/12 -- Open 21000 01/03/13 -- OBC 13910 15/06/12 -- Open Comp. Prog. 15600 – 39100 GP 5400 15600 – 39100 GP 5400 9300-34800 GP 4200 9300-34800 GP 4200 13910 26/06/12 -- OBC Agron omy 9300-34800 GP 4200 13910 20/06/12 -- Open 1 11 12 13 14 15 16 ger Acco untant / Super intend ent Steno graph er Drive r Drive r Supp orting staff Supp orting staff 1.6. S. No. 1 2. 3. 4. 5. 1.7. ger Acco untan t/ Super inten dent Steno graph er Drive r Drive r Supp orting staff Supp orting staff Mr.Padmakar Shankarao Deshpande Mr. Sudhir Sureshrao Deshpande Mr.Dnyaneshwar Mohanrao Jadhav Mr. Maroti Sambhaji Jadhav Mr. Manik Shankar Mutyepod Mr. Shankar Govind Dhangar -- 9300-34800 GP 4200 13500 01/03/13 -- Open -- 5200-20200 GP 2400 7830 15/06/12 -- Open -- 5200-20200 GP 2000 5200-20200 GP 2000 5200-20200 GP 1800 7420 12/06/12 -- Open 7420 12/06/12 -- Open 7210 12/06/12 -- ST 5200-20200 GP 1800 7210 12/06/12 -- Open ---- -- Total land with KVK (in ha) : 21.17 ha Item Under Buildings Under Demonstration Units Under Crops Orchard/Agro-forestry Others (specify) Area (ha) 1.12 1.35 18.70 ---- Infrastructural Development: A) Buildings Sr. No. Name of building Sourc e of fundi ng Stage Complete Comple Plinth tion area Date (Sq. m) --- Expen diture (Rs.) -- May 2012 Starting Date 1. Administrative Building ICAR 2. Farmers Hostel ICAR -- -- -- May 2012 3. 4. 5 6 7 8 Staff Quarters (6) Demonstration Units (2) Fencing Rain Water harvesting system Threshing floor Farm godown ------- ------- ------- ------- ------- Incomplete Plinth Status of area construction (Sq. m) 1448.82 First Floor completed 2285.08 Excavation and PCC ------------- B) Vehicles Type of vehicle Mahindra Bolero Tractor C) Equipments and AV aids Year of purchase 2011-12 2011-12 Cost (Rs.) 6,58,000 7,00,840 Total km Run 70020 km 61.2 hr Present status working working Name of the equipment LCD Projector Sony Handy Camera Sony Digi Cam 16 Mp Table Plywood Revolving chair Canon Digital Multifunction Printer 2 CPU and 6 Monitor with Accessories Panasonic Fax Machine Year of purchase 2011-12 2011-12 2011-12 2011-12 2011-12 2011-12 2011-12 2011-12 Cost (Rs.) 30250 15,200 9500 65380 54149 45811 104725 19550 Present status working working working working working working working working 1.8. A). Details SAC meeting* conducted in the year Sr. No. Date 1. 22012013 2. Name and Designation of Participants 1. Mr. Pramod Deshmukh, Chairman, Sanskriti Samvardhan Mandal, Sagroli Salient Recommendations Action taken SAC meeting should include more number of farmers More number of farmers will be invited. 2. Dr. K. Dattatri, Sr. Scientist, Zonal Project Directorate, Hyderabad 3. Dr. Anil Khillari, Veternery officer, Animal Husubardy, Nanded Line departments are communicated the importance of their presence in the meeting. Linkages are strengthened with line departments 4. Mr. Kishor Kulkarni, District Manager, NABARD, Nanded 5. Shri. Ratnakar Kadam, Farmers representative, Cholakha, Tq. Dharmabad Mr. Sambhaji Murke, Farmer representative, Atkali, Tq. Biloli Dist. Nande Mrs. AnitabaiGajegaonkar, Farm Women’ representative, Gajegaon, Tq. Biloli Dist. Nanded Care should be taken to be presence of the line department in the SAC meeting. Linkages with the line department should be increased particularly with ATMA and Agril. Department Farm should have all the representation of the jurisdiction Demonstration units should be established for training purpose Recent varieties should be used for FLD and OFT Training should be conducted for rural youths for self employment. Vocational training for the rural youths are scheduled in action plan Submit the demonstrating units and other activities in collaboration with PPP mode demonstration units are submitted to line department. Fund raising for the KVK should be done from other sources. Different projects are submitted to the ATMA, NHM, and NABARD A farmers advisory committee should be organized for regular advise to KVK A progressive farmer’s Advisory committee is organized. 6. 7. 8. 9. Mrs. Savitabaik Ingole, Farm Women’ representative, Lath, Tq. Kandhar Mr. Sudhir Deshpande, Technical Officer, DSAO office, Agriculture Department, Nanded 10. Programme Coordinator, KVK, Sagroli Action plan prepared as per discussion and representative of the district. Proposals are prepared and submitted to funding agency. Action plan is prepared as per discussion. 2. DETAILS OF DISTRICT (2012-13) 2.1 Major farming systems/enterprises (based on the analysis made by the KVK) S. No 1 2.2 2.4. Only Agriculture (most of the farmers) 2 Agriculture + Animal Husbandry (1-2 Deshi milch animals) 3 Agriculture + Poultry (10-20 deshi birds) 4 Agriculture + Goatery (2-3 goats) 5 Agriculture+ Horticulture (Mango, Guava, Sapota, Sweet orange etc few plants) 6 Agriculture + Vegetable production on small scale. 7 Nonfarm enterprises – sewing and stitching, Rope making bamboo sheets. Description of Agro-climatic Zone and major agro ecological situations (based on soil and topography) Sr. No 1 2.3 Farming system/enterprise Agro-climatic Zone Central Maharashtra Plateau Zone /Assured Rainfall Zone (VII) Characteristics Climatic condition- Maximum temp. 41 C Minimum temp. 21 C. Average annual rainfall- 700 to 900 mm 75 % rains received Soil type- Soil color ranges from black to red. Type- 1) vertisols 2) entisols and 3) incept sols PH 7-7.5. Crops and cropping pattern- In kharif Rainfed cotton(32.24%) ,soybean (25.40%), Kharif Jawar (17.77%), Pigeon pea(7.8%), Black gram(7.38%), Greean gram (6.06%) are predominant crops .In Rabi sesson Bengal gram(44.87%), Rabi Jawar (37.39%),Wheat(10.12%), Safflower(5.72%) Sugarcane and summer groundnut are taken on availability of irrigation. Soil types S. No Soil type 1 Deep black soil 2 Medium deep black 3 Shallow deep black Characteristics ---- Area in ha 394000.65 (36.81%) 101000.12 (9.43%) 576000.26 (53.75%) Area, Production and Productivity of major crops cultivated in the district year (2012-13) S. No Crop Area (ha) Production (Qtl) Productivity (Qtl /ha) 1 Kharif rice 13 06 449 2 Kharif Jawar 883 21 2843 3 Pigeon pea 568 326 566 4 Green gram 28248 56 666 5 Black gram 3000 172 568 6 Rabi Jawar 292 271 927 7 Wheat 490 794 1621 8 Bengal gram 529 468 884 9 Sugarcane 154 8275 60 10 Cotton 2765 6039 331 11 Kharif sesamum 10 3 202 12 Niger 7 2 286 13 Kharif sunflower 2 0 NCR 2 15 16 17 18 19 Rabi sunflower Summer sunflower Soybean Castor Safflower Mustard 44 17 154 6 56 1 28 12 3249 2 45 0 630 726 1549 357 800 300 Area production and productivity of fruit corps (2011-12) Sr. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Name of fruit Mango Banana Lime/Lemon Mosambi Orange Guava Papaya Pomegranate Sapota Area (ha) 633 15000 51 202 10 18 253 6 74 Production (MT) 3133.35 1425000 255 2828 140 171 2024 24 296 Productivity (MT/ha) 4.95 95 5 14 14 9.5 8 4 4 *Source– Districts. A.O., Nanded. Area production and productivity of Vegetable crops: (2011-12) Sr. Name of veg. 1. Potato 2. Onion 3. Tomato 4. Brinjal 5. Cabbage 6. Cauliflower 7. Okra 8 Peas Area (ha) 20 380 465 217 26 34 168 30 Production (MT) 300 6840 8370 5425 494 646 1848 120 Productivity (q./ha) 15 18 18 25 19 19 11 4 *Source–District S.A.O., Nanded. 2.5. Weather data Month Rainfall (mm) Temperature 0 C Maximum Minimum 40 26 36 20 34 21 32 22 36 22 Relative Humidity (%) June-2013 201.18 87.9 July-2013 430.82 87.2 Aug-2013 220.61 86.8 Sep-2013 130.38 90.0 Oct-2013 108.24 81.1 Total 1091.23 2.6. Production and productivity of livestock, Poultry, Fisheries etc. in the district 2.7 Sr. No. Animal Number 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 3,48,000 2,48,000 3,79,000 52,000 1,26,000 4,31,000 Cattle Buffaloes Goat Sheep Poultry Commercial Poultry Backyard Details of Operational area / Villages (2012-13) Sr. No. Talu k Name of the block Name of the village Major crops and enterprises Major problem identified Identified Thrust Areas Atkali, Rampurthadi, Doulatapur, Hiparga, Sagroli, Bolegaon, Karla Kharif: Cotton, Soybean, Tur, Moog, Udid Rabi: Bengalgram, Wheat, RabiSorghum, Summer: Groundnut, Bhendi, Brinjal 1) Wrong selection of verities/Hybrids as per soil type, farming situation (Rain fed/Irrigated) 2) No seed treatment 3) Inadequate use of fertilizers, Do not apply fertilizers in split doses especially N. 4) Lack of in situ soil moisture conservation measures. 5) Timely and quality agriculture inputs availability 1) Use of Improved verities /Hybrids. 2) Integrated Nutrient Management 3) Integrated weed management 4) Water management 5) Integrated pest management Bilol i Biloli 2 Naig aon Naigao n Kedarwadgaon , Narsi, Gadga, Hotal Kharif: Cotton, Soybean, Tur, Moog, Udid Rabi: Bengalgram, Wheat, RabiSorghum, Summer: Groundnut, Bhendi, Brinjal Mango,Turmeric, chilli, brinjal 1) Wrong selection of verities/Hybrids as per soil type, farming situation (Rain fed/Irrigated) 2) No seed treatment 3) Inadequate use of fertilizers, Do not apply fertilizers in split doses especially N. 4) Lack of in situ soil moisture conservation measures. 5) Timely and quality agriculture inputs availability 6)Irregular fruiting, 7)Nutrient deficiency and low productivity 1) Use of Improved verities /Hybrids. 2) Integrated Nutrient Management 3) Integrated weed management 4) Water management 5) Integrated pest management 6) Use of Growth regulators, INM and 7) Use of improved varieties 3 Kan dhar Kandh ar Lath(khurd), Bamni, Shelali Kharif: Cotton, Soybean, Tur, Moog, Udid Rabi: Bengalgram, Wheat, RabiSorghum, Summer: Groundnut, Bhendi, Brinjal Mango, Onion, Chilli and Tomato 1) Wrong selection of verities/Hybrids as per soil type, farming situation (Rain fed/Irrigated) 2) No seed treatment 3) Inadequate use of fertilizers, Do not apply fertilizers in split doses especially N. 4) Lack of in situ soil moisture conservation measures. 5) Timely and quality agriculture inputs availability 6)Irregular fruiting, 7)Nutrient deficiency 1) Use of Improved verities /Hybrids. 2) Integrated Nutrient Management 3) Integrated weed management 4) Water management 5) Integrated pest management 6) INM And Growth regulator 1 2.8 Priority / Thrust areas Crop/Enterprise Thrust area Agronomy Cotton Soybean Kharif Sorghum Pigeon pea Black gram/Green gram Bengal gram Rabi Jawar Wheat Safflower Summer groundnut Integrated Nutrient Management Integrated weed management Water management Integrated pest management Use of Improved varites/Hybrids Integrated Nutrient Management Integrated pest management Integrated Nutrient Management Integrated weed management Integrated pest management Integrated Nutrient Management Integrated weed management Integrated pest management Use of Improved varites/Hybrids. Integrated Nutrient Management Integrated weed management Integrated pest management Use of Improved varites/Hybrids Integrated Nutrient Management Integrated weed management Integrated pest management Use of Improved varieties/Hybrids Integrated Nutrient Management Soil and water conservation. Integrated pest management Use of Improved varieties/Hybrids Integrated Nutrient Management Integrated weed management Integrated pest management Water Management. Use of Improved varieties/Hybrids Integrated Nutrient Management Soil and water conservation. Integrated pest management Integrated pest management Integrated Nutrient Management Integrated weed management Water Management. Horticulture Mango Brinjal Turmeric Integrated Nutrient Management Introduction of new varieties Integrated micro nutrient management Plant Protection Cotton Soybean IPM, Trainings, Publications Awareness about seed treatment and bio-pesticides, Demonstration on pest management, Trainings, Field Days, Publications FLD on Gram, Trainings, Field Day, Publications IPM, FLD, Training, Publications Bengal gram Rice Home Science Improvement in nutritional status of women and children Increasing self-employment by value addition through agro based small scale enterprises. Reduce drudgery by popularizing hand operated agricultural tools among farm women Balanced diet through kitchen gardening and available food items. Awareness about importance of hygiene and sanitation. Awareness of consequences of early marriage. Health and Nutrition Drudgery Reduction Veterinary Science Poultry Increase in area under fodder crop and productivity of livestock. Feed cost reduction through exploiting nutrient efficient local resources. Self-employment generation through income generating activity. To increase productivity and to reduce metabolic diseases through proper feeding and balanced diet. Corrective measures for various common ailments in livestock. Better profitability through market driven production. Increase in area under fodder crop and productivity of livestock. Feed cost reduction through exploiting nutrient efficient local resources. Self-employment generation through income generating activity. To increase productivity and to reduce metabolic diseases through proper feeding and balanced diet. Corrective measures for various common ailments in livestock. Better profitability through market driven production. Goats /sheep Cattle / buffaloes 3. TECHNICAL ACHIEVEMENTS 3. A. Details of target and achievements of mandatory activities by KVK during 2012-13 OFT (Technology Assessment and Refinement) 1 Number of OFTs Targets Achievement 15 15 Number of Farmers Targets Achievement 177 177 Training (including sponsored, vocational and other trainings carried under Rainwater Harvesting Unit) 3 Number of Courses Number of Participants FLD (Oilseeds, Pulses, Cotton, Other Crops/Enterprises) 2 Number of FLDs Number of Farmers Targets Achieveme Targets Achievement nt 29 29 239 384 Extension Activities Number of activities 4 Number of participants Clientele Targets Targets 48 14 Achieveme nt 58 17 876 251 Achieve ment 1224 389 Farmers Rural youth Extn. Function aries 12 11 227 201 Seed Production (Qtl.) 5 Target Achievement Cereals - 6.00 9.75 Pulses - 3.00 9.27 Oil seed – 15.00 26.49 Targ ets 339 Achieveme nt 472 Target s 20500 Achievement 534542 Planting material (Nos.) 6 Target Achievement Vegetable Seedlings - 10000 767450 Fodder - 10000 203231 3. B. Abstract of interventions undertaken Interventions S. No Thrust area Crop/ Enterp rise Identified Problem Soybea n Yield losses due to weed infestation, Higher cost of weed management, Unable to control both type (Broad leaved and grassy) weeds. Safflow er (PBNS40) Safflower is dry land crop grown in Nanded dist. But area under this crop is goes on decreasing day by day because of low yielding traditional varieties, disease pest problems & difficulties in harvesting thorny verities. Agronomy Weed Manage ment 1 Varietal evaluatio n 2 Title of OFT if any Weed managemen t in soybean crop through use of post emergence herbicide. Assessment of improved and nonspiny variety in Safflower (PBNS- 40) with local spiny variety to increase productivity and easiness in harvesting. Title of train ing for exten sion pers onne l if any Exten sion activit ies Supply of seeds, planting materials etc. Title of FLD if any Title of Training if any - Improved varieties in Cotton & Soybean - Field day HerbicideChlorimur on methy and Quazalfop ethyl -- ICM in safflower, Agronomical measures in soil moisture conservation in rabi jawar, safflower. -- - Seeds of PBNS-40 Integrate d crop Manage ment Bengal gram (Jaki9218) 3 Lower yield due to traditional package of practice. - Integrated crop managem ent by using recomme nded package of practices - Integrated crop managem ent by using recomme nded package of practices Integrate d crop Manage ment Green gram (Utkars h) 4 Lower yield due to traditional package of practice. ICM in Gram, Seed production technology Bengal gram - Field day Field day Integrate d crop Manage ment 5 Pigeon pea (Vipula ) Lower yield due to traditional package of practice . - Integrated crop managem ent by using recomme nded package of practices Field day Soil testingNormal test Seed(Jaki 9218) Trichoder ma Rhizobiu mPSBSulphurZinc SulphateFerrous sulphatePheromon e trapHaNPV Neem oil (1500 PPM) SeedUtkarsh Seed treatment – Rhizobiu m PSB. FertilizerUrea SSP Metysysto xSoil Testing SeedVipula Seed treatment – Rhizobiu m -250 gm. PSB- 250 gm. FertilizerUrea SSP Sulphur Pheromon e traps Indoxacar b- Varietal evaluatio n Pigeon pea (BDN711) 6 Lower yield due to use of traditional variety also suscsceptabality to wilt. - Varietal evaluatio n 7 Soybea n (MAUS -71) Lower yield due to use of traditional variety also suscsceptabality grain shattering in late harvesting. - Wheat (Kudrat -17) Lower yield due to use of traditional variety. - Varietal evaluatio n 8 Increase the productivi ty of crop by introducin g new improved high yielding, early variety BDN-711 under dyland condition. Increase the productivi ty of crop by introducin g new improved high yielding variety MAUS 71(Samru dhi) reduce the loses by shattering in late harvesting in soybean crop Increase the productivi ty of wheat crop by introducin g new improved high yielding variety Kudrat-17 SeedBDN-711 Field day SeedMAUS-71 SeedKudrat-17 Varietal evaluatio n Rabi sorghu m(Parb hani moti) 9 Lower grain yield due to use of traditional variety. - Varietal evaluatio n Rabi sorghu m(Parb hani Jyoti) 10 Lower grain yield due to use of traditional variety - Varietal evaluatio n Rabi sorghu m(Akol a kranti) 11 Lower grain yield due to use of traditional variety - Varietal evaluatio n 12 Horticulture Rabi sorghu m(Phul e vasudh a) Lower grain yield due to use of traditional variety - Increase the productivi ty of rabi sorghum crop by introducin g new improved high yielding variety prabhani moti. Increase the productivi ty of rabi sorghum crop by introducin g new improved high yielding variety prabhani moti. Increase the productivi ty of rabi sorghum crop by introducin g new improved high yielding variety prabhani moti. Increase the productivi ty of rabi sorghum crop by introducin g new improved high yielding variety prabhani moti. Panchasutri yojana in production of rabi sorghum, SeedParbhani Moti Agronomical measures in soil moisture conservation in rabi jawar, safflower. Panchasutri yojana in production of rabi sorghum. Agronomical measures in soil moisture conservation in rabi jawar, safflower. Panchasutri yojana in production of rabi sorghum. Agronomical measures in soil moisture conservation in rabi jawar, safflower. Field day SeedParbhani Jyoti SeedAkola kranti Panchasutri yojana in production of rabi sorghum. Agronomical measures in soil moisture conservation in rabi jawar, safflower. SeedPhule vasudha 1 Integrate d nutrient managem ent Mango Nutrient deficiency Nutrition and fruit set managemen t - 2 Growth regulator Mango Irregular and less fruiting Use of cultar in mango - 3 Quality vegetable productio n Tomato Rotting of fruits - Staking in hybrid tomato okra Less yield and YMV - Brinjal Less attractive fruits Varietal assessment in okra - Cucurbi ts Low yield and less marketable fruits 4 New variety Plant Protection 1 IPM Brinjal 2 IPM Paddy 3 IPM 4 IPM - Field day Balanced fertilizer supply according to soil testing report Paclobutr azol supply Seedling material supply Seed supply New variety introducti on in brinjal cv. Arjun Improved varieties of cucurbits cv. Samrat Field day Seedling supply Field day Seed supply Fruit and shoot borer infestation decreased the yield and quality of fruit. Injudicious use of chemical insecticides spray can damage the parasitoids, predator and human health. Resurgence of pest after repeated application of insecticides Farmers do not recognise hoppers at early stages Population of BPH increases at flowering stage No use of bio pesticide. Control of shoot and fruit borer in brinjal -- -- -- News paper covera ge 1) Vota traps for brinjal. 2) Neem oil. 1500 ppm. Managemen t of Paddy plant hopper using fungal pathogen Metarrhiziu m anisopleae. -- IPM of paddy -- --- Metarrhizi um anisoplea e Okra Low yield of okra due to infestation of fruit borer. Managemen t of okra fruit borer. -- --- --- Chickp ea Low yield of chick pea due to infestation of pod borer -- Managem ent of pod borer in Chick pea. IPM in Bengal gram IPM in Beng al gram News Spinosad paper 45 SC @ covera 0.005% ge Extens 1) Pheromo ion ne traps literat for gram ure 2)NSKE 5% 3) HaNPV 250 LE. 5 IPM Soybe an Agriculture Engineering 1 Resource Use of conservat Bullock ion drawn technolo ridger gy Low yield of soybean due to infestation of leaf defoliator -- Low productivity due to scarcity of water In-situ soil and water conserva tion in soybean In-situ soil and water conserva tion in cotton Assessme nt of triple fertiliser hoe in maize 2 Resource conservat ion technolo gy Use of Bullock drawn ridger Low productivity due to scarcity of water 3 Farm machiner ies triple fertilis er hoe broad costing of fertiliser, leaching problem 4 Farm machiner ies Uneven distribution of seed and fertilizer 5 Farm machiner ies See d cu m ferti lizer drill MK V ferti hoe in Rab i sor ghu m Home Science Drudgery 1 Reduction 2 Drudgery Reduction Managem ent of Leaf defoliator in soybean. IPM in soyb ean Extens 1) Pheromo ion ne traps literat for gram ure 2)NSKE 5% 3) Quinalp hos 0.05%. In-situ soil and water conservation Radio talk, Folder Bullock drawn ridger In-situ soil and water conservation Radio talk, Folder Bullock drawn ridger triple fertiliser hoe Use of tractor drawn Seed cum fertiliz er drill MKV ferti hoe in Rabi sorghu m broad costing of fertiliser, leaching problem Importance of seed treatment in soybean Milkin g stool and stand Leg pain while milking the animals Assessment of Milking stool and stand for milking the animals Groun d nut decor ticato r Bhen di cutter Back Pain and finger pain while decorticating the ground nuts Ground nut decorticat or Finger injuries while harwesting bhendi and brinjal Bhendi cutter News paper Seed cum fertiliz er drill News paper MKV ferti hoe 3 Health and nutrition Smok e less Chula Vaibh av sickle Laxmi Sickle VNM KV Khurp i Iron rich toffee Veterinary Science Increase in area under fodder crop and 1 productivity of livestock. 2 3 Increase in milk yield of lactating animals Urea treatment to straw Eye problems while cooking on traditionan Chula Palm pain while using traditional sickle Smoke less Chula Palm pain while using traditional sickle Palm pain while using traditional khurpi Laxmi Sickle VNMKV Khurpi Anemia is major problem identified in women due to which they face many health problems like weakness, leg pain, back pain etc. Vaibhav sickle Assessment of iron rich toffee to increase the hemoglobin content in blood. Cat tle & buf falo Scarcity of green fodder, mortality in new born calves Cat tle & buf falo Cat tle & buf falo Reduced milk yield,hide and bound condition etc - Scarcity of green fodder during summer season - Better forage yield by cultivating jaywant fodder crop Use of mineral mixture to increase milk yield Increasing the quality of low grasses straw by urea treatment - - - - - - Increasing the quality of low grasses straw by urea treatment Incre asing the qualit y of low grass es straw by urea treat ment Ureac hi kimay a bhari nikrus hta chara utkrus htha kari 3.1 Achievements on technologies assessed and refined: A.1 Abstract of the number of technologies assessed* in respect of crops/enterprises Thematic areas Varietal Evaluation Seed / Plant production Weed Management Integrated Crop Management Integrated Nutrient Management Integrated Farming Cereals Oilseeds 1 Pulse s Commercial Crops Vegetabl es Frui ts 1 Flowe r Planta tion crops Supplied eye buds of jayawant fodder crops Chelated Mineral mixture Tuber Crops Urea and jiggery TOTA L 2 1 1 2 2 System Mushroom cultivation Drudgery reduction Farm machineries Value addition Integrated Pest Management Integrated Disease Management 2 1 1 Resource conservation technology Small Scale income generating enterprises TOTAL 2 1 4 1 1 1 3 1 1 3 2 2 3 13 * Any new technology, which may offer solution to a location specific problem but not tested earlier in a given micro situation. A.2. Abstract of the number of technologies refined* in respect of crops/enterprises: NIL Thematic areas Cere als Oilsee ds Puls es Commer cial Crops Vegeta bles Fr uit s Flo wer Plantat ion crops Tub er Cro ps TOT AL Varietal Evaluation Seed / Plant production Weed Management Integrated Crop Management Integrated Nutrient Management Integrated Farming System Mushroom cultivation Drudgery reduction Farm machineries Post Harvest Technology Integrated Pest Management Integrated Disease Management Resource conservation technology Small Scale income generating enterprises TOTAL * Technology that is refined in collaboration with ICAR/SAU Scientists for improving its effectiveness. A.3. Abstract of the number of technologies assessed in respect of livestock / enterprises Thematic areas Evaluation of Breeds Nutrition Management Disease of Management Value Addition Production and Management Feed and Fodder Small Scale income generating enterprises TOTAL Cattle Poultry Sheep Goat Piggery Rabbitary Fisheries TOTAL 2 02 02 02 A.4. Abstract on the number of technologies refined in respect of livestock / enterprises: NIL Thematic areas Cattle Poultr y Sheep Goat Piggery Rabbitr y Fisheries Evaluation of Breeds Nutrition Management Disease of Management Value Addition Production and Management Feed and Fodder Small Scale income generating enterprises TOTAL B. Details of each On Farm Trial to be furnished in the following format A. Technology Assessment 1. Agronomy Assessment – 1 Title: Weed management in soybean crop through use of post emergence herbicide. Objectives: 1 To find out the effective method of weed control. 2 To study the effect of weed control treatments on yield of soybean crop. 3. To study the weed management economics. Problem identified and its intensity: Area under soybean crop is increasing fast in region. One of the limiting factor for manual weed control is labour cost and availability in time .therefore farmers facing problems in controlling the weeds effectively & economically. Due to negligence in timely weed control .the crop yield losses to the extent of 20-77 % were recorded (Kurchania et al., 2010.) Hence weed control is an important factor to be considered for increasing the productivity. Hence present investigation is proposed. Description of micro-farming situation: Mostly Soybean is grown on medium to heavy type of soil after harvest of cotton, Chickpea, Rabi jawar without irrigation. Interventions planned: Assessment of effect of post emergence application of tank mix Chlorimuron ethyl 25 % WP (Quarin)@ 0.010 ai /ha (0.04 kg/ha) + Quazalofop-p-ethyl 5 % EC (Turgasuper) @ 0.050 a.i /ha (1 lit/ha) at 20 DAS in Soybean crop. Treatments: T1: Farmers practice: One hand weeding & one hoeing at 15 and 30 DAS. T2: Technology for assessment: PoE-Tank mix Chlorimuron ethyl 25 % WP (Quarin) @ 0.010 a.i kg / ha (0.04 kg /ha) + Quazalofop-p-ethyl 5 % EC (Turgasuper) @ 0.050 a.i /ha ( 1 lit /ha) at 20 DAS Source of technology: MKV Parbhani. Observations/parameters of study: 1 .Weed Count (No. of weeds/sq.m). 2. Weed control Efficiency (%). 3. Yield (qt/ha). 4. Weed management economics. Performance of the Technology with Performance indicators Results shown that post emergence application of tank mix Chlorimuron ethyl 25 % WP (Quarin)@ 0.010 ai /ha (0.04 kg/ha) + Quazalofop-p-ethyl 5 % EC (Turgasuper) @ 0.050 a.i /ha (1 lit/ha) at 20 DAS in Soybean crop found that TOTA L 1. Weed control efficiency at 20 DAS was 43.46 % and at 40 DAS 91.38 % which shows very effective and efficient control of weeds. 2. Weed count (No of weeds/sq.m) found to be 14 and 6 at 20 and 40 DAS respectively after application of herbicide weed count fount to be very less. 3. In herbicide applied plot recorded highest yield 23.12 qt/ha as compared to farmers practice 21.25 qt/ha 4. There is saving in cost of weed management ( Rs 1775 /ha) as compared to farmers practice (Rs 1725 /ha and Rs 3500/ha respectively) 5. With the use of tank mix Chlorimuron ethyl 25 % WP (Quarin)@ 0.010 ai /ha (0.04 kg/ha) + Quazalofop-p-ethyl 5 % EC (Turgasuper) @ 0.050 a.i /ha (1 lit/ha) at 20 DAS in Soybean able to control both broad and grassy weeds. Final recommendation for Micro level situation Put forth for second year assessment. Constraints identified and feedback for research If timely application of herbicide is not done, farmer will not get proper results. Process of farmer’s participation and their reaction. We have provided post emergence herbicide Chlorimuron ethyl 25 % WP 16 gm and Quazalofop-p-ethyl 5 % EC 400 ml to each for 13 farmers in Sagroli village for soybean crop. Generally farmers they are adopting one hand weeding and one hoeing which is labor oriented and costly weed management practice. In herbicide treated plot found to be very less weed count ( 6 weeds /sq.m at 40 DAS) and better weed control efficiency (91.38 % at 40 DAS) and saving in cost of weed management (Rs 1775 /ha) and also with the use of tank mix different two herbicide able to control broad leaved and grassy weeds effectively. So farmers are happy with the herbicide provided and its results. Results of On Farm Trials Agronomy (Assessment – 1): Crop/ enterprise 1 Soybean Farming situation 2 Rainfed Problem Diagnosed 3 Higher weed manage ment cost and labour oriented. Also lower yield due to crop weed competiti on Title of OFT 4 Weed managem ent in soybean crop through use of post emergenc e herbicide No. of trials* 5 13 Technology Assessed 6 1. One hand weeding & hoeing at 15 and 30 DAS. (Farmers Practice) Parameters of assessment 7 Weed count (no/sq.m), Data on the parameter 8 20DAS- 3.61 40 DAS- 2 Weed control efficiency (%), 20 DAS94.87 40 DAS- 92.34 Grain yield(qt/ha) Weed management cost (Rs) 2. PoE-Tank mix Chlorimuro n ethyl 25 % WP (Quarin) @ 0.010 a.i kg / ha (0.04 kg /ha) + Quazalofop -p-ethyl 5 % EC (Turgasupe r) @ 0.050 a.i /ha ( 1 lit /ha) at 20 DAS Max- 24.56 Min- 18.42 Avg- 22.90 Max- 3800 Min- 3450 Avg- 3500 Weed count(no/sq.m), 20 DAS- 14 40 DAS- 6 Weed control efficiency (%), 20 DAS43.46 40 DAS91.38 Grain yield(qt/ha) Weed management cost (Rs) Max- 25.16 Min- 22.11 Avg- 23.12 Max- 1725 Min- 1725 Avg- 1725 (Fixed cost) 19 Results of assessment 9 PoE-Tank mix Chlorimuron ethyl 25 % WP (Quarin) @ 0.010 a.i kg / ha (0.04 kg /ha) + Quazalofop-p-ethyl 5 % EC (Turgasuper) @ 0.050 a.i /ha ( 1 lit /ha) at 20 DAS able to control both broad leaved and grassy weeds effectively with minimum expenses on rain fed black soils of Nanded district of Maharashtra. Feedback from the farmer 10 -- Farmers are happy with the performance of herbicide in controlling both type of weeds with minimum expenses. Technology Assessed Weed control efficiency (%), Weed count (no/sq.m), 11 1. One hand weeding & hoeing at 15 and 30 DAS. (Farmers Practice) 2. PoE-Tank mix Chlorimuron ethyl 25 % WP (Quarin) @ 0.010 a.i kg / ha (0.04 kg /ha) + Quazalofop-p-ethyl 5 % EC (Turgasuper) @ 0.050 a.i /ha ( 1 lit /ha) at 20 DAS ( Assessment) 12 13 20DAS- 3.61, 40 DAS- 2 20 DAS-94.87 , 40 DAS- 92.34 20 DAS- 14 , 40 DAS- 6 20 DAS- 43.46 , 40 DAS- 91.38 Weed management cost (Rs) 14 Max- 3800 Min- 3450 Avg- 3500 Max- 1725 Min- 1725 Avg- 1725 (Fixed cost) Max- 24.56 Min- 18.42 Avg- 22.90 Max- 25.16 Min- 22.11 Avg- 23.12 Economic Impact (continuation of previous table) Average Cost of cultivation (Rs./ha) Average Gross Return (Rs./ha) Assessment Local Check Assessment Local Check 15 31125 16 34625 17 73984 18 73280 (Avg. cost of soybean grain @Rs 3200/qt) Average Net Return (Profit) (Rs./ha) Local Assessment Check 19 42859 20 38655 Cost-Benefit Ratio (Gross Return / Gross Cost) Assessment Local Check 21 1:2.37 22 1:2.11 Assessment – 2 Title: Assessment of improved and non-spiny variety in Safflower (PBNS- 40) with local spiny variety to increase productivity and easiness in harvesting. Objectives: 1. To assesses performance of Safflower variety PBNS-40 with Bhima for grain yield. 2. To study harvesting economics. Thematic area: Varietal evaluation Problem identified and its intensity: Safflower is dry land crop grown in Nanded dist. But area under this crop is goes on decreasing day by day because of low yielding traditional varieties, disease pest problems and difficulties in harvesting thorny verities. Most of the farmers using variety Bhima ( Farmers seed don’t have purity ) it is more susceptible to leaf spot, wilt, aphids etc and low yielding, thorny in nature that’s why labours deny to harvest. So there is need to introduce non spiny, high yielding varieties in safflower. Description of micro-farming situation: Safflower is mostly grown in light to medium soils immediately after the harvest of soybean, Kharif Jowar on residual moisture of Kharif without irrigation. Interventions planned: Assessment of improved non spiny variety PBNS-40 over traditional variety Bhima Treatments: T1 Farmers practice –Bhima (low yield, spiny susceptible to aphids, leaf spot, wilt) T2: Improved varieties- PBNS-40 (High yielding, on spiny, resistant to aphids, leaf spot, wilt) Source of technology: MKV Parbhani. Observations/parameters of study: 1. No of capsules/plant. . 2. Grain yield/ha 4. Harvesting economics (aH/tsev gnitsevraH) Final recommendation for Micro level situation PBNS-40 may be grown in place of Bhima on rain fed black soils of Nanded district of Maharashtra. Constraints identified and feedback for research No specific constrains. Process of farmer’s participation and their reaction. We have supplied foundation seed (PBNS-40) 5 kg per farmers to 13 farmers in Kedarwadgaon village of Naigaon taluka in Nanded dist. In Nanded dist of Maharashtra, most of the rain fed farmers grows safflower after harvest of soybean, Kharif sorghum without irrigation. Most of the farmers using their own seed for sowing which don’t have purity ,low yielding, susceptible to aphids, leaf spot, spiny in nature so most of the time labours deny to harvest and farmers getting more cost to harvest crop. So area under this crop is decreased. We have given the variety PBNS-40 which is high yielding, less susceptible to aphids, leaf spot, non spiny in nature so crop easily gets harvested with minimum cost. This variety is having more number of capsules as compared to Bhīma. So farmers are happy with the PBNS-40 variety. 21 Agronomy (Assessment – 2) Crop/ Farming Problem enterprise situation Diagnosed 1 2 3 Safflower Rainfed Low productivity of local varieties, spiny in nature. Title of OFT 4 Varietal evaluation No. of trials* 5 10 Technology Assessed 6 1.Bhima (Farmers Practice) 2. PBNS40 Parameters of assessment 7 No. of Capsules/plant, Data on the parameter 8 Max- 25 Min- 5 Avg- 8 Yield/ha, Max- 7.5 Min- 3.9 Avg- 5.9 Harvesting economics(Rs/ha) No. of Capsules/plant, 2390 Max- 11.5 Min- 7.9 Avg- 9.8 Yield/ha, Harvesting economics(Rs/ha) Technology Assessed 11 1. Bhima (Farmers Practice) 2. PBNS-40( assessment) No of capsules/plant Max- 25 Max- 220 12 Min- 5 Min- 28 Max- 220 Min- 28 Avg- 42 Results of assessment 9 -- PBNS-40 may be grown in place of Bhima on rain fed black soils of Nanded district of Maharashtra. 1880 Max- 7.5 Max- 11.5 Farmers are happy with the performance of variety in terms of grain yield, no of capsules/plant. Less efforts and cost in harvesting. Avg- 5.9 Avg- 9.8 Harvesting economics(Rs/ha) 14 2390 1880 Average Net Return (Profit) (Rs./ha) Cost-Benefit Ratio (Gross Return / Gross Cost) Yield/ha (qt/ha) 13 Avg- 8 Avg- 42 Feedback from the farmer 10 Min-3.9 Min- 7.9 Economic Impact (continuation of previous table) Average Cost of cultivation (Rs./ha) Average Gross Return (Rs./ha) Assessment (PBNS-40) Local Check (Bhima) Assessment (PBNS-40) Local Check (Bhima) Assessment (PBNS-40)) 15 13000 16 13490 17 24500 18 14750 19 11500 (Avg. cost of Safflower grain @Rs 2500 /qt) 22 Local Check (Bhima) 20 1260 Assessment (PBNS-40) Local Check 21 1:1.88 22 1:1.09 2. Horticulture A. 1-Technology Assessment (2013-14) Trial 1 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) Title : Nutrition and fruit set management Problem diagnose/defined : low fruit yield and irregular fruiting in the Sagroli, kedarwadgaon and Lath village mango orchard Details of technologies selected for assessment T1 No nutrition and no use of growth regulators T2 1000:500:1000g NPK in June and September and NAA 20 ppm at pea size stage of fruits Source of technology :MKV Parbhani (source: MKV Diary 2013) Thematic area: Integrated Nutrient Management Performance of the technology with performance indicators: Improved yield with superior quality (weight) fruits. Experiment for 2013-14 (second year is ongoing) Final recommendation for micro level situation: Use of recommended fertilizer dose 1000:500:1000g NPK and growth regulators like NAA 20ppm at Pea size stage only after soil analysis. Constraints identified and feedback for research :Uniform orchard is not found due to farmers carelessness and unsuitable intercropping affect the crop growth and development Process of farmer’s participation and their reaction: An awareness meeting was taken before implementing of experiment. Farmers enthusiastically participated. For easy supervision of orchard, the orchards were selected which are nearer to road for easy approach. Ten plants were selected for experiment with remaining as control. Farmers reacted that due to use of the combination of RDF and Growth regulators the yield was increased considerably than control. Trial 2 1) 2) 3) Title : Use of cultar in mango Problem diagnose/defined: low fruit yield and irregular fruiting in the Sagroli, kedarwadgaon and Lath village mango orchard Details of technologies selected for assessment i. No use of cultar (paclobutazaol) ii. Use of cultar @ 1ml per metre square canopy of mango tree 4) 5) 6) Source of technology : Dr. BSKKV Dapoli recommendations of 2012-13 Thematic area : Integrated Nutrient Management Performance of the technology with performance indicators: Experiment for 2013-14 (first year) is ongoing 7) Final recommendation for micro level situation : Continued this year 8) Constraints identified and feedback for research :Uniform orchard is not found due to farmers carelessness and unsuitable intercrops affect the crop growth and development 9) Process of farmer’s participation and their reaction: An awareness meeting is taken before installation of experiment. Farmers enthusiastically participated and care should be taken only for good orchard and near to road for easy supervision. Farmers are voluntary participated and inspired by the working and advisory visit from time to time. 23 Trial 3 1) Title : Varietals Assessment in Okra 2) Problem diagnose/defined : Low fruit yield 3) Details of technologies selected for assessment i. Parbhani Kranti ii. Parbhani Ok 4) 4 ) Source of technology: MKV Parbhani (source: MKV Diary 2012) 5) Thematic area: Varietal Assessment 6) Performance indicators: Use of improved cultivar of Parbhani OK found effective in increasing yield of Okra. The improved cultivar found higher (138.45 qtl/ha) yield over old cultivar Parbhani Kranti (114.4 qtl/ha). 7) Final recommendation for micro level situation : PBN Ok is superior over old strain of Parbhani Kranti. For getting higher yield and quality fruits farmers should prefer the new PBN OK cultivar. 8) Constraints identified and feedback for research : Most of the farmers concentrated on cotton crop and previous crop was also cotton. 9) Process of farmer’s participation and their reaction: Among the farmers interest group for vegetables, the awareness meeting is taken and only interested peoples involved for the experiments. Results of On Farm Trials Crop/ enterpri se Farming situatio n 1 Okra 2 Irriga ted Man go Man go Irriga ted Irriga ted Problem Diagnosed 3 Low fruit yield Imbalance d nutrition and fruit drop Low and irregular fruits Title of OFT No. of trials* Technology Assessed 4 5 6 Use of Parbhani Ok cultivar over Parbhani Kranti Varital assessment in okra Nutrition and fruit set managemen t Use of cultar 13 10 13 Use of fertilizer dose 1000:500:1000 NPK and NAA Use of paclobutrazol 4 ml /m Parameters of assessment Data on the parameter 7 Height of plant 8 T1- 169.15 T2-156.92 Time for first picking Yield qtl/ha T1-55.15 T2-46.12 T1-84.23 T2-108.67 Result awaited No. of fruits per tree (nos.) Average fruit weight (g) Yield qtl/ha No. of fruits Results of assessment Feedback from the farmer 9 Use of improved cultivar Parbhani Ok found less height, less time, for first picking and increased (29.01%) yield than control Parbhani Kranti. 10 Result awaited Fruits weight Yield qtl / ha Technology Assessed 1. Varietal assessment in Okra *Production per unit Farmers practice Parbhani Kranti Technology assessed Parbhani OK 84.23 qtl/ha 108.67 Net Return (Profit) in Rs. / unit 210575 271675 *Field crops – kg/ha, * for horticultural crops -= kg/t/ha, * milk and meat – litres or kg/animal, * for mushroom and vermi compost kg/unit area. 25 BC Ratio 5.49 7.13 A. 2-Technology Assessment (2012-13) Trial 1 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) Title : Nutrition and fruit set management: Problem diagnose/defined : low fruit yield and irregular fruiting in the Sagroli, kedarwadgaon and Lath village mango orchard Details of technologies selected for assessment i. No nutrition and no use of growth regulator ii. 1000:500:1000g NPK in June and September and NAA 20 ppm at pea size stage of fruits Source of technology :MKV Parbhani (source: MKV Diary 2013) Thematic area: Integrated Nutrient Management : Performance of the technology with performance indicators: Experiment for 2013-14 (second year) is ongoing. Result of 2012-13 is – Use of recommended fertilizers and plant growth regulators were found effective in increasing farmers mango yield. The assed technology recorded (69.13 qtl/Ha) yield over farmers practice (36.81 qtl/ha) Final recommendation for micro level situation : Use of recommended fertilizer dose 1000:500:1000g and growth regulators like NAA 20ppm at proper time and after soil analysis. Constraints identified and feedback for research : Uniform orchard is not found due farmers carelessness and unsuitable intercrops affect the crop growth and developement Process of farmers participation and their reaction : An awareness meeting is taken before installation of experiment. Farmers enthusiastically participated and care should be taken only for good orchard and near to road for easy supervision. Trial 2 1) Title : Varietals Assessment in chilli 2) Problem diagnose/defined : low fruit yield 3) Details of technologies selected for assessment i. Local Chilli (Shevala Mirchi) ii. Pusa Jwala 4) Source of technology:MKV Parbhani (source: MKV Diary 2012) 5) Thematic area: Varietal Assessment 6) Performance indicators : The experiment was conducted during winter 2012-13 the result was- Use of improved cultivar of chilli Jwala found effective in increasing yield of chilli. The improved cultivar found higher (138.45 qtl/ha) yield over local cultivar Shevala (114.4 qtl/ha). 7) Final recommendation for micro level situation: The cultivar Jwala is useful to increase the chilli yield and production over traditional local cultivar. 8) Constraints identified and feedback for research:Rural Peoples are refusing for growing modern seeds due less pungency in Jwala cultivar as well as the cultivar gives less quality red chillies. 9) Process of farmer’s participation and their reaction : Among the farmers interest group the awareness meeting is taken and only interested peoples involved for the experiments 26 10) Crop/ enterprise Farming situation Problem Diagnosed Title of OFT No. of trials* Technology Assessed Parameters of assessment Data on the parameter Results of assessment 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Mango (2012-13) Irrigated Irrigated Chilli (201213) Imbalanced nutrition and fruit drop Nutrition and fruit set management Low fruit yield and no mechanization Planting of chilli in paire row system 10 10 Use of fertilizer dose 1000:500:1000 NPK and NAA Use of improved cultivar Pusa Jwala over Shewala as local Technology Assessed 1. 2. Fruit set management in Mango Varietal Assesment in chilli Farmers Practice Technology assessed Farmers Practice (Shevala) Technology assessed (Jwala) No. of fruits per tree (nos.) T2-298.53 T1-199.53 Average fruit weight (g) Yield qtl/ha T2-232.76 T1-185.84 T2-69.13 T1-36.81 Plant height (cm) T1-66.61 T2-81.00 Days required fro flowering Yield T1-55.84 T2 -46.30 T1-45.76 T2-55.38 *Production per unit Net Return (Profit) in Rs. / unit BC Ratio 36.81 qtl/ha 110430 3.68 69.13 114.4 qtl/ha 138 qtl/ha 27 Use of fertilizers and plant growth regulators found effective in increasing 49.61% more fruits and 25.24% avg fruit weight and 87.80% farmers yield Use of improved cultivar of chilli found effective in increased height increased days for flowering increased (21.02%) yield of chilli. 207390 205920 276900 4.50 8.23 11.07 Feedback from the farmer 10 3. Plant Protection Technology Assessment Trial 1 1 2 Title Problem diagnose 3 Details of technologies selected for assessment 4 5 Source of technology Production system / thematic area Thematic area Performance of the Technology with performance indicators 6 7 8 9 10 Final recommendation for micro level situation Constraints identified and feedback for research Process of farmers participation and Farmers reaction Control of shoot and fruit borer in brinjal Fruit and shoot borer infestation decreased the yield and quality of fruit. Injudicious use of chemical insecticides spray can damage the parasitoids, predator and human health. T1 – Farmers practice: Heavy use of pesticides and its mixture T2 – Recommended practice: Mechanical removal of affected shoots and fruits Application of azadirachtin 1500 ppm @ 1500ml/ha Installation of 5 traps/ 1000 sq. M. since flower initiation (45 days crop) for mass trapping of shoot and fruit borer moths. MPKV, Rahuri. Rabi Irrigated system IPM i) Cost of production in assessed technology was less Rs. 37500/ha as compared to farmer practice Rs. 45000/ha. ii) Total yield obtained in technology assessed plot was 137.3 qtl/ha more than farmer practice 115.25 qtl/ha. Assessment trial has been once again replicated in next rabi 2013 -2014 for the confirmation of assessed technology. Pheromone traps catches following two sprayings of Azadirchtin 1500 ppm was found more effective to reduce the shoot and fruit borer infestation than farmer practice. The assessed technology recorded the (137.3 qtl/ha) yield as compare to farmer practice (115.25 qtl/ha.) Farmers meetings for information collection, general consensus, Selection of trial farmers. Filling information of trial farmers in designed format. Input distribution and farmers feedback. The pheromone traps catches and mechanical removal of affected shoot and low cost spraying of Azadirchtin 1500 ppm controls the shoot and fruit borer and helps in reducing the cost of plant protection over chemical spray. 28 Trial-1 Crop/ enterpri se Farming situation Problem Diagnosed Title of OFT 1 Brinjal 2 Irrigated 3 Incidence of shoot and fruit borer fetches the low yield in brinjal and low market price. 4 Managem ent of shoot and fruit borer in brinjal No. of trials* 5 13 Technology Assessed 6 7 T1 – Farmers practice: Heavy use of pesticides and its mixture T2Recommendedpractice: Mechanical removal of affected shoots and fruits Application of azadirachtin 1500 ppm @ 1500ml/ha Installation of 5 traps/ 1000 sq. M. since flower initiation (45 days crop) for mass trapping of shoot and fruit borer moths. Technology Assessed 11 Parameters of assessment %Shoot infestation % fruit infestation Yield Qt/ha %Shoot infestation % fruit infestation Yield Qt/ha *Production per unit Qt/ha 12 T1 – Farmers practice: Heavy use of pesticides and its mixture 115.25 T2Recommendedpractice: Mechanical removal of affected shoots and fruits Application of azadirachtin 1500 ppm @ 1500ml/ha Installation of 5 traps/ 1000 sq. M. since flower initiation (45 days crop) for mass trapping of shoot and fruit borer moths. 137.3 29 Data on the parameter 8 12.38 12.14 115.25 5.13 5.76 137.3 Results of assessment 9 Pheromone traps catches following two sprayings of Azadirchtin 1500 ppm was found more effective to reduce the shoot and fruit borer infestation than farmer practice. The assessed technology recorded the (137.3 qtl/ha) yield as compare to farmer practice (115.25 qtl/ha.) Feedback from the farmer 10 The pheromone traps catches and mechanical removal of affected shoot and low cost spraying of Azadirchtin 1500 ppm controls the shoot and fruit borer and helps in reducing the cost of plant protection over chemical spray. Net Return (Profit) in Rs. / unit 13 BC Ratio 14 1,72,875 3. 84 2,05,950 5.49 Trial 2 1 Title 2 Problem diagnose 3 Details of technologies selected for assessment 4 5 Source of technology Production system / thematic area Thematic area Performance of the Technology with performance indicators 6 7 8 9 Final recommendation for micro level situation Constraints identified and feedback for research 10 Process of farmers participation and Management of Paddy plant hopper using fungal pathogen Metarrhizium anisopleae. Resurgence of pest after repeated application of insecticides Farmers do not recognise hoppers at early stages Population of BPH increases at flowering stage No use of bio pesticide. T1 - Farmers practice Heavy and indiscriminate use of pesticide on paddy commencing from the pest incidence. T2 - Technology assessed Broadcasting of M. anisopliea @ 2.5 kg /ha after withdrawing water from paddy bandhies on attaining the ETL (5-10 hopper per hill) Dr. PDKV, Akola Kharif, Sandy loam Soil, Môno cropping of paddy IPM i) Cost of production in assessed technology was less Rs. 24400/ha as compared to farmer practice Rs. 25600/ha. ii) ii)Total yield obtained in technology assessed plot was 67.19 qtl/ha more than farmer practice 62.12 qtl/ha. Assessment trial has been once again replicated in next kharif 2014 -2015 for the confirmation of assessed technology. Broadcasting of M. anisopliea @ 2.5 kg/ha reduces the infestation of plant hopper over the control. The assessed technology recorded the (67.19 qtl/ha) yield as compare to farmer practice (62.12 qtl/ha.) Farmers meetings for information collection, general consensus, Selection of trial farmers. Filling information of trial farmers in designed format. Farmers reaction Input distribution and farmers feedback. Broadcasting of M. anisopliea @ 2.5 kg/ha reduces the infestation of plant hopper which was very cost effective as compared to chemical spray over farmer’s practice. 30 Trial-2 Crop/ enterprise 1 Paddy Farming situation 2 Irrigated Problem Diagnosed Title of OFT 3 4 Resurgence of pest after repeated application of insecticides Farmers do not recognise hoppers at early stages Population of BPH increases at flowering stage No use of bio pesticide. Management of Paddy plant hopper using fungal pathogen No. of trials* 5 13 Technology Assessed Parameters of assessment 7 6 T1 - Farmers practice Heavy and indiscriminate use of pesticide on paddy commencing from the pest incidence. Metarrhizium anisopleae. T2 - Technology assessed Broadcasting of M. anisopliea @ 2.5 kg /ha after withdrawing water from paddy bandhies on attaining the ETL (5-10 hopper per hill) Technology Assessed 11 %plant hopper infestation at 45 DAT 4.99 65 DAT 95 DAT Yield Qt/ha 5.5 7.88 62.12 C:B ratio 3.88 %plant hopper infestation at 45DAT 3.48 65 DAT 3.87 95 DAT 5.67 Yield Qt/ha C:B ratio 67.19 *Production per unit Qt/ha 12 T1 - Farmers practice Heavy and indiscriminate use of pesticide on paddy commencing from the pest incidence. T2 - Technology assessed Broadcasting of M. anisopliea @ 2.5 kg /ha after withdrawing water from paddy bandhies on attaining the ETL (5-10 hopper per hill) 62.12 67.19 31 Data on the parameter 8 Results of assessment Feedback from the farmer 9 10 i)Cost of production in assessed technology was less Rs. 24400/ha as compared to farmer practice Rs. 25600/ha. Broadcasting of M. anisopliea @ 2.5 kg/ha reduces the infestation of plant hopper which was very cost effective as compared to chemical spray over farmer’s practice. ii)Total yield obtained in technology assessed plot was 67.19 qtl/ha more than farmer practice 62.12 qtl/ha. 4.40 Net Return (Profit) in Rs. / unit 13 BC Ratio 14 99392 3.88 107504 4.40 Trial 3 1 2 3 Title Problem diagnose Details of technologies selected for assessment 4 5 Source of technology Production system / thematic area Thematic area IPM Performance of the i) Total yield obtained in technology assessed plot was 108.67 qtl/ha which Technology with was more than farmer practice 84.23 qtl/ha. performance indicators Final recommendation Assessment trial has been once again replicated in next kharif 2014 -2015 for micro level situation for the confirmation of assessed technology. Constraints identified The three spraying at 15 days interval of Microbial insecticide Spinosad and 45% SC @ 0.005% was found more effective to reduce the fruit borer feedback for research infestation than farmer practices. The assessed technology recorded the 108.67qt/ ha yield as compare to farmer practices (84.23 qt/ ha.) Process of farmers Farmers meetings for information collection, general consensus, participation and Selection of trial farmers. 6 7 8 9 10 Management of okra fruit borer. Low yield of okra due to infestation of fruit borer. T1 - Farmers practice Spraying with cypermethrin 25 EC (4 ml) or quinalphos 36 EC (20 ml) in 10 lit of water commencing from the pest incidence. T2 - Technology assessed For effective management of okra fruit borer, with higher yield, net profit and ICBR three spraying of spinosad 0.005% at an interval of 15 days commencing from the pest incidence Maha. Ag. Univ. Proceedings of Joint Agrosco Kharif, Sandy loam Soil Filling information of trial farmers in designed format. Farmers reaction Input distribution and farmers feedback. Three spraying with microbial insecticide Spinosad 45% SC @ 0.005% was found more effective to reduce the fruit borer infestation than chemical spray. 32 Trial-3 Crop/ enterprise 1 Okra Farming situation 2 Rainfed Problem Diagnosed Title of OFT 3 Low yield of okra due to infestation of fruit borer. 4 Management of okra fruit borer. No. of trials* 5 13 Technology Assessed Parameters of assessment 6 7 T1 - Farmers practice Spraying with cypermethrin 25 EC (4 ml) or quinalphos 36 EC (20 ml) in 10 lit of water commencing from the pest incidence. T2 - Technology assessed For effective management of okra fruit borer, with higher yield, net profit and ICBR three spraying of spinosad 0.005% at an interval of 15 days commencing from the pest incidence Technology Assessed 11 Data on the parameter 8 % Shoot infestation 12.78 % fruit infestation 9.57 Yield Qt/ha 84.23 % Shoot infestation 6.96 % fruit infestation 5.74 Yield Qt/ha 108.67 Results of assessment 9 i) Total yield obtained in technology assessed plot was 108.67 qtl/ha which was more than farmer practice 84.23 qtl/ha. Feedback from the farmer 10 Three spraying with microbial insecticide Spinosad 45% SC @ 0.005% was found more effective to reduce the fruit borer infestation than chemical spray. *Production per unit Qt/ha 12 Net Return (Profit) in Rs. / unit 13 BC Ratio 14 84.23 160306 6.41 108.67 214074 8.56 T1 - Farmers practice Spraying with cypermethrin 25 EC (4 ml) or quinalphos 36 EC (20 ml) in 10 lit of water commencing from the pest incidence. T2 - Technology assessed For effective management of okra fruit borer, with higher yield, net profit and ICBR three spraying of spinosad 0.005% at an interval of 15 days commencing from the pest incidence 33 4. Agriculture Engineering Technology Assessment (1) Sr.no. 1 Title 2 Problem diagnose/defined: 3 Details of technologies selected for assessment 4 Source of technology In situ rainwater conservation in soybean Low yield due to water scarcity. As cotton is grown in rainfed condition, dry spells occurs at interval of 10 to 22 days in peak growth period. So it is necessary to conserve the rain water and use in the dry spell. T1 – Farmers practice: no opening of furrow T2 - Technology assessed: Opening of furrow @ 45 DAS PDKV, Akola 5 Production system thematic area Soybean crop management 6 7 Thematic area Performance of the Technology with performance indicators. Final recommendation for micro level situation Soil and water conservation T2 recorded 15.88 % higher yield 8 9 10 Constraints identified and feedback for research Process of farmers participation and their reaction It is advocated to adopt the technology recommended by Dr.PDKV, Akola for effective management of soybean for higher grain yield in light to medium black soils of Nanded district Opening of furrow is expensive. Group meeting was conducted for giving information about assessment of technology. List out interested farmers. 34 11). Results of On Farm Trials Crop/ enterprise Farming situation Problem Diagnosed 1 soybean 2 Rainfed 3 Low productivity due to scarcity of water Title of OFT 4 In-situ soil and water conservation No. of trials* 5 13 Technology Assessed 6 T1- no opening of furrow T2 -Opening of furrow 45 DAS Parameters of assessment 7 Moisture at 20 cm 60 DAS No of pod/ plants Data on the parameter 8 0.08 80 Yield Q/ha 18 Moisture at 20 cm 60 DAS No of pod/ plants Yield Q/ha 0.15 130 20.86 Results of assessment Feedback the farm 9 10 Yield incre due to Exce water removes. T2 recorded 15.88 % higher yield * No. of farmers Technology Assessed *Production per unit 11 1. No opening of furrow (Farmers Practice) 2. Opening of furrow after 6 rows 12 18 q/ha 20.86 q/ha Net Return (Profit) in Rs. / unit 13 38200 44797 *Field crops – kg/ha, * for horticultural crops -= kg/t/ha, * milk and meat – litres or kg/animal, * for mushroom and vermi compost kg/unit area. 35 BC Ratio 14 2.72 2.85 Technology Assessment (2) Sr.no. 1 Title 2 Problem diagnose/defined: 3 Details of technologies selected for assessment In situ rainwater conservation in cotton Low yield due to water scarcity. As cotton is grown in rainfed condition, dry spells occurs at interval of 10 to 22 days in peak growth period. So it is necessary to conserve the rain water and use in the dry spell. T1 – Farmers practice: no opening of furrow T2 - Technology assessed: Opening of furrow @ 60 DAS 4 5 Source of technology Production system thematic area PDKV, Akola Cotton crop management 6 Thematic area Soil and water conservation 7 Performance of the Technology Results showed that due to opening of furrow in with performance indicators. cotton, yields 24.80 q/ha with maximum price in the market having B:C ratio 2.10 compared to farmers practice the cotton yield is 21.20 q/ha with B:C ratio 1.65. Final recommendation for micro Opening of furrow 60 DAS after 2 rows level situation Constraints identified and Nil feedback for research Process of farmers participation Group meeting was conducted for giving information about assessment of technology. List out interested and their reaction farmers. Farmers gained 16.88 % higher yield. 8 9 10 36 11). Results of On Farm Trials Crop/ enterpri se Farming situation 1 cotto n 2 Rainfe d Problem Diagnosed 3 Low productiv ity due to scarcity of water Title of OFT 4 In-situ soil and water conservat ion No. of Technology trials Assessed * 5 6 10 T1-Growing cotton without ridge and furrow T2- Opening of furrow after 60 days DAS Parameters of assessment 7 Moisture at 20 cm 90 DAS No of pod/ plants Data on the parameter 8 Results of assessme nt 9 0.09 60 Yield Q/ha 21.20 Moisture at 20 cm 90 DAS No of pod/ plants Yield Q/ha 1.16 16.98 % more yield in T2 65 24.80 * No. of farmers Technology Assessed 11 1. cotton without ridge and furrow 2. Opening of furrow after 60 days DAS *Production per unit 12 21.20 24.8 37 Net Return (Profit) in Rs. / BC unit Ratio 13 14 66000 1.65 84038 2.10 Feedback from the farmer 10 Excess water remove safely and moisture hold for more days Technology Assessment (3) Sr.no. 1 Title 2 Problem diagnose/defined: 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Assessment of triple fertiliser hoe in maize Due to broad costing of fertiliser, leaching problem occur. Details of technologies selected T1 – Farmers practice: Weeding and for assessment broad costing of fertiliser T2 - Technology assessed: Use of MKV triple fertiliser hoe Source of technology MKV, Parbhani Production system thematic area Weed and fertiliser management Thematic area Farm Machinery Performance of the Technology Results showed that due to use of triple fetri with performance indicators. hoe in maize, yields 26.40 q /ha with maximum price in the market having B:C ratio 1.66 compared to farmers practice the maize yield is 24.8 q/ha with B:C ratio 1.488. Final recommendation for micro Use of MKV triple fertilizer hoe for weeding and level situation fertilizer applicatio Constraints identified and feedback for research Process of farmers participation and their reaction As rows are not in straight line, some plants may damage. Group meeting was conducted for giving information about assessment of technology. List out interested farmers. 38 11). Results of On Farm Trials Crop/ enterprise 1 Triple fertilizer hoe Farming situation 2 Irrigated Problem Diagnosed 3 due to broad costing of fertiliser, leaching problem occur Title of OFT 4 Assessment of triple ferti hoe in maize No. Technology Parameters of of Assessed assessment trials* 5 6 7 13 T1Field capacity Faremers (ha/hr) practice Labour required (Man hr/ha) Yield Q/ha 13 T2- Use of Field capacity MKV twin (ha/hr) ferti hoe Labour required (Man hr/ha) Yield Q/ha Data on the parameter 8 0.3 2.5 Results of assessment 9 15.84 % yield increase 40.27 0.4 2.0 46.65 * No. of farmers Technology Assessed 11 T1: Farmers practice T2: Use of MKV twin ferti hoe Net Return (Profit) in Rs. / unit 13 48324 55980 *Production per unit 12 40.27 46.65 39 BC Ratio 14 1.34 1.59 Feedback from the farmer 10 Proper application of Fertilizer. 5. Home Science Trial 1: Milking stool and stand 1 Title 2 Problem diagnose/defined 3 Details of technologies selected for assessment Source of technology Production system 4 5 6 7 8 9 Thematic area Performance of the Technology with performance indicators Final recommendation for micro level situation Constraints identified and feedback for research 10 Process of farmers participation and their reaction : Assessment of revolving milking stool and stand to increase work efficiency of women at the time of milking the animals. : In traditional method of milking the animals, women face uncomfortable conditions and health hazards. Also many times due to kick of animals milk losses are there. Traditional method is not hygienic also. : Milking stool and stand : Vasantrao Naik Marathwada Krushi Vidyapeeth, Parbhani : -: Drudgery reduction of farm women : Results showed that 16.15% time saved while milking the animals. Also it reduces the leg pain by 90%. : To reduce the drudgery while milking the animals, milking stool and stand is beneficial for women. : Milking floor should be plane. Use of milking stool and stand is very useful for clean milk production. Leg pain reduced 90% and time saved 1.19 min / lit (16.15%). No loss of milk. Milking efficiency increases and milker feels confort, : Farm women, who have buffaloes and doing milk sale, were selected for the testing. Women were from village Atkali and Sagroli. Farm women are satisfied by using milking stool and stand. 40 Crop/ enterprise 1 Livestock Farming situation 2 -- Problem Diagnosed 3 Leg pain and uncomfortable condition during milking the animals Title of OFT 4 Assessment of milking stool and stand No. Technology Parameters Data on Results of of Assessed of the assessment trials assessment parameter 5 6 7 8 9 13 Milking Time 16.15% Use of milking stool and time stool and stand stand saved is very useful for clean milk production, leg Leg pain 90% pain reduced reduced 90%, and time saved up to 10%, Milk loss 0% no loss of milk. 41 Feedback from the farmer 10 Use of milking stool and stand is beneficial to reduce leg pain while milking the animals. It is comfortable to use. Only some times when surface is uneven, it is uncomfortable. Trial 2: Assessment of iron rich toffee 1 Title 2 Problem diagnose/defined 3 4 Details of technologies selected for assessment Source of technology 5 Production system 6 7 Thematic area Performance of the Technology with performance indicators Final recommendation for micro level situation Constraints identified and feedback for research 8 9 : Assessment of iron rich toffee to increase the hemoglobin content in blood. : Anemia is major problem identified in women due to which they face many health problems like weakness, leg pain, back pain etc. : Iron rich toffee. : College of Home Science, Vasantrao Naik Marathwada Krushi Vidyapeeth, Parbhani : - 10 Process of farmers participation and their reaction Crop/ enterprise Problem Diagnosed 1 Nutrition 3 Anemi a in women Title of OFT 4 Assessment of iron rich toffee : Health and Nutrition : Before intervention Hb level of women was 8.43 gm% (Min 7.5 and Max 9.5) changed to 9.19 gm% (Min 7.8 and Max 10.00) after two months intervention : Iron rich toffee can be used to increase Hb level of the women upto 1 to 2 gm% : Toffees are not easy to prepare at house hold level for women as the procedure is quite critical SHG can prepare it as an enterprise and distribute to needy women/adolescent girls. : Women who show signs and symptoms of anemia were tested for Hemoglobin content of blood in hospital. Who have hemoglobin in 7 to 9 gm/dl were selected for the test. No. of trials* Technology Assessed 5 10 6 Iron rich toffee Paramet ers of assessm ent 7 Hb, Data on the parame ter 8 Before After 42 Results of assessment Feedback from the farmer 9 8.43 gm% (Min 7.5 and Max 9.5) 9.19 gm% (Min 7.8 and Max 10.00) 10 women are very satisfied after getting the result and feels healthy and fresh also ready to continue the use 6. Veterinary Science Technology Assessment Trial 1 i. ii. iii. iv. v. vi. vii. viii. ix. Title : Use of hormonal preparations to regulate oestrus in cattle Problem diagnose/defined : Irregular heat, anoestrous in cattle Details of technologies selected for assessment /refinement: use of hormone in cattle. Treatments: i. T1 – Farmers practice: Farmer’s practice-no treatment ii. T2—assessed Practice: Use of GNRH/PGF 2 alpha to induce heat Source of technology : MAFSU Nagpur Thematic area: disease management Performance of the Technology with Performance indicators : induction of oestrous 18 animals showed in heat out of 20 animals and 16animals conceived out of 18 animals Micro level situation feedback for research: used hormones are said to be the best as almost all animals shown intense heat and high conception rate Process of farmer’s participation and their reaction: all the selected animals for trials were being brought to doctor voluntarily as and when needed .the other animal owners also purchased the hormones for their animals in anoestrus. Farmers now relying the hormones by seeing the results and conception rate of the animals.18 animals showed heat out of 20 animals (2) 16 animals’ conceived out of 18 animals. Trial 1I i. Title use of Bordeaux mixture and topicure spray to cure dermatophytosis in cattle ii. Problem diagnose/defined: itching, loss of hairs, particularly on neck, hump, back and up to the rump region in working bullock, locally there is no such a reliable and curative remedy is available to cure this chronic fungal disease with veterinarian farmers would be getting very low depreciation value of this valuable working bullock because of the ugly look caused by the disease. iii. Details of technologies selected for assessment /refinement: Use of Bordeaux mixture and topicure spray iv. v. vi. vii. viii. ix. Treatments: a. T1 – Farmers practice: Farmer’s practice-no treatment b. T2—recommended Practice: local application of Bordeaux mixture and topicure spray Source of technology : MAFSU Nagpur Thematic area : disease management Performance of the Technology with Performance indicators: Itching is stopped, hairs are regain, look of the animal is improved, farmers got good resell price. Micro level situation feedback for research: local application of Bordeaux mixture is proved to be the best and cheaper medicine to cure the dermatophytosis. Process of farmers Participation and Their reaction : all the selected animals for trials were being brought to doctor voluntarily as and when needed .the other animal owners also purchased the Bordeaux mixture to cure their affected animals farmers are happy to get such a cheap and easy way to get riddoff such a chronic disease.1) 20 animals showed recovery out of 20 animals Veterinary Science Crop/ enterprise Farming situation Problem Diagnosed Title of OFT No. of trials* Technology Assessed Parameters of assessment Data on the parameter Results of assessment Feedback from the farmer 1 Cattle 2 Rainfed 3 Anoestrus 4 Use of hormonal preparations to regulate oestrus in cattle 5 20 6 Use of injections GnRh and Pgf2alpha 7 1. Induction of oestrus 2. Non return pregnancy rate 8 1) 18 animals showedin heat out of 20 animals 2)16animals conceieved out of 18 animals 9 1) 18 animals showedin heat out of 20 animals 2)16animals conceieved out of 18 animals 10 Expressed their happiness as their animals were not showing heat since 2-3 years . other animal owners following the same hormones for their animals now Cattle Rainfed Dermatophy tosis Use of bordeaux mixture and topicure spray to cure dermatophytosis in cattle 20 bordeaux mixture and topicure spray 1. Incidence of disease 2. Recovery of disease. out of 20 animals 18 animals recovered totally 2 animals required second dose of the drug out of 20 animals 18 animals recovered totally 2 animals required second dose of the drug Farmers are now advising the other animals to approach to kvk and get the medicine for the same 44 3.2 Achievements of Front Line Demonstrations a.Follow-up for results of FLDs implemented during previous years List of technologies demonstrated during previous year and popularized during 2013-14 and recommended for large scale adoption in the district S. No Agrono my Crop/ Enterp rise Bengal Gram Thematic Area* Varietal evaluation Technology demonstrated Varietal evaluation of improved varieties in Bengal gram. a) Digvijay Wheat Weed Weed management management through post emergence herbicides in wheat. a)PoEMetasulphuraonmetyl 20 WP@20 gml/ha. Horticul ture Chilli Planting method Plant Protecti Bengal gram IPM The paired row method is improved over conventional method having 45X60X120 cm over cultural method of planting For effective management of gram pod borer, Details of popularization methods suggested to the Extension system By publishing the IPM folder By conducting the Field Day By Conducting the training for EF of state dept personnel Print and Electronic media, Training, Demonstrations etc. By publishing the IPM folder By conducting the Field Day By Conducting the training for EF of state dept personnel Print and Electronic media, Training, Demonstrations etc. Print and Electronic media, Training, Demonstrations etc. By publishing the IPM folder By conducting the Field Day I Horizontal spread of technology No. of No. of Area in villages farmers ha 13 1652 1573 8 420 165 3 45 4.2 2 50 20 on Home Science installation of pheromone traps @ 4/acre for monitoring the pest attack and following the 1st spray of Azadirectin 1500 ppm @ 2ml/lit. and 2nd spray of HaNPV 250 LE after 15 days of first spray. Smoke less Chula Enterp rise Drudgery reduction Enterp rise Health and nutrition Kitchen garden Veterina Cattle ry and Science buffalo 1 Fodder production Better forage yield – Hybrid Nappier grass phule Javant, 2 Dairy High milk yield – By management supplementing mineral mixture. Cattle and buffalo By Conducting the training for EF of state dept personnel Print and Electronic media, Training, Demonstrations etc. Through Mahila Arthik Vikas Mahamandal and Popularize through Self help groups of DRDA and ICDS Through Mahila Arthik Vikas Mahamandal and Popularize through Self help groups of DRDA, ICDS and Manva Vikas Mission By publishing the folder By conducting the Field Day By Conducting the training for EF of state dept personnel Print and Electronic media, Training, Demonstrations etc. 01 12 - 05 75 - 2 10 0.2 By publishing the folder By conducting the Field Day By Conducting the training for EF of state dept personnel Print and Electronic media, Training, Demonstrations etc. 2 10 10 animals 3 b. Cattle and buffalo fodder To enhance quality of management dry fodder by adopting urea treatment. By publishing the folder By conducting the Field Day By Conducting the training for EF of state dept personnel Print and Electronic media, Training, Demonstrations etc. 1 10 10 farmers Details of FLDs implemented during 2013-14 (Information is to be furnished in the following three tables for each category i.e. cereals, horticultural crops, oilseeds, pulses, cotton and commercial crops.) Sl. Crop Thematic area Technology Demonstrated No. / Disciplin e 1/Agron omy Soybean Varietal evaluation Variety: MAUS-71 Pigeon pea Varietal evaluation Variety: BDN-711 Green gram To test recommended PoP ‘s verses farmers practice under pulses program Pigeon pea To test recommended PoP ‘s verses farmers practice under pulses program Bengal gram To test recommended PoP ‘s verses farmers practice under pulses program Wheat Varietal evaluation Whole package of practice recommended by VNMKV.Parbhani Whole package of practice recommended by VNMKV.Parbhani Whole package of practice recommended by VNMKV.Parbhani Variety: Kudrat 17 Rabi sorghum Varietal evaluation Variety: Parbhani moti Rabi sorghum Varietal evaluation Variety: Parbhani Jyoti Season and year Area (ha) No. of farmers/ demonstration Reasons for shortfall in achievemen t Proposed 5.2 Actual 5.2 SC/ST 2 Others 11 Total 13 -- 5.2 5.2 2 11 13 --- 12 12 7 23 30 -- Kharif 2013 12 12 3 27 30 -- Rabi 2013-14 12 12 8 22 30 - Rabi 2013-14 Rabi 2013-14 Rabi 2013-14 5.2 5.2 2 11 13 - 19.2 19.2 8 40 48 - 10.4 10.4 3 23 26 - Kharif 2013 Kharif 2013 Kharif 2013 1/ Horticult ure 1/Plant Prot 1/Agri. Engg. 1/ Veterina ry Science 2 3 Rabi sorghum Varietal evaluation Variety: Akola kranti Rabi Sorghum Varietal evaluation Variety: Phule vasudha Total Bottle gourd Varital evaluation Tomato Disease mangement Brinjal Varital evaluation Total Bengal gram IPM Soybean IPM Total Seed cum fertilizer drill MKV ferti hoe in Rabi sorghum Farm machineries Farm machineries Use of Phule Samrat Variety with local check Use of wired staking in tomato over non-staking Use of Phule Arjun cultivar over local varieties Rabi 2013-14 Rabi 2013-14 Monsoo n 2013 Winter 2013-14 Summe r 201314 Pheromone traps. Azadirectine 1500 PPM (neem oil). HaNPV 250 LE Pheromone traps. NSKE 5% Quinalphos 0.05% Rabi2013 Tractor drawn seed cum fertilizer drill Use of MKV ferti hoe in Rabi sorghum Khariff 2013 Rabi 2013 Rabi 2012 Cattle buffalo and Fodder production Better forage yield Kharif 2012-13 Cattle buffalo Cattle and Dairy management High milk yield and fodder management enhance quality of fodder Kharif 2012-13 Rabbi 6.8 6.8 3 14 17 - 3.6 3.6 2 7 9 - 91.6 1.5 91.6 1.5 40 2 189 13 229 15 - 1.5 1.5 5 10 15 - 1.5 1.5 4 11 15 4.5 5.00 4.5 5.00 11 0 34 13 45 13 -- 5.20 5.20 2 11 13 -- 10.2 13 10 13 2 3 23 10 25 13 13 13 4 9 13 26 26 7 19 26 0.2 0.2 3 7 10 - 2 8 10 - 10 0 10 - Crop Agronomy Soil type Farming situation (RF/Irrigated) Season Status of soil N P K 15 40 15 97 No. of rainy days 0.2 20.2 Seasonal rainfall (mm) 0.2 20.2 Harvest date Sowing date Previous crop buffalo Sub Total Total 30 137 Details of farming situation Kharif2013 Rain fed Black cotton L M H Soybean 15 Jun 2013-30 Jun 2013 24 sept-30 sept 2013 Kharif2013 Rain fed Black cotton L M H Soybean 15 Jun 2013-30 Jun 2013 30 Dec-15 Jan 2014 Soybean Pigeon pea Green gram Pigeon pea Bengal gram Wheat Rabi sorghum Rabi sorghum Rabi sorghum Rabi Sorghum Kharif2013 Kharif2013 Rabi 201314 Rabi 201314 Rabi 201314 Rabi 201314 Rabi 201314 Rabi 201314 Rain fed Rain fed Black cotton Black cotton L L M M H H Rain fed Black cotton L M H Irrigated Rain fed Black cotton L Medium to L black soil M M H H Rain fed Medium black soil Medium black soil Medium black soil to L M H to L M H to L M H M edi um H ig h es Rain fed Rain fed 15 Jun-25 Jun 2013 15 Jun 2013-30 Jun 2013 10 Oct -25 Oct 2013 15 Oct-25 Oct 2013 15 Oct-30 Oct 2013 15 Oct-30 Oct 2013 15 Oct-30 Oct 2013 15 Oct-30 Oct 2013 1 Sept-15 Sept 2013 30 Dec-15 Jan 2014 8 Feb-15 feb 2014 20 feb-30 feb 2014 20 feb-30 feb 2014 20 feb-30 feb 2014 20 feb-30 feb 2014 20 feb-30 feb 2014 Cotton 06-06-2013 16-6-2013 896 48 Horticulture Bottle gourd Monsoon 2-13 Rainfed Medium P o or to 01-08-2013 onwards 896 48 t Tomato Winter 2013 Irrigated Medium P o or M edi um H ig h es t M e di u m Soyabean 12-10-2013 22-10-2013 to 15-12-2013 onwards 896 48 Brinjal Summer 2013-14 irrigated Medium M e di u m Po or Gram 20-01-2014 30-1-2014 to Continue - - Rabi-2012 Rainfed Medium light L M H Bengal gram 30/9/2013 L M H Soybean 21/6/2013 to 306-2013 23/11/2012 to 2911-2013 Rabi-2012 Irrigated Medium light Khariff 2013 Rainfed Medium L M H Bengal gram 12-06-13 to 25-62013 23-09-13 Rabi 2013 Irrigated 15-8-2013 to 208-2013 18-2-2014 Plant Prot Soybean Bengal gram 15 Jan-30 Jan 2012 843.80 56 896.7 48 896.7 48 896.7 48 Agri. Engg. Seed cum fertilizer drill Ferti hoe maize Medium L M H Soybean Performance of FLD Sr. No. Crop Technology Demonstrated Variety No. of Farmers Area (ha.) 1 2 3 4 5 6 Yield of local Check Qtl./ha 10 Demo. Yield Qtl/ha H 7 L 8 26.12 20.7 8 A 9 Increase in yield (%) 11 Data on parameter in relation to technology demonstrated Demo Local 12 13 Agronomy Soybean 1 2 Pigeon pea (Cotton +Pigeon pea 6:1) Varital demonstration-BDN711 Local check: BSMR736 Green gram Whole Package of practice by VNMKV,Parbhani Local check: Farmers practice Whole Package of practice by VNMKV,Parbhani Local check: Farmers practice 3 4 Pigeon pea (Soyben+Pigeon pea 6:1) Bengal gram 5 Wheat 6 7 8 9 10 Varital demonstrationMAUS-71 Local check: JS-335 Rabi sorghum Rabi sorghum Rabi sorghum Rabi Sorghum Demo:MAUS-71 Local: JS-335 Demo:BDN711 Local: BSMR736 13 13 5.2 5.2 11.25 8.12 23.75 9.75 20.00 7.25 15.79 25.65 Demo:Uttkarsh Local:Chamka Mung 30 12 8.20 5.60 6.75 5.25 22.23 Demo:Vipula Local: BSMR-736 30 12 18.12 11.7 5 13.25 10.70 19.25 Pods/plantMax-75 Min- 22 Avg-52 Pods/plantMax-62 Min-16 Avg- 43 Pods/plantMax-600 Min- 190 Avg-395 Pods/plantMax-336 Min-112 Avg- 124 Pods/plantMax-16 Min- 10 Avg-14 Pods/plantMax-1030 Min- 304 Avg-667 Pods/plantMax-10 Min-6 Avg- 8 Pods/plantMax-320 Min-106 Avg- 213 Pods/plantMax-335 Min-55 Avg- 195 No. of pod borer larvae per MRL – 3.05 No of tillers/plant Max-18 Min- 6 Avg-12 Whole Package of practice by VNMKV,Parbhani Local check: Farmers practice Demo:Jaki 9218 Local:Annagari 30 12 30.00 12.5 18.17 14.23 27.68 Pods/plantMax-530 Min- 115 Avg-332 No. of pod borer larvae per MRL - 2.36 Varital demonstrationKudrat-17 Local check: Lok-1 Demo:Kudrat-17 Local: LOK-1 13 5.2 26.25 17.8 20.5 13.75 32.93 No of tillers/plant Max-32 Min- 12 Avg-27 Varital demonstrationParbhani moti Local check: Dukari Varital demonstrationParbhani Jyoti Local check: Dukari Varital demonstrationAkola kranti Local check: Dukari Varital demonstrationPhule vasudha Local check: Dukari Demo:Parbhani moti Local:Dukari Demo:Parbhani Jyoti Local:Dukari Demo:Akola kranti Local:Dukari Demo:Phule vasudha Local:Dukari 48 19.2 26 10.4 Crop is 100% damage due to Hailstrom so unable to take the data 17 6.8 9 3.6 15 1.5 ha Horticulture 1 Bottle gourd Use of Phule Samrat Phule Samrat 220 I 156 188 140 34 Yield of fruits-188 qtl/ha Yield days-88 Yield of fruits-140 qtl/ha Yield days-70 Variety with local check 2 Tomato Use of tomato staking Syngeta Heem Sona 15 1.5 ha 3 Brinjal Use of improved cultivar Phule arjun Phule Arjun 15 1.5 ha 440 360 400 286 Yield of fruits-400qtl/ha Marketable fruit percentage-90 71.5 Experiment is ongoing; result awaited…. Incidence of leaf defoliator (Larvae per Meter Row) 0.56 S. litura Plant Prot Pheromone traps. NSKE 5% Quinalphos 0.05% 1.20 1 Soybean JS-335 13 5.20 18.0 8 24.68 21.33 19.28 Semilloper 10.63 0.26 Hairy Caterpiller 1 Bengal gram Pheromone traps. Azadirectine 1500 PPM (neem oil). HaNPV 250 LE Jaki 9218 Yield of fruits286qtl/ha Marketable fruit percentage-64 Incidence of leaf defoliator (Larvae per Meter Row) 0.71 S. litura Semi llope r Hair y Cater piller 1.93 0.43 No. of pod borer larvae per MRL 30 12 30.00 12.5 18.17 14.23 27.68 2.36 3.05 Veterinary Science 1 cattle and buffalo Better forage yield Jayawant napier 10 0.2 263 189 219.7 179 22.73 200-250mt/hectare 100-150mt/hectare 2 cattle and buffalo Increase milk yield Chealated mineral mixture 10 1kg/ anim al 1.5 lit/day 0.5 lit/da y 0.0.952li t/day 0.75 81.01 4-5lit/day 2-3 lit /day Due to use of dry and low quality fodder, detoriated their heath during summer season -- -- - 3 cattle and buffalo enhance quality of fodder Urea treatment 10 10 farm ers Animal weight is mainteained during summer season no significant change in milk yield Economic Impact (continuation of previous table) Average Cost of cultivation (Rs./ha) Average Gross Return (Rs./ha) Average Net Return (Profit) (Rs./ha) Demonstration Local Check Demonstration Local Check Demonstration Local Check 14 15 16 17 18 19 Benefit-Cost Ratio (Gross Return / Gross Cost) Cost-Benifit Ratio (Gross Return / Gross Cost) Local Check 20 21 Agronomy 31125 18175 13500 20725 30555 21325 20150 20150 20150 20150 Horticulture 12000 46000 31125 18175 13500 20725 27500 21325 20150 20150 20150 20150 10000 35000 76000 39000 30375 53000 54510 36900 64000 29000 23625 42800 42690 24750 44875 20825 16875 32275 23955 15575 32875 10825 10125 22075 15190 3425 1:2.44 1:2.1 1:2.25 1:2.55 1:1.78 1:1.73 1:2.05 1:1.5 1:1.75 1:2.06 1:1.55 1:1.16 Crop is 100% damage due to Hailstrom 75200 160000 49000 63200 85800 114000 Experiment is ongoing; result awaited…. 39000 50800 1:5.26 1:2.47 1:39 1:1.45 Plant Protection 16360 15360 Veternery Science 2600 1400 100 16120 14600 2800 1600 50 -- 61857 56327 57478 44113 45497 40967 41358 29527 1:2.78 1:2.66 1:2.56 1:2.02 4800 4920 3600 3600 1000 3520 800 2000 1:1.84 1:3.5 -- 1:1.28 1:2.25 -- -- -- -- (Avg. Cost of grains considered as Soybean @ Rs 3200 /qt, Pigeon pea @ 4000/qt, Green gram@ 4500/qt, Bengal gram @ 3000/qt,Wheat 1800/qt) ) Analytical Review of component demonstrations (details of each component for rainfed / irrigated situations to be given separately for each season). Crop Season Farming situation Component Agronomy Soybean Kharif2013 Single componenentVarietal evaluation Rain fed Pigeon pea (Cotton +Pigeon pea 6:1) Green gram Kharif2013 Single componenentVarietal evaluation Rain fed Kharif2013 Kharif2013 Multi componenentWhole package Multi componenentWhole package Rain fed Soybean Kharif-13 Plant Protection Soybean Bengal gram Kharif-13 Multi componenentWhole package Single componenentVarietal evaluation Single componenentVarietal evaluation Single componenentVarietal evaluation Single componenentVarietal evaluation Single componenentVarietal evaluation Single component Plant Protection Single component Plant Protection Single component Plant Protection Rain fed Bengal gram Rabi 2013-14 Rabi 2013-14 Rabi 2013-14 Rabi 2013-14 Rabi 2013-14 Rabi 2013-14 Rabi 2013 Single component Plant Protection Pigeon pea (Soyben+Pigeon pea 6:1) Bengal gram Wheat Rabi sorghum Rabi sorghum Rabi sorghum Rabi Sorghum Rabi 2013 Demo.average yield (q/ha) Local check (q/ha) Percentage increase in productivity over local check 23.75 20.00 15.79 9.75 7.25 25.65 6.75 5.25 22.23 13.25 10.70 19.25 18.17 14.23 27.68 20.5 13.75 32.93 Rain fed Irrigated Rain fed Rain fed Rain fed Crop is 100% damage due to Hailstrom Rain fed Irrigated 15.3 Results are awaited Rainfed 21.33 19.28 10.63 Rainfed 21.33 19.28 10.63 Irrigated 18.17 14.23 27.68 Technical Feedback on the demonstrated technologies Sr. No Agronomy Soybean (MAUS-71) Pigeon pea BDN-711 (Cotton +Pigeon pea 6:1) Green gram (Uttakarsh) Pigeon pea (Vipula) (Soyben+Pigeon Feed Back Soybean variety MAUS-71(Samrudhi) having Purple color flowers with bold grains. If delay in harvesting pods will not shatter after 10-15 days after maturity. It recorded 15.79% more grain yield as compared to JS-335 (Jawahar) so farmers should cultivate MAUS-71(Samrudhi) instead of JS335 (Jawahar) on medium to black soil under rain fed condition in Nanded district of Maharashtra. Pigeon pea BDN-711 variety is early duration ( 150-160 days) which is normally 20-25 days early than BSMR-736 (Local) which is suitable for rain fed condition. Due to earliness crop will escape from frost and moisture stress. Also tolerant to wilt and sterility mosaic. Bold size grains having 4-5 seeds /pod. It recorded 25.65% more grain yield as compared to BSMR-736. It is more suitable for inter cropping system with cotton and soybean. So farmers should cultivate BDN-711 instead of other varieties on medium to black soil under rain fed condition in Nanded district. Green gram variety Utkarsh (Research variety of MAHABEEJ)) having more no of pods (1213/plants), grains per plant (14-15/plant) and having bold size than local variety (Chamka mung) .It is less susceptible to powdery mildew and sucking pest. It recorded 22.23 % more grain yield as compared to Chamka mung (Local) so farmers should cultivate Utkarsh instead of chamka mung (Local) on medium to black soil under rain fed condition in Nanded district of Maharashtra. Pigeon pea Vipula variety is medium duration (145-160 days) having medium size red grains. tolerant to wilt and sterility mosaic. It recorded 19.25 % more grain yield as compared to BSMR736 (Local) so farmers should cultivate Vipula instead of BSMR-736 (Local) on medium to black I pea 6:1) Bengal gram (Jaki 9218) Wheat (Kudrat-17) Rabi sorghum (Parbhani Moti) Rabi sorghum (Parbhani Jyoti) Rabi sorghum (Akola Kranti) Rabi Sorghum (Phule vasudha) Horticulture Bottle gourd Samrat Tomato staking Plant Protection Management of leaf defoliators in soybean Management of gram pod borer Agri. Engg. Tractor Drawn Seed drill Ferti hoe soil under rain fed condition in Nanded district of Maharashtra. Jaki 9218 variety of Bengal gram is better than Annagiri as it has having more number of pods /plant, and high grain yield as 27.68% more than annagari . It is less susceptible to wilt. This variety is giving better response under zero tillage sowing. So farmers should cultivate Jaki 9218 instead of Annagiri on medium to black soil in Nanded district of Maharashtra. Kurat -17 is research variety developed by UP farmer Raghuwansh Singh having more no of tillers (25-30/plant) as compared to LOK - (10-12 /plant) and giving high response to irrigation and fertilizers. Duration is high 130-140 days (10-15 days more than LOK-1.) . Kudrat -17 having long panicle with more no of bold grains. It recorded 32.93 % more grain yield as compared to LOK-1 (Local) so farmers should cultivate Kudrat-17 instead of LOK-1 (Local) on medium to black soil under irrigated condition where assured 6-7 irrigation available with farmer. Parbhani moti suitable to sow under rain fed condition crop was at flowering to grain filling stage but due to unexpected hailstorm crop get 100% damaged. Parbhani jyoti suitable to sow under irrigated condition crop was at flowering to grain filling stage but due to unexpected hailstorm crop get 100% damaged. Akola Kranti suitable to sow under rain fed as well as irrigated condition crop was at flowering to grain filling stage but due to unexpected hailstorm crop get 100% damaged. Phule vasudha suitable to sow under rain fed condition crop was at flowering to grain filling stage but due to unexpected hailstorm crop get 100% damaged. The variety found superior over local cultivar in market as compare to yield as well as price The staking method resulted more yield with quality fruits and more market price. Pheromone traps monitoring of leaf defoliators and need based two spraying of NSKE 5% and Quinalphos 0.05% increases the 10.63 % yield over local check. Pheromone traps monitoring of gram pod borer and ETL based two spraying of Azadirachtin 1500 ppm followed by HaNPV 250 LE 15 days after first spray increases the 27.63 % yield over local check. Due to use drilling method of sowing plant population is as per require Proper application of fertilizer without leaching. Home Science Smoke less Chula Groundnut decorticator Bhendi ring cutter Bhendi cutter PDKV khurpi Vaibhav sickle Lakshmi sickle 15.21% time saved for cooking as compared to traditional Chula. Eye problems reduced by 90% and smoke free house. Time required to decorticate the groundnuts is 177.14 min/qt with decorticator as compaird to hand decorticating (2226.19min/qt) which is 92.04% less. Finger and back pain Reduced by 90% On an average 3.94% time saved by using bhendi cutter. It is more useful to reduce finger injury (75%) Time saved 5.12% but reduced finger injury 90%. Average 22.68% time saved by using PDKV khurpi with easy to use and less finger pain (50%) Near about 29.30% time saved as compared to traditional sickle with 50% reduced palm pain. Ground level cutting can possible. Near about 25.58% time saved as compared to traditional sickle with 50% reduced palm pain. Veterinary Science Mineral mixture Milk yield is increased by 1 to 2 lit / day in high yielding animals after commencement of mineral mixture that too with economic way. Animals body condition is also improved, animals showed regular cycles after 21 days. Animals which have come in heat conceived timely. Fodder production Increases fodder production, 250 to 300 tons of green fodders have been revealed from 1 ha of land because of that milking animals showed improvement in milk yield. Working bullocks also improved their draft ability. Bordeaux mixture 15 applications on alternate days are required for chronic cases there after we could see improvement in health status of animal. Farmers’ reactions on specific technologies Sr. No Feed Back Agronomy Soybean Soybean variety MAUS-71(Samrudhi) having bold grains. If delay in harvesting pods (MAUS-71) will not shatter after 10-15 days after maturity. More productive as compared to JS-335 Pigeon pea BDN-711 (Cotton +Pigeon pea 6:1) Green gram (Uttakarsh) Pigeon pea (Vipula) (Soyben+Pigeon pea 6:1) Bengal gram (Jaki 9218) Wheat (Kudrat-17) Rabi sorghum (Parbhani Moti) Rabi sorghum (Parbhani Jyoti) Rabi sorghum (Akola Kranti) Rabi Sorghum (Phule vasudha) Horticulture Bottle gourd Samrat Tomato Staking Plant Protection Management of leaf defoliators in soybean Management of gram pod borer Agri. Engg. Tractor Drawn Seed drill Ferti hoe Home Science Smoke less Chula Groundnut decorticator Bhendi ring cutter Bhendi cutter PDKV khurpi Pigeon pea BDN-711 variety is early duration (150-160 days) suitable for rain fed condition. Due to earliness crop will escape from frost and moisture stress. Tolerant to wilt . Bold size grains having 4-5 seeds /pod. Green gram variety Utkars having more no of pods, grains per plant with bold size grains than local variety (Chamka mung) .It is less susceptible to powdery mildew and sucking pest. Pigeon pea Vipula variety is medium duration (145-160 days) having medium size red grains. Tolerant to wilt .Giving more response under irrigated condition. Jaki 9218 is good variety of Bengal gram, as compared to Annagiri in terms of no of pods /plant and grain yield, susceptibility to wilt. Kudrat -17 having more no of tillers, long panicle and more of bold grains per panicle as compared to LOK-1.Requires more no of irrigations (6-7) and fertilizers. Parbhani moti sturdy in nature suitable to sow under rain fed condition. Crop was at flowering to grain filling stage but due to unexpected hailstorm crop get 100% damaged. Crop was at flowering to grain filling stage farmers expected good quality fodder with more grain yield but due to unexpected hailstorm crop get 100% damaged. Crop was at flowering to grain filling stage farmers expected good quality fodder with more grain yield but due to unexpected hailstorm crop get 100% damaged Crop was at flowering to grain filling stage farmers expected good quality fodder with more grain yield but due to unexpected hailstorm crop get 100% damaged Samrat variety having good yield and attractive fruits having more demand in market This method of tomato staking produce High quality yield Low cost effective management of leaf defoliators as compared to heavy use of insecticides in soybean overcomes the cost of plant protection. Low cost effective management of gram pod borer as compared to heavy use of insecticides in Bengal gram overcomes the cost of plant protection. Use of seed drill saving of seed and fertilizer No leaching of fertilizer produce high yield. This Chula is very useful as it creates no smoke and required less fuel. Decorticator is very beneficial as it required very less time as compared to traditional method. Time saved is negligible but useful for safety of fingers. Time saved is negligible but useful for safety of fingers Light in weight, easy for weeding. Vaibhav sickle Light in weight as compared to traditional sickle. Work output is more. Lakshmi sickle Light in weight as compared to traditional sickle. Work output is more. But easily breakable when used on little hard stem. It’s material should be hard. Veterinary Science Mineral mixture Fodder production Bordeaux mixture Animals are totally cured with increased lusture . Animals are calm and quite ,weight gain ,increased draughtability. Could come across to improved variety of fodder crop Increases fodder yield in minimum cultivable area. Extension and Training activities under FLD Sr. No. Activity No. of activities organised Agronomy 1 Field days 4 2 Farmers Training 2 3 Media coverage Training for extension functionaries Horticulture 1 Field days 4 Farmers Training Media coverage Training for extension functionaries Plant Protection 1 Field days 2 Farmers Training 3 Media coverage Date Number of participants 1 27/8/2013 20/9/2013 11/1/2014 24/1/2014 15/6/2013 9/10/2013 21/7/2013 44 42 97 52 21 13 0 0 0 0 2 12-08-2013 Bottle gourd 22-01-2014 Toamto 39 02 03 02 10/01/2014 17/5/13, 9/7/13, 1/10/13 62 58 1 12/06/13 32 01 01 12/11/2013 16/8/2013 15 15 2 3 4 4 Training for extension functionaries Agri. Engg. 1 Field days 2 Farmers Training 3 Media coverage 4 Training for extension functionaries Home Science 1 Field days 2 Farmers Training 3 Media coverage 4 Training for extension functionaries Veterinary Science 1 Field days 2 Farmers Training 3 Media coverage 4 Training for extension functionaries 5 Video show 2 Remarks 0 0 Sakal daily news paper 0 c. Details of FLD on Enterprises (i) Farm Implements Name of the implemen t crop No. of farm ers Area (ha) Performance parameters / indicators Seed cum fertilizer drill Ferti hoe soybe an 13 5.2 Rabi sorgh um 13 5.2 1.Field capacity (ha/hr) 2.Operating cost (Rs/ha) 3.Yield (q/ha) 1.Field capacity (ha/hr) 2.Labour required (Man hr/ha) 3.Yield Q/ha 3. Operation cost (Rs/ha.) Smoke less Chula Ground nut decortic ator Bhendi ring cutter - - 10 21 - - Fuel Eye problem Time Time Finger and back pain Bhend i and brinjal 10 1 ha * Data on parameter in relation to technology demonstrated Demon. Local check 1.2 0.4 1750 312.5 25.15 22.99 0.4 0.3 % change in the parameter 200 460 9.39 33.33 2.1 2.5 19.04 46.65 420 40.27 500 15.84 19.04 250 gm fuel saved/d ay Reduce d 90% eye problem s On an average 10.5 min. saved 177.14 min/qt Reduce d by 90% Eye burning Average time requird is 69 min. 15.21% time saved 2226.19mi 92.04% n/qt time saved Finger injury and back pain Time 1460 min/ha 1520 min/ha Finger injuri Reduce d by 75% Injured fingers Remarks 3.94% time saved This Chula is very useful as it creates no smoke and required less fuel Decortic ator is very benefici al as it required very less time as compare d to tradition al method Time saved is negligibl e but useful for Bhendi cutter PDKV khurpi Vaibhav sickle Bhend i and brinjal Weed 10 1 ha Time 10 1 ha Work output 25 1 ha Work output Finger pain Palm pain Lakshmi sickle Soybe an 1560 min/ha Reduce d by 90% Injured fingers 1500 min/ha 1940 min/ha Finger pain reduced by 50% 1035 min/ha Finger and palm pain Finger injuri Finger pain Palm pain Rice 1480 min/ha 25 1 ha Work output Finger pain Palm pain Finger pain and palm pain reduced by 50% 1464 min/ha Finger pain and palm pain reduced by 50% 1464 min/ha 5.12% time saved 22.68% time saved 29.30% time saved Finger pain and palm pain 1978 min/ha Finger pain and palm pain 25.98% time saved safety of fingers. Time saved is negligibl e but useful for safety of fingers Light in weight, easy for weeding . Light in weight as compare d to tradition al sickle. Work output is more. Light in weight as compare d to tradition al sickle. Work output is more. But easily breakabl e when used on little hard stem. It’s material should be hard. (ii) Livestock Enterprises Enterp rise Breed Cattle Non descrip t Cattle Non descrip t No. of farme rs 10 No. of Performa animal nce s, paramete poultr rs / y birds indicators etc. 10 Milk yield Change in health status Fodder productio n 10 10 Increased Milk yield, Improvem ent in health status, Increased Fodder productio n * Data on parameter in relation to technology demonstrated Demon. Local check % change in the parameter Remarks 1) Increased milk productio n 2) Health status was improved 3) Fodder productio n was increased Increased milk yield by 1 to 2 lit per day Health status is improved Fodder production was received 250 ton per ha. Milk yield was low, Health status was poor Fodder productio n was 25 ton per ha. 1)Increased milk yield by 18% 2) Health status was improved 3) Fodder production was increased by 10 times more than local check 50 gm twice daily has been offered dailyfor 30 days Daily milk yield is counted 2)animal health is improved 3)milk production is increased by 3540% * Milk production, meat production, egg production, reduction in disease incidence etc. (iii) Other Enterprises Enterprise Mushroom Apiary Sericulture Vermi compost Variety/ breed/Spec ies/others No. of farmers No. of Units Performance parameters / indicators Data on parameter in relation to technology demonstrated Demon Local check % change in the parameter Remarks 3.3 Achievements on Training (Including the sponsored, vocational, FLD and trainings under Rainwater Harvesting Unit) : A) ON Campus Thematic area No. of courses Participants SC/ST Male Female Total Male Others Female Total 1 24 0 24 6 0 6 30 0 30 1 24 0 24 6 0 6 30 0 30 1 31 0 31 6 0 6 37 0 37 1 23 0 23 2 0 2 25 0 25 4 66 0 66 14 0 14 80 0 80 2 53 0 53 12 0 12 65 0 65 1 12 0 12 5 0 5 17 0 17 1 1 12 16 0 0 12 16 3 3 0 0 3 3 15 19 0 0 15 19 1 11 0 11 2 0 2 13 0 13 1 0 15 15 0 2 2 0 17 17 1 15 0 15 3 0 3 18 0 18 Male Grand Total Female Total (A) Farmers and Farm Women I Crop Production Weed Management Resource Conservation Technologies Cropping Systems Crop Diversification Integrated Farming Water management Seed production Nursery management Integrated Crop Management Fodder production Production of organic inputs Dry land farming II Horticulture a) Vegetable Crops Production of low volume and high value crops Off-season vegetables Nursery raising Exotic vegetables like Broccoli Export potential vegetables Grading and standardization Protective cultivation (Green Houses, Shade Net etc.) b) Fruits Training and Pruning Layout and Management of Orchards Cultivation of Fruit Management of young plants/orchards Rejuvenation of old orchards Export potential fruits Micro irrigation systems of orchards Plant propagation techniques c) Ornamental Plants Nursery Management Management of potted plants Export potential of ornamental plants Propagation techniques of Ornamental Plants d) Plantation crops Production and Management technology Processing and value addition e) Tuber crops I Production and Management technology Processing and value addition f) Spices Production and Management technology Processing and value addition g) Medicinal and Aromatic Plants Nursery management Production and management technology Post harvest technology and value addition III Soil Health and Fertility Management Soil fertility management Soil and Water Conservation Integrated Nutrient Management Production and use of organic inputs Management of Problematic soils Micro nutrient deficiency in crops Nutrient Use Efficiency Soil and Water Testing IV Livestock Production 1 23 0 23 2 0 2 25 0 25 1 20 0 20 5 0 5 25 0 25 1 18 15 33 2 8 10 20 23 43 4 81 0 81 20 0 20 101 0 101 and Management Dairy Management Poultry Management Piggery Management Rabbit Management Disease Management Feed management Production of quality animal products V Home Science/Women empowerment Household food security by kitchen gardening and nutrition gardening Design and development of low/minimum cost diet Designing and development for high nutrient efficiency diet Minimization of nutrient loss in processing Gender mainstreaming through SHGs Storage loss minimization techniques Value addition Income generation activities for empowerment of rural Women Location specific drudgery reduction technologies Rural Crafts 1 0 11 11 0 13 13 0 24 24 1 0 13 13 0 12 12 0 25 25 2 17 12 29 10 18 28 27 30 57 1 0 3 3 1 19 20 1 22 23 Women and child care VI Agril. Engineering Installation and maintenance of micro irrigation systems Use of Plastics in farming practices Production of small tools and implements Repair and maintenance of farm machinery and implements Small scale processing and value addition Post Harvest Technology VII Plant Protection Integrated Pest Management Integrated Disease Management Bio-control of pests and diseases Production of bio control agents and bio pesticides VIII Fisheries Integrated fish farming Carp breeding and hatchery management Carp fry and fingerling rearing Composite fish culture Hatchery management and culture of freshwater prawn Breeding and culture of ornamental fishes Portable platic carp hatchery Pen culture of fish and prawn Shrimp farming Edible oyster farming Pearl culture Fish processing and value addition IX Production of Inputs at site Seed Production Planting material production Bio-agents production Bio-pesticides production Bio-fertilizer production Vermi-compost production Organic manures production Production of fry and fingerlings Production of Bee-colonies and wax sheets Small tools and implements Production of livestock feed and fodder Production of Fish feed X Capacity Building and Group Dynamics Leadership development Group dynamics 1 0 3 3 1 19 20 1 22 23 Formation and Management of SHGs Mobilization of social capital Entrepreneurial development of farmers/youths WTO and IPR issues XI Agro-forestry Production technologies Nursery management Integrated Farming Systems TOTAL (B) RURAL YOUTH Mushroom Production Bee-keeping Integrated farming Seed production Production of organic inputs Integrated Farming Planting material production Vermi-culture Sericulture Protected cultivation of vegetable crops and Biological pest management Commercial fruit production Repair and maintenance of farm machinery and implements Nursery Management of Horticulture crops Training and pruning of orchards Value addition Production of quality animal products Dairying Sheep and goat rearing Quail farming Piggery Rabbit farming Poultry production Ornamental fisheries Para vets Para extension workers Composite fish culture Freshwater prawn culture Shrimp farming Pearl culture Cold water fisheries Fish harvest and processing technology Fry and fingerling rearing Small scale processing Post Harvest Technology Tailoring and Stitching Rural Crafts TOTAL (C) Extension Personnel Productivity enhancement in field crops under dry land 31 500 69 569 111 72 183 611 141 752 1 17 0 17 2 0 2 19 0 19 2 31 0 31 6 0 6 37 0 37 3 0 4 4 0 49 49 0 53 53 3 43 0 43 9 0 9 52 0 52 2 35 0 35 10 0 10 45 0 45 1 0 10 10 0 19 19 0 29 29 12 126 14 140 27 68 95 153 82 235 1 11 0 11 5 0 5 16 0 16 farming Integrated Pest Management Integrated Nutrient management Soil and water testing Rejuvenation of old orchards Protected cultivation technology Formation and Management of SHGs Group Dynamics and farmers organization Information networking among farmers Capacity building for ICT application Care and maintenance of farm machinery and implements WTO and IPR issues Management in farm animals Livestock feed and fodder production Household food security Women and Child care Low cost and nutrient efficient diet designing Production and use of organic inputs Gender mainstreaming through SHGs 3 1 33 16 1 0 34 16 10 4 1 0 11 4 44 20 2 0 46 20 1 1 13 13 0 0 13 13 7 3 0 0 7 3 20 16 0 0 20 16 1 30 0 30 10 0 10 40 0 40 2 0 11 11 0 27 27 0 38 38 Total (C) 10 116 12 128 39 28 67 156 40 196 TOTAL (A+B+C) 53 742 95 837 177 168 345 920 263 1183 B) OFF Campus Thematic area No. of courses Participants SC/ST Male Female Total Male Others Female Total 1 1 14 13 0 0 14 13 1 6 0 0 1 6 15 19 0 0 15 19 1 15 0 15 1 0 1 16 0 16 4 60 0 60 6 0 6 66 0 66 1 17 0 17 0 0 0 17 0 17 1 27 0 27 6 0 6 33 0 33 1 18 0 18 4 0 4 22 0 22 1 1 15 14 0 0 15 14 2 5 0 0 17 5 17 19 0 0 17 19 1 15 0 15 3 0 3 18 0 18 Male Grand Total Female Total (A) Farmers and Farm Women I Crop Production Weed Management Resource Conservation Technologies Cropping Systems Crop Diversification Integrated Farming Water management Seed production Nursery management Integrated Crop Management Fodder production Production of organic inputs Use of improved verities/hybrids Dry land farming II Horticulture a) Vegetable Crops Production of low volume and high value crops Off-season vegetables Nursery raising Exotic vegetables like Broccoli Export potential vegetables Grading and standardization Protective cultivation (Green Houses, Shade Net etc.) Kitchen Gardening b) Fruits Training and Pruning Layout and Management of Orchards Cultivation of Fruit Management of young plants/orchards Rejuvenation of old orchards Export potential fruits Micro irrigation systems of orchards Plant propagation techniques c) Ornamental Plants Nursery Management Management of potted plants Export potential of ornamental plants Propagation techniques of Ornamental Plants d) Plantation crops Production and Management technology Processing and value addition e) Tuber crops Production and Management technology Processing and value addition f) Spices Production and Management technology Processing and value addition g) Medicinal and Aromatic Plants Nursery management Production and management technology Post harvest technology and value addition III Soil Health and Fertility Management Soil fertility management Soil and Water Conservation Integrated Nutrient Management Production and use of organic inputs Management of Problematic soils Micro nutrient deficiency in crops Nutrient Use Efficiency Soil and Water Testing IV Livestock Production and 1 23 0 23 2 0 2 25 0 25 3 1 37 28 12 0 49 28 22 7 7 0 29 7 59 35 19 0 78 35 2 34 0 34 6 0 6 40 0 40 1 0 0 0 0 15 15 0 15 15 1 0 13 13 0 2 2 0 15 15 1 0 5 5 0 13 13 0 18 18 1 0 9 9 0 6 6 0 15 15 2 0 9 9 0 37 37 0 46 46 Management Dairy Management Poultry Management Piggery Management Rabbit Management Disease Management Feed management Production of quality animal products V Home Science/Women empowerment Household food security by kitchen gardening and nutrition gardening Design and development of low/minimum cost diet Designing and development for high nutrient efficiency diet Minimization of nutrient loss in processing Gender mainstreaming through SHGs Storage loss minimization techniques Value addition Income generation activities for empowerment of rural Women Location specific drudgery reduction technologies Rural Crafts Women and child care VI Agril. Engineering Installation and maintenance of micro irrigation systems Use of Plastics in farming practices Production of small tools and implements Repair and maintenance of farm machinery and implements Small scale processing and value addition Post Harvest Technology VII Plant Protection Integrated Pest Management Integrated Disease Management Bio-control of pests and diseases Production of bio control agents and bio pesticides VIII Fisheries Integrated fish farming Carp breeding and hatchery management Carp fry and fingerling rearing Composite fish culture Hatchery management and culture of freshwater prawn Breeding and culture of ornamental fishes Portable plastic carp hatchery Pen culture of fish and prawn Shrimp farming Edible oyster farming Pearl culture Fish processing and value addition IX Production of Inputs at site Seed Production Planting material production Bio-agents production Bio-pesticides production Bio-fertilizer production Vermi-compost production Organic manures production Production of fry and fingerlings Production of Bee-colonies and wax sheets Small tools and implements Production of livestock feed and fodder Production of Fish feed X Capacity Building and Group Dynamics Leadership development Group dynamics Formation and Management of 4 58 0 58 18 0 18 76 0 76 SHGs Mobilization of social capital Entrepreneurial development of farmers/youths WTO and IPR issues XI Agro-forestry Production technologies Nursery management Integrated Farming Systems TOTAL (B) RURAL YOUTH Mushroom Production Bee-keeping Integrated farming Seed production Production of organic inputs Integrated Farming Planting material production Vermi-culture Sericulture Protected cultivation of vegetable crops Commercial fruit production Repair and maintenance of farm machinery and implements Nursery Management of Horticulture crops Training and pruning of orchards Value addition Production of quality animal products Dairying Sheep and goat rearing Quail farming Piggery Rabbit farming Poultry production Ornamental fisheries Para vets Para extension workers Composite fish culture Freshwater prawn culture Shrimp farming Pearl culture Cold water fisheries Fish harvest and processing technology Fry and fingerling rearing Small scale processing Post Harvest Technology Tailoring and Stitching Rural Crafts TOTAL (C) Extension Personnel Productivity enhancement in field crops Integrated Pest Management Integrated Nutrient management Rejuvenation of old orchards 30 388 48 436 89 80 184 477 128 605 1 1 20 23 0 0 20 23 5 5 0 0 5 5 25 28 0 0 25 28 2 43 0 43 10 0 10 53 0 53 Protected cultivation technology Formation and Management of SHGs Group Dynamics and farmers organization Information networking among farmers Capacity building for ICT application Care and maintenance of farm machinery and implements WTO and IPR issues Management in farm animals Livestock feed and fodder production Household food security Women and Child care Low cost and nutrient efficient diet designing Production and use of organic inputs Gender mainstreaming through SHGs Total ( C ) TOTAL (A+B+C) 1 82 0 82 35 0 35 117 0 117 1 82 0 82 35 0 35 117 0 117 33 513 48 561 134 80 229 647 128 775 C) Consolidated table (ON and OFF Campus) Thematic area (A) Farmers and Farm Women I Crop Production Weed Management Resource Conservation Technologies Cropping Systems Crop Diversification Integrated Farming Water management Seed production Nursery management Integrated Crop Management Fodder production Production of organic inputs Use of improved verities/hybrids Dry land farming II Horticulture a) Vegetable Crops Production of low volume and high value crops Off-season vegetables Nursery raising Exotic vegetables like Broccoli Export potential vegetables Grading and standardization Protective cultivation (Green Houses, Shade Net etc.) Kitchen Gardening b) Fruits Training and Pruning Layout and Management of Orchards Cultivation of Fruit Management of young plants/orchards Rejuvenation of old orchards Export potential fruits Micro irrigation systems of orchards Plant propagation techniques c) Ornamental Plants Nursery Management Management of potted plants Export potential of ornamental plants Propagation techniques of Ornamental Plants d) Plantation crops Production and Management technology Processing and value addition e) Tuber crops Production and Management technology Processing and value addition No. of courses Participants SC/ST Male Female Total Male Others Female Total 2 1 38 13 0 0 38 13 7 6 0 0 7 6 45 19 0 0 45 19 1 28 0 28 7 0 7 35 0 35 1 31 0 31 6 0 6 37 0 37 2 38 0 38 3 0 3 41 0 41 8 126 0 126 20 0 20 146 0 146 1 3 17 80 0 0 17 80 0 18 0 0 0 18 17 98 0 0 17 98 1 1 18 12 0 0 18 12 4 5 0 0 4 5 22 17 0 0 22 17 1 1 12 16 0 0 12 16 3 3 0 0 3 3 15 19 0 0 15 19 1 11 0 11 2 0 2 13 0 13 1 1 15 14 0 0 15 14 2 5 0 0 17 5 17 19 0 0 17 19 1 0 15 15 0 2 2 0 17 17 2 30 0 30 6 0 6 36 0 36 Male Grand Total Female Total f) Spices Production and Management technology Processing and value addition g) Medicinal and Aromatic Plants Nursery management Production and management technology Post harvest technology and value addition III Soil Health and Fertility Management Soil fertility management Soil and Water Conservation Integrated Nutrient Management Production and use of organic inputs Management of Problematic soils Micro nutrient deficiency in crops Nutrient Use Efficiency Soil and Water Testing IV Livestock Production and Management Dairy Management Poultry Management Piggery Management Rabbit Management Disease Management Feed management Production of quality animal products V Home Science/Women empowerment Household food security by kitchen gardening and nutrition gardening Design and development of low/minimum cost diet Designing and development for high nutrient efficiency diet Minimization of nutrient loss in processing Gender mainstreaming through SHGs Storage loss minimization techniques Value addition Income generation activities for empowerment of rural Women Location specific drudgery reduction technologies Rural Crafts Women and child care VI Agril. Engineering Installation and maintenance of micro irrigation systems Use of Plastics in farming practices Production of small tools and implements Repair and maintenance of farm machinery and implements Small scale processing and value 2 46 0 46 4 0 4 50 0 50 1 20 0 20 5 0 5 25 0 25 1 18 15 33 2 8 10 20 23 43 7 1 118 28 12 0 130 28 42 7 7 0 49 7 160 35 19 0 179 35 2 34 0 34 6 0 6 40 0 40 2 0 11 11 0 28 28 0 39 39 2 0 26 26 0 14 14 0 40 40 1 0 5 5 0 13 13 0 18 18 3 1 17 0 21 3 38 3 10 1 24 19 34 20 27 1 45 22 72 23 2 0 9 9 0 37 37 0 46 46 addition Post Harvest Technology VII Plant Protection Integrated Pest Management Integrated Disease Management Bio-control of pests and diseases Production of bio control agents and bio pesticides VIII Fisheries Integrated fish farming Carp breeding and hatchery management Carp fry and fingerling rearing Composite fish culture Hatchery management and culture of freshwater prawn Breeding and culture of ornamental fishes Portable plastic carp hatchery Pen culture of fish and prawn Shrimp farming Edible oyster farming Pearl culture Fish processing and value addition IX Production of Inputs at site Seed Production Planting material production Bio-agents production Bio-pesticides production Bio-fertilizer production Vermi-compost production Organic manures production Production of fry and fingerlings Production of Bee-colonies and wax sheets Small tools and implements Production of livestock feed and fodder Production of Fish feed X Capacity Building and Group Dynamics Leadership development Group dynamics Formation and Management of SHGs Mobilization of social capital Entrepreneurial development of farmers/youths WTO and IPR issues XI Agro-forestry Production technologies Nursery management Integrated Farming Systems 7 61 TOTAL (B) RURAL YOUTH Mushroom Production Bee-keeping Integrated farming Seed production Production of organic inputs Integrated Farming Planting material production 108 1 0 108 26 0 26 134 0 134 888 117 1005 200 152 367 1088 269 1357 17 0 17 2 0 2 19 0 19 Vermi-culture Sericulture Protected cultivation of vegetable crops and biological pest management Commercial fruit production Repair and maintenance of farm machinery and implements Nursery Management of Horticulture crops Training and pruning of orchards Value addition Production of quality animal products Dairying Sheep and goat rearing Quail farming Piggery Rabbit farming Poultry production Ornamental fisheries Para vets Para extension workers Composite fish culture Freshwater prawn culture Shrimp farming Pearl culture Cold water fisheries Fish harvest and processing technology Fry and fingerling rearing Small scale processing Post Harvest Technology Tailoring and Stitching Rural Crafts TOTAL (C) Extension Personnel Productivity enhancement in field crops Integrated Pest Management Integrated Nutrient management Soil and water testing Rejuvenation of old orchards Protected cultivation technology Formation and Management of SHGs Group Dynamics and farmers organization Information networking among farmers Capacity building for ICT application Care and maintenance of farm machinery and implements WTO and IPR issues Management in farm animals Livestock feed and fodder production Household food security Women and Child care Low cost and nutrient efficient diet 2 31 0 31 6 0 6 31 6 37 3 0 4 4 0 49 49 0 53 53 4 1 63 23 0 0 63 23 14 5 0 0 14 5 77 28 0 0 77 28 2 35 0 35 10 0 10 45 0 45 0 169 10 14 10 183 0 37 19 68 19 105 0 200 29 88 29 288 1 11 0 11 5 0 5 16 0 16 3 1 1 1 33 16 13 13 1 0 0 0 34 16 13 13 10 4 7 3 1 0 0 0 11 4 7 3 44 20 20 16 2 0 0 0 46 20 20 16 2 112 0 112 45 0 45 157 0 157 2 0 11 11 0 27 27 0 38 38 1 14 designing Production and use of organic inputs Gender mainstreaming through SHGs 11 Total ( C ) TOTAL (A+B+C) 86 198 1255 12 143 210 74 1398 311 28 248 102 273 574 1561 40 397 313 1958 Note: Please furnish the details of above training programmes as Annexure in the proforma given below Date Client ele Agronomy 25RY 27/4/20 13 Title of the training programme Pre & post harvest management and marketing in pulses ( MACP project ) Improved varieties in Cotton & Soybean. 16/5/20 13 PF 2324/5/20 13 15/6/20 13 1516/6/20 13 2021/6/20 13 2628/6/20 13 RY 15/7/20 13 PF 16/7/20 13 PF Importance of soil and water testing 10/8/20 13 3/9/201 3 PF IWM in Bt cotton. PF Seed production technology Bengal gram. 12/9/20 13 PF 1415/9/20 13 PF Agronomical measures in soil moisture conservation in rabi jawar, safflower. Panchasutri yojana in production of rabi sorghum. 8/10/20 13 9/10/20 13 11/10/2 013 12/11/2 PF PF Sweet & pop corn production technology & its marketing. ICM in Pigeon pea Themat ic area disc ipli ne Dur atio n in days Ven ue (Off / On Cam pus) Number of other participants Number of SC/ST Total number of participangs Mal e Fem ale To tal M ale Fem ale Tot al Mal e Fe mal e Tot al ICM Marketi ng Agr o 3 ON 20 0 20 5 0 5 25 0 25 Varietal evaluati on ICM Marketi ng ICM Agr o 1 OFF 17 0 17 0 0 0 17 0 17 Agr o 2 ON 13 0 13 2 0 2 15 0 15 Agr o Agr o 1 OFF 18 0 18 3 0 3 21 0 21 2 ON 16 0 16 5 0 5 21 0 21 PF INM in BT cotton for control of reddening INM PF Planting Systems in Bt cotton. ICM Agr o 2 ON 11 0 11 5 0 5 16 0 16 RY Pre & post harvest measures and marketing in soybean (MACP Project) Importance of soil and water testing ICM Marketi ng Agr o 3 ON 15 0 15 5 0 5 20 0 20 Soil and water Health Soil and water Health IWM Agr o 1 ON 6 8 14 0 5 5 6 13 19 Agr o 1 ON 6 7 13 2 3 5 8 10 18 Agr o Agr o 1 OFF 14 0 14 1 0 1 15 0 15 1 OFF 15 0 15 1 0 1 16 0 16 Agr o 1 OFF 13 0 13 6 0 6 19 0 19 Agr o 2 ON 14 0 14 3 0 3 17 0 17 Agr o Agr o Agr o Agr 1 ON 16 0 16 0 0 0 16 0 16 1 OFF 12 0 12 1 0 1 13 0 13 1 OFF 17 0 17 0 0 0 17 0 17 1 OFF 13 0 13 2 0 2 15 0 15 Seed product ion Dry land agricult ure ICM ICM PF Sugarcane Production Technology ICM in Wheat PF ICM in Gram. ICM PF ICM in safflower. ICM ICM 013 17/12/2 013 PF Mulching in groundnut. Summer 18/2/20 14 EF Importance of soil & water testing. 4/3/201 4 EF Micronutrient deficiencies in agronomical crops & its correction through soil test based fertilizers application. Horticulture 16/05/2 PF Preparaion to practice in 013 Turmeric 11/06/2 013 PF Dryland fruit production 21/06/2 013 RY Nursery Raising for Kharip vegetables 16/07/2 013 PF Marigold flower production 14/08/2 013 PF INM in cole crops 24/08/2 013 EF Nutritional care in Papaya and banana 10/10/2 013 RY 13/11/2 013 EF Pre and post harvest management in chilli, bhendi Bahar management in sweet orange 13/01/2 014 PF 23/01/2 014 PF Care of indoor and outdoor ornamental plants Vegetables growing under protected cultivation High tech agri. Soil and Water testing Soil and Water testing Manag ement of fertilize rs Fruit cultivati on Vegeta ble Cultivat ion Flower product ion Vegeta ble product ion Fruit product ion PHT in vegetab les Special horticul tural practice s Floricul ture Vegeta ble product ion o Agr o 2 ON Agr o 2 ON 13 0 13 3 0 3 16 0 16 Agr o 2 ON 16 0 16 4 0 4 20 0 20 31 0 281 15 29 6 52 8 60 333 23 356 Hor t 1 OFF 16 0 16 2 0 2 18 0 18 Hor t 2 OFF 15 0 15 2 0 2 17 0 17 Hor t 2 ON 12 0 12 5 0 5 17 0 17 Hor t 1 OFF 13 0 13 3 0 3 16 0 16 Hor t 2 OFF 15 0 15 4 0 4 19 0 19 Hor t 1 OFF 11 0 11 5 0 5 16 0 16 Hor t 1 ON 12 0 12 3 0 3 16 0 16 Hor t 2 ON 11 0 11 2 0 2 13 0 13 Hor t 2 ON 0 15 15 0 2 2 0 17 17 Hor t 2 ON 16 0 16 3 0 3 19 0 19 121 15 13 6 29 2 31 151 17 168 16 Plant Protection 17/05/2 PF Seed treatment in 013 soybean 08/06/2 PF Importance of seed 013 treatment in paddy and management of nursery pest 09/07/2 PF Management of leaf 013 defoliators in soybean 13/08/2 PF IPM in cotton 013 14/08/2 EF Management of sucking IPM/ID M IPM/ID M 16 0 16 4 0 4 20 0 20 P.P. 1 OFF 12 0 12 4 0 4 16 0 16 P.P. 1 OFF 20 0 20 3 0 3 23 0 23 IPM P.P. 1 ON 18 0 18 6 0 6 24 0 24 IPM P.P. 1 ON 14 0 14 3 0 3 17 0 17 IPM P.P. 1 ON 14 0 14 0 0 0 14 0 14 013 17/08/2 013 RY 06/09/2 013 21/09/2 013 01/10/2 013 30/10/2 013 PF EF PF EF 17/12/2 013 RY 21/01/2 014 PF pest in cotton, and leaf defoliators in soybean Preparation of 5 % Neem Seed Kernel Extract for the management of different pest and diseases IPM in paddy and soybean Management of pest in tur and Bengal gram Importance of seed treatment in rabi crops Pest management in pigeon pea and Bengal gram Different techniques of biological pest management Integrated pest management in ground nut IDM IPM IDM P.P. 1 ON 17 0 17 0 0 0 17 0 17 IPM P.P. 1 OFF 15 0 15 4 0 4 19 0 19 IPM IDM IPM IDM IPM IDM P.P. 1 ON 18 0 18 0 0 0 18 0 18 P.P. 1 ON 16 0 16 2 0 2 16 2 18 P.P. 1 ON 11 0 11 2 0 2 11 2 13 IPM IDM P.P. 1 ON 0 14 14 0 6 6 0 20 20 IPM P.P. 1 OFF 13 0 13 4 0 4 17 0 17 168 14 18 2 28 12 Agricultural Engineering 20/05/2 EF Watershed planning and 013 Management 05/06/2 013 PF Rainwater harvesting and drip irrigation 12/06/2 013 PF Repair and maintenance of Seed cum ferti drill 06/07/2 013 PF In-situ soil and water conservation in cotton 21/08/2 013 PF In-situ soil and water conservation in Soybean 23/08/2 013 PF Repair and maintenance of power weeder 15/10/2 013 PF Repair and maintenance of Rotavetor Capacit y building Installat ion of micro irrigatio n system Repair and mainte nance of farm machin ery Installat ion of micro irrigatio n system Installat ion of micro irrigatio n system Repair and mainte nance of farm machin ery Repair and mainte nance of farm machin 6 34 192 24 216 Ag. En gg. Ag. En gg. 1 ON 15 1 16 2 0 2 17 1 18 1 OFF 19 0 19 3 0 3 22 0 22 Ag. En gg. 1 OFF 30 0 30 2 0 2 32 0 32 Ag. En gg. 1 OFF 13 0 13 3 0 3 16 0 16 Ag. En gg. 1 OFF 13 0 13 2 0 2 15 0 15 Ag. En gg. 1 ON 14 0 14 4 0 4 18 0 18 Ag. En gg. 1 ON 14 0 14 2 0 2 16 0 16 18/10/2 013 PF Repair and maintenance of Boom sprayer 2122/11/1 3 11/12/2 013 RY Mini dal mill RY Mini dal mill 17/01/2 013 PF Repair and maintenance of drip irrigation syatem ery Repair and mainte nance of farm machin ery Value additio n Value additio n Installat ion and mainte nance of micro irrigatio n systems Ag. En gg. 1 ON 22 0 22 3 0 3 25 0 25 Ag. En gg. Ag. En gg. Ag. En gg. 2 ON 29 3 32 7 0 7 36 3 39 1 ON 9 9 18 2 2 4 11 11 22 1 ON 13 0 13 5 0 5 18 0 18 191 13 20 4 35 2 37 226 15 241 12 Home Science 05/04/2 RY Anemia in girls 013 21/05/2 013 PF Soyabean processing 10-1112/06/1 3 PF Fruits processing 24-2526/06/1 3 PF Vegetable processing to control the losses 03/07/2 013 PF Use of user friendly equip to reduce the drudgery 16/07/2 013 PF Care to be taken while cooking 25-2627/07/1 3 RY Decorative articles Women and child care Design and develop ment of low cost diet Income generat ion activity for empow erment of rural women Minimiz ation of nutrien ts losses in process ing Locatio n specific drudger y reducin g tech. Minimiz ation of nutrien t losses Rural crafts Ho me Sc. 1 ON 0 0 0 0 16 16 0 16 16 Ho me Sc. 1 OFF 0 0 0 0 15 15 0 15 15 Ho me Sc. 3 ON 0 3 3 1 19 20 1 22 23 Ho me Sc. 3 ON 0 17 17 0 12 12 0 29 29 Ho me Sc. 1 OFF 0 6 6 0 25 25 0 31 31 Ho me Sc. 1 OFF 0 13 13 0 2 2 0 15 15 Ho me Sc. 3 ON 0 10 10 0 19 19 0 29 29 12-1314/08/1 3 PF Food processing for food and nutrients 16/08/2 013 PF Fuel saving divices in kitchen 06/09/2 013 PF Store grain problems at house hold level 2021/09/1 3 EF Care and development of preschool children 1415/10/1 3 2627/11/1 3 14/12/2 013 PF Value addition through amla processing RY Masala processing for entrepreneurship development Importance of food processing and masala processing Care and development of preschool children RY 09/01/2 014 EF 14/02/2 014 PF Tomato Processing Design and develop ment of high nutrien ts efficien cy diet Locatio n specific drudger y reducti on tech Storage loss minimiz ation tech. Women and child care Value additio n Value additio n Value additio n Women and child care Value additio n Ho me Sc. 3 ON 0 11 11 0 13 13 0 24 24 Ho me Sc. 1 OFF 0 3 3 0 12 12 0 15 15 Ho me Sc. 1 OFF 0 5 5 0 13 13 0 18 18 Ho me Sc. 2 ON 0 17 17 0 13 13 0 30 30 Ho me Sc. Ho me Sc. Ho me Sc. Ho me Sc. 2 ON 0 12 12 0 15 15 0 27 27 2 ON 0 0 0 0 20 20 0 20 20 1 ON 0 4 4 0 15 15 0 19 19 1 ON 0 2 2 0 21 21 0 23 23 Ho me Sc. 1 OFF 0 9 9 0 6 0 15 15 112 11 2 348 349 27 Veterinary Science 18/04/2 RY introduction of 013 Osmanabadi goat farming 23/05/2 PF Integrated Endo 013 Ectoparasitic Management In Livestock 20/06/2 PF Prevention of bacterial 013 diseases occurring during monsoon 25/06/2 PF Care and management 013 of milch animals 21/08/2 013 PF First Aid In Snake Bite In Animals 23/08/2 013 PF 15/08/2 013 PF Importance of mineral mixture in milch animals. Selection criteria for bullock purchasing. 04/09/2 PF Clean milk production. 0 1 6 236 237 1 Animal manage ment Disease Manag ement Vet . Sci. Vet . Sci. 1 OFF 13 0 13 5 0 5 18 0 1 8 1 OFF 14 0 14 3 0 3 17 0 1 7 Disease Manag ement Dairy manage ment Disease manage ment Dairy manage ment Animal manage ment Dairy Vet . Sci. Vet . Sci. Vet . Sci. Vet . Sci. Vet . Sci. Vet 1 OFF 10 0 10 8 0 8 18 0 1 8 2 ON 18 0 18 3 0 3 21 0 2 1 1 OFF 20 0 20 3 0 3 23 0 2 3 1 OFF 15 0 15 6 0 6 21 0 2 1 1 OFF 17 0 17 2 0 2 19 0 1 9 1 OFF 11 0 11 4 0 4 15 0 1 013 19/09/2 013 RY Clean milk production. 23/09/2 013 RY Typical characters of high yielding animals 24/10/2 013 PF 20/11/2 013 PF 23/11/2 013 EF Management and production of Green fodder round the year. Care and management of dairy animals during winter season Urea treatment to straw 24/11/2 013 PF Managenent of fodder round the year 29/11/2 013 PF Management of Reproductive disorders 11/12/2 013 PF 11/12/2 013 RY Integrated endo and ecto parasitic management in livestock. Importance of deworming in animals for their good health. manage ment Dairy manage ment Dairy manage ment Dairy manage ment Dairy manage ment Dairy manage ment Dairy manage ment Disease manage ment Disease manage ment . Sci. Vet . Sci. Vet . Sci. Vet . Sci. Vet . Sci. Vet . Sci. Vet . Sci. Vet . Sci. Vet . Sci. Disease manage ment Vet . Sci. 5 3 ON 19 0 19 3 0 3 22 0 2 2 1 OFF 44 0 44 13 0 13 57 0 5 7 2 ON 30 0 30 15 0 15 45 0 4 5 1 OFF 7 10 17 0 2 2 7 12 1 9 2 ON 18 0 18 2 0 2 20 0 2 0 3 ON 11 0 11 7 0 7 18 0 1 8 2 ON 82 0 82 35 0 35 117 0 1 OFF 12 0 12 5 0 5 17 0 1 1 7 1 7 1 OFF 12 0 12 5 0 5 17 0 1 7 121 7 143 13 60 30 6 248 569 432 1 9 1 4 86 1482 (D) Vocational training programmes for Rural Youth Crop / Enterpris e Date Training title* Thematic Area Durati on (days) No. of Participants Male Female *training title should specify the major technology /skill transferred Total Self employed after training Type Number Number of of of units persons units employed Number of persons employed else where (E) Sponsored Training Programmes Sr. No Date 1 9/4/2013 2 16/4/2013 3 4 1718/4/2013 2327/4/2013 5 2527/4/2013 6 2628/6/2013 7 8 9 2630/11/2013 4/12/2013 5-7/12/2013 Title Dist level Study tour Programme Dist Level Training Programme State Level Training Programme State Level Study Tour Programme Pre & post harvest management and marketing in pulses ( MACP project ) Pre & post harvest measures and marketing in soybean (MACP Project) Dry land farming Staff Training. Pulse crop management Dry land farming No. of Participants SC/ST Fe Male ma Total le Thematic area Du rati on (da ys) Clien t (PF/ RY/E F) No. of cours es M ale Fema le To tal NHM -- 1 pf 60 0 60 0 0 0 0 60 0 NHM -- 1 pf 100 0 100 0 0 0 0 100 NHM -- 2 PF 25 0 25 0 0 0 0 NHM -- 5 PF 72 0 72 0 0 0 Agro. ICM Marketing 3 PF 20 0 20 5 0 Agro ICM Marketing 3 15 0 15 5 0 Discipli ne Agrono my Plant protecti on Horticul ture Agrono my Plant protecti on Agrono my Plant protecti on Horticul ture Others Sponsor ing Agency Amoun t of fund receive d (Rs.) 60 NHM 15000 0 100 NHM 40000 25 0 25 NHM 18750 0 72 0 72 NHM 108207 5 25 0 25 MACP 30000 5 20 0 20 MACP 30000 30000 Total Fe Tota Male ma l le Dry land farming 5 EF 20 11 0 11 5 0 5 16 0 16 State Agril. Departm ent ICM 1 PF 5 9 0 9 2 0 2 11 0 11 ALC India Ltd 2750 Dryland Agri 3 PF 15 19 0 19 6 0 6 25 0 25 State Agril. Departm ent 30020 I 10 9/12/2013 IPM in Pigeon pea 11 11/12/2013 IPM in Pigeon pea 12 13 14 15 12/12/2013 19 Plant protecti on Agrono my Plant protecti on Horticul ture 1 PF 2 26 0 26 3 0 3 29 0 29 ATMA 35200 IPM 1 PF 2 10 0 10 2 0 2 12 0 12 ATMA 16800 IPM 1 PF 2 41 0 41 5 0 5 46 0 46 ATMA 18000 Dry land farming 3 PF 15 34 0 34 6 0 6 40 0 40 State Agril. Departm ent 43200 16 0 16 4 0 4 20 0 20 ATMA 19200 20 MACP 50000 Dry land farming 17/12/201 3 Mulching in Summer groundnut. Agoron omy High tech agri. 1 1821/3/2014 Pre & Post Harvest Management in Cotton Agrono my PHT 3 20 0 20 0 0 0 0 0 0 Trials of Sweet Sorghum Agrono my -- - - - - - - - - - - -- -- -- 25020 Horticul ture PHT 7 Pf 7 20 0 25 0 0 0 20 0 20 MACP 70000 Horticul ture Vegetable Production 1 PF 1 35 - 35 10 - 10 45 - 45 TAO and ATMA Mukhed 18000 Home sceince Income generation activity for empower ment of rural women 07 RY 17 00 17 10 03 13 27 03 30 MACP 70002 Kharif 2013 18 Plant protecti on IPM 1214/12/2013 16 17 IPM in Bengal gram Plant protecti on 1723/6/2013 13-12-2013 15-21/04/13 Total Pre &Post Harvest Management in Vegitable Watermelon production technology Soybean processing and marketing 670149 3.4. Extension Activities (including activities of FLD programmes) Nature of Extension Activity Date Title/topic No. of activitie s Farmers (Others) I Male Fema Total le Participants SC/ST (Farmers) Extension Officials II III Mal Fema Total Male Fe Total e le mal e Field Day 1 23/08/2013 Sweet sorghum as fodder crop 1 62 0 62 12 0 12 4 0 4 2 27/08/2013 1 35 0 35 6 0 6 3 0 3 3 28/08/2013 Green gram production technology (Utkarsh) Field day on Green gram (Moong) 1 35 0 35 9 0 9 4 0 4 4 03/09/2013 Field day on Bottle gourd 1 16 0 16 3 0 3 0 0 0 5 20/09/2013 1 30 0 32 7 0 7 3 0 3 6 21/09/2013 Soybean varietal evaluation (MAUS-71) Field day on Soybean 1 22 0 22 8 0 8 5 0 5 7 25/09/2013 2 28 5 28 13 1 13 5 0 5 8 9 12/11/2013 30/12/2013 1 2 0 28 14 5 14 28 0 13 1 1 1 13 0 5 1 0 10 11/01/2014 1 76 0 76 17 0 17 4 11 11/01/2014 Better forage yield Mineral mixture for increase milk production Smoke less Chula Better forage yield Mineral mixture for increase milk production Pigeon pea production technology (Vipula) Field day on pigeonpea 1 69 0 69 16 0 16 12 22/01/2014 Field day on Tomato Staking 1 22 0 22 5 0 13 24/01/2014 Bengal gram production technology (Jaki-9218) 1 42 0 42 10 0 I Grand Total (I+II+III) M Fem Total al ale e 7 8 4 4 4 8 1 9 4 2 3 6 4 6 0 78 0 44 0 48 0 19 0 42 0 36 6 46 1 5 0 4 6 16 6 16 46 0 4 0 97 3 0 3 0 85 5 0 0 0 0 27 10 4 0 4 9 7 8 5 2 7 5 6 0 56 14 24/01/2014 Field day on Bengal gram 1 16 Kisan Mela 1 42 507 0 42 10 0 10 4 0 4 5 6 0 56 24 523 129 3 130 44 1 45 6 8 0 28 696 2829/12/2013 Technology week 1 2938 2006 4844 1190 465 1655 22 4 26 1 10/08/2013 1 26 0 26 8 0 8 2 0 2 2 16/08/2013 1 66 0 66 16 0 16 2 0 2 3 16/08/2013 1 10 0 10 0 0 0 2 0 2 4 16/08/2013 1 43 0 43 11 0 11 8 0 8 5 16/08/2013 1 43 0 43 11 0 11 8 0 8 6 21/08/2013 1 10 0 10 1 0 1 3 0 3 7 22/08/2013 1 11 0 11 2 0 2 4 0 4 8 12/10/2013 1 16 0 16 5 0 5 5 0 5 9 12/10/2013 1 16 0 16 5 0 5 5 0 5 2 6 0 26 10 19/12/2013 Seed production for rabi sorghum at Marvali Rabi Sorghum Seed production at atkali Rabi Sorghum Seed production at Takali Rabi Sorghum Seed production at Sagroli Seed production for rabi sorghum at Sagroli Rabi Sorghum Seed production at Sagroli Rabi Sorghum Seed production at atkali Bengal gram production technology and importance of soil testing at sangvi IPM in Bengal gram, tur and cotton also discussion on current pest situation Sangvi tq-Degloor Technology Mohasav 1 55 0 55 12 0 12 0 0 0 0 67 11 23/12/2013 Technology Mohasav 1 42 0 42 6 0 6 0 0 0 0 48 12 24/12/2013 Technology Mohasav 1 49 0 49 13 0 13 0 0 0 6 7 4 8 6 2 0 62 13 13/5/13, 16/5/13, Disease management in poultry,vaccination of broiler 7 47 5 52 33 3 36 5 0 5 9 0 8 98 415 0 2 4 7 5 6525 Kisan Ghosthi 3 6 8 4 1 2 6 2 6 2 1 4 1 7 2 6 0 36 0 84 0 12 0 62 0 62 0 14 0 17 0 26 14 5/6/13, 14/6/13, 12/7/13, 29/7/13, 15/10/13 22-2-14 birds,routine management of dairy animals care and management of newborncalf,care of parturated animals ,prevention of bacterial diseases of bovines Inaugural programme of Turmeric Steamer developed by Shivaji Supare son of Dhondu Supare Progressive farmer at Takalgaon 1 0 36 11 0 11 6 1 7 53 1 54 36 20 434 41 450 123 14 132 45 7 97 6 0 7 62 650 1 1 3 9 5 1 114 0 95 Exhibition 4-5/05/2013 Mahadev Kathi Yatra Sagroli 1 81 0 81 27 0 27 5 1 6 1112/05/2013 Muktai Pratistan and panchayat sameeti Degloor sponcered farmers mela Dhanya mahotsav at Biloli 1 80 0 80 11 0 11 4 0 4 1 880 0 880 370 0 370 1 0 1 1 2 5 0 0 1251 Food processing , fashion designing and arts and crafts TECHNICAL mahotsv, KVK 1 10 25 35 15 15 30 0 3 3 43 68 1 3500 1000 4500 1200 500 1700 25 12 27 2 5 4 7 2 5 1522 6247 1025 5576 04/06/2013 09/08/2013 28/12/2013 5 4551 162 3 515 2138 35 16 41 Film Show 1 17/05/2013 Smole less chula 1 3 3 6 6 22 28 2 1 3 2 17/08/2013 Bt cotton production tech at Atkali 1 55 0 55 8 0 8 2 0 2 6 2 0 8 156 6 7775 1 1 6 5 26 37 0 65 3 12/11/2013 Farm machination 1 12 0 12 3 0 3 0 0 0 1 5 0 15 4 08/12/2013 Senderia sati at Babali 1 13 0 13 7 0 7 3 0 3 0 23 5 08/12/2013 IPM of rabi crops 1 13 0 13 7 0 7 3 0 3 2 3 2 3 0 23 6 13/12/2013 Agricultural processing machineries 1 11 0 11 3 0 3 0 0 0 0 14 7 13/12/2013 Back Yard Poultry Farming 1 12 1 13 7 0 7 0 0 0 1 20 8 08/01/2014 Dary Business And Fodder Management 1 17 0 17 7 0 7 0 0 0 1 4 1 9 2 7 0 24 9 7/3/2014 1 22 0 22 7 0 7 2 0 2 3 1 0 31 10 9/3/2014 1 28 0 28 4 0 4 2 0 2 3 4 0 34 11 15/3/2014 1 25 0 25 9 0 9 2 0 2 3 6 0 36 12 21/3/2014 1 20 0 20 8 0 8 2 0 2 3 0 0 30 13 22/3/2014 1 37 0 37 2 0 2 2 0 2 4 1 0 41 14 25/2/14 1 31 0 31 17 0 17 3 0 3 5 1 0 51 15 5/3/14 Dairy Management, Goat farming, Deshi broiler farming, buffalo farming Dairy Management, Goat farming, Deshi broiler farming, buffalo farming Dairy Management, Goat farming, Deshi broiler farming, buffalo farming Dairy Management, Goat farming, Deshi broiler farming, buffalo farming Dairy Management, Goat farming, Deshi broiler farming, buffalo farming Integrated Pest Management in Vegetable at Laghul Improved farm implements 1 0 0 0 0 46 46 2 2 4 2 48 50 15 299 4 303 95 163 25 3 28 4 2 2 75 494 1 23 0 23 7 0 7 2 0 2 3 2 0 32 1 11 0 11 2 0 2 1 0 1 1 4 0 14 1 23 0 23 7 0 7 2 0 2 3 0 32 Method Demonstrations 08/06/2013 1 2 12/06/2013 Seed treatment in Green gram Moong Use of Seed cum fertilizer drill 3 15/06/2013 Seed treatment in Red gram Tur 68 2 Soya products Groundnut decorticator 1 4 2 1 6 23 8 24 0 2 0 7 0 9 0 1 1 4 1 5 2 4 7 34 9 38 6 15/06/2013 20,21,22,28/ 06/2013 01/08/2013 Use of boom sprayer for soybean 1 8 0 8 2 0 2 3 0 3 0 13 7 24/08/2013 Nutritious recipes for preschool children 2 9 19 28 0 0 0 1 2 3 21 31 8 23/09/2013 Different types of sickles 1 11 0 11 0 0 0 1 1 2 1 13 9 17/10/2013 1 6 0 6 2 0 2 0 0 0 0 8 10 16/11/2013 Use of Reaper for harvesting soybean Use of Reaper for harvesting Paddy 1 3 1 0 1 2 8 1 8 0 8 2 0 2 0 0 0 0 10 11 12 13 21/12/2013 03/02/2014 7/3/2014 1 1 0 0 4 4 4 4 0 0 6 3 6 3 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 8 0 8 14 9/3/2014 15 15/3/2014 16 21/3/2014 17 22/3/2014 Dal mill, Utkarsh project Coconut Processing Urea treatment to straw, Azola production, Preparation of wormi compost, Management of Slurry Urea treatment to straw, Azola production, Preparation of wormi compost, Management of Slurry Urea treatment to straw, Azola production, Preparation of wormi compost, Management of Slurry Urea treatment to straw, Azola production, Preparation of wormi compost, Management of Slurry Urea treatment to straw, Azola production, Preparation of wormi compost, Management of Slurry 4 5 1 0 0 0 1 22 0 22 7 0 7 2 0 2 3 1 0 31 1 28 0 28 4 0 4 2 0 2 3 4 0 34 1 25 0 25 9 0 9 2 0 2 3 6 0 36 1 20 0 20 8 0 8 2 0 2 3 0 0 30 1 37 0 37 2 0 2 2 0 2 4 1 0 41 21 234 56 290 54 16 70 21 9 30 3 0 9 71 380 4 0 0 7 166 566 Farmers Seminar 04/06/2013 KIsan Mela Biloli 1 320 110 430 65 48 113 15 8 05/06/2013 KIsan Mela Degloor 1 560 20 580 150 25 175 12 2 23 14 57 779 06/06/2013 Kisan Mela Unri 1 350 50 400 45 15 60 9 1 01/07/2013 Participated in krishi Bhushan programme of Nanded district at Nanded Bhokar 1 573 0 573 180 0 180 3 0 3 1 28 0 28 6 0 6 2 0 2 KVK 1 30 0 30 4 0 4 3 0 3 1861 180 2041 04/07/2z01 3 05/07/2013 6 Group meeting 10/05/2013 1 450 88 538 44 11 10 55 Formation of farmers group for NABARD at Kedarwadgaon 1 27 0 27 2 0 2 7 0 7 2 14/05/2013 Formation of farmers group for NABARD at Bolegaon 1 17 0 17 2 0 2 3 0 3 3 15/05/2013 Formation of farmers group for NABARD at Daulatpur 1 14 0 14 2 0 2 3 0 3 4 15/05/2013 Formation of farmers group for NABARD at Shimpala 1 7 0 7 1 0 1 3 0 3 5 13/6/13 Formation of groups at Bolegaon 1 20 0 20 0 0 0 0 0 0 6 13/07/13, 18/07/13, 20/07/13 Snails problem in soybean, green gram crop at Kedarwadgaon ,Sawali, Chainpur 3 54 0 54 13 0 13 6 0 6 7 13/08/2013 Current pest and disease situation of soybean and cotton at Shimpala 1 11 0 11 1 0 1 2 0 2 8 19/08/2013 Rabi Sorghum Seed production 1 9 0 9 1 0 1 10 1 11 9 10/08/2013 Kharif crops weed and Nutrient management 1 26 0 26 8 0 8 2 0 2 2 2 4 0 4 7 5 6 3 6 3 7 2 3 5 5 66 470 0 756 0 36 0 37 289 2644 3 6 2 2 1 9 1 1 2 0 7 3 0 36 0 22 0 19 0 11 0 20 0 73 1 4 2 0 3 6 0 14 1 21 0 36 10 29/08/2013 Cotton and soybean crop Nutrient and weed management at Chandola Bengal gram production technology at Krushnoor 1 30 0 30 8 0 8 8 0 8 4 6 0 46 11 24/09/2013 1 15 0 15 7 0 7 3 0 3 0 25 14/09/2013 Current pest and disease situation of soybean and cotton at Atkali 1 15 0 15 7 0 7 3 0 3 0 25 13 19/09/2013 1 10 0 10 3 0 3 4 0 4 0 17 14 24/09/2013 1 16 0 16 3 0 3 3 0 3 2 2 0 22 15 10/10/2013 Current pest and disease situation in cotton-soybean and tur.at Kathewadi Pest and disease management in cotton and tur and fertilizer management in tur at Krushnur Current pest and disease situation of Tur and cotton at Shimpala 2 5 2 5 1 7 12 1 11 0 11 3 0 3 3 0 3 0 17 16 15/10/2013 1 6 0 6 5 0 5 3 0 3 0 14 17 19/12/2013 Current pest and disease situation in cotton-tur and sugancane at Lath Biloli Block 1 7 1 4 1 13 3 16 4 2 6 2 0 5 24 18 21/12/2013 Naigaon Block 1 14 2 16 2 5 5 2 0 7 25 19 23/12/2013 Dharmabad Block 1 11 4 15 4 4 6 2 0 8 25 20 10/05, 17/05, 31/05, 15/06, 9/07, 3/07, 10/08,14/0 9, 09/10, 10/12 Health, farm implements, entrepreneurship development 10 0 71 71 0 29 29 0 10 10 1 9 1 8 1 7 0 110 110 21 27/12/13, 3/1/14 Fodder management,clean milk production 2 32 3 35 8 4 12 0 0 0 4 0 7 47 22 8.02.14 vegetable pest management at Shimpala 1 16 0 16 4 0 4 1 0 1 2 1 0 21 23 21/2/2014 Fodder crops production 1 12 0 12 2 0 2 3 0 2 2 2 3 1 7 0 17 35 386 83 469 90 44 130 73 11 1 75 15 90 26 10 36 6 0 Soybean production technology,Plant proction measures in soybean, cotton at Degloor Soil testing Bt cotton production technology at Mahegaon 1 78 0 78 13 0 13 0 0 0 1 105 0 105 43 0 43 0 0 0 Lectures delivered as resource persons 11-12/5/13 IPM of kharif crops,Degloor 1 84 6 2 1112/05/2013 3 16/05/2013 4 24/05/2013 Bt cotton production technology, Plant proction measures in soybean,cotton at Naigaon 1 115 0 115 52 0 52 0 0 0 5 25/05/2013 Soil testing, Importance of soil and water conservation, Dairy Management at Degloor 1 378 0 378 79 0 79 0 0 0 6 26/05/2013 Bt cotton production technology, Plant proction measures in soybean,cotton at Dharma bad 1 790 0 790 191 0 191 0 0 0 7 26/05/2013 Bt cotton production technology at Dharmbad 1 852 25 877 112 299 411 32 50 82 8 26/05/2013 IPM of kharif crops Dhr’bad 1 959 0 959 411 0 411 1 0 1 9 28/05/2013 Bt cotton production technology at Kinwat 1 648 110 758 985 65 1050 32 10 42 10 01/06/2013 Bt cotton production technology at Mudkhed 1 1080 380 1460 148 72 220 12 10 22 5 4 9 138 687 1 0 1 9 1 25 126 0 91 1 4 8 1 6 7 4 5 7 9 8 1 9 9 6 1 3 7 1 1 6 6 5 1 2 4 0 0 148 0 167 0 457 0 981 374 1370 0 1371 185 1850 390 1630 11 04/06/2013 Bt cotton production technology At Biloli 1 703 135 838 258 112 370 20 22 42 12 04/06/2013 IPM of kharif crops Biloli 1 880 0 880 370 0 370 1 0 1 13 11/06/2013 IPM of kharif crops Mukhed 1 920 0 920 130 0 130 1 0 1 14 11/06/2013 Bt cotton production technology at Muked 1 700 182 882 108 22 130 20 18 38 15 18/06/2013 Vegetable pest management under MACP at KVK 1 13 0 13 7 0 7 1 0 1 16 29/06/2013 KVK Sagroli 1 15 0 15 5 0 5 1 0 1 17 05/07/2013 Kisan Din Weed Management in kharif crops 1 573 0 573 180 0 180 3 0 3 18 05/07/2013 KVK Sagroli 1 30 0 30 4 0 4 3 0 3 19 20/07/2013 SSM Crop Science Students 1 18 0 18 5 0 5 1 0 1 20 20/07/2013 Food and nutrition of school going children 1 34 - 34 49 - 49 2 1 21 17/10/2013 Bt cotton cultivation technology at Sonkhed 1 39 0 39 3 0 3 4 0 4 22 18.10.13 1 37 0 37 26 0 26 1 0 1 23 22.10.13 1 17 0 17 21 0 21 1 0 24 23/10/2013 Role of SHG, role of kvk and IPM of tur and Bengal gram under SSM’s IWMP at Lingapur Role of SHG, role of kvk and IPM of tur and Bengal gram under SSM’s IWMP at Bhatapur Watershed and Self help group 1 27 6 33 6 0 6 0 0 9 8 1 1 2 5 1 1 0 5 1 8 2 8 2 1 1 6 7 5 6 3 7 2 4 8 5 4 6 6 4 269 1250 0 1251 0 1051 222 1050 0 21 0 16 0 756 0 37 0 24 1 86 0 46 0 64 1 3 9 0 39 0 3 3 6 39 3 25 28/10/2013 Water shade management at Sangvi 1 24 0 24 3 0 3 0 0 0 26 29/10/2013 Water shade management at Ambulga 1 39 0 39 8 0 8 0 0 0 27 21/11/2013 1 30 4 34 5 0 5 0 0 0 28 26-30 Nov 13 Bt cotton cultivation technology/Wheat production technology at KVK Dry land mission E. F. training 1 9 0 9 3 0 3 0 0 0 29 03/12/2013 Watershed Management 1 23 0 23 12 0 12 0 0 0 30 04/12/2013 ALC India/Mini Dal mill 1 9 0 9 2 0 2 0 0 0 31 5 to 7-12-13 Dry land farmers Training 1 17 0 17 8 0 8 0 0 0 32 06/12/2013 1 14 0 14 6 0 6 1 0 1 33 12 to 14 -1213 Integrated pest management in Bengal gram, pigeon pea and cotton under ATMA at KVK Dry land farmer Training 1 33 0 33 8 0 8 0 0 0 34 17/12/2013 1 13 0 13 4 0 4 1 0 1 35 12.1.14 1 142 0 142 22 0 22 0 0 0 36 30.1.14 1 42 0 42 14 0 14 5 0 5 37 3.2.14 1 38 0 38 11 0 11 3 0 3 38 31/12/2013 Integrated pest management in Bengal gram, pigeon pea and cotton Summer crops ground nut soybean and sesamum pest management at karadkhed Importance of IPM in kharif and rabi crops at Daulatapur Apiculture as a side business in sustainable agriculture at kavtha Summer groundnut cultivation at Malegaon Yatra 1 580 65 645 85 12 97 0 0 0 39 12/01/2013 Summer crops cultivation-Summer groundnut,Sesamum, Soybean at Karadkhed 1 142 0 142 22 0 22 0 0 0 40 12/01/2014 Summer crops ground nut soybean and sesamum pest management at 1 142 0 142 22 0 22 0 0 0 2 7 4 7 3 9 0 27 0 47 0 39 1 2 3 5 1 1 2 5 2 1 0 12 0 35 0 11 0 25 0 21 4 1 1 8 0 41 0 18 1 6 4 6 1 5 2 0 164 0 61 0 52 6 6 5 1 6 4 1 6 77 742 0 164 0 164 41 27/01/2013 42 30/01/2014 43 30/01/2014 44 8/9/13,13/9 /13,19/9/13, 22/9/13,23/ 9/13 45 30/01/14 46 3/2/14 Newspaper coverage 11-18/06/13 1 2 11-18/06/13 3 25/06/2013 4 25-30/06/13 karadkhed Kharif and summer crops cultivation at Bilali 1 57 0 57 3 0 3 0 0 0 Soybean , Bengal gram cultivation and Capabilities building for farmers group at Daulatpur Importance of IPM in kharif and rabi crops at Daulatapur 1 42 0 42 14 0 14 0 0 0 1 42 0 42 14 0 14 5 0 5 Water management of animals ,care of animals during winter, mastitis and its prevention, annual vaccination of animals ,layers vaccination, clean milk production Cotton and soybean production technology organized by Krishi vibhag Biloli at Daulatapur Importance of soil and eater testing 5 112 18 130 20 5 25 0 0 0 1 47 0 47 11 0 11 5 0 5 1 38 0 38 11 0 11 3 0 3 50 10721 93 11661 354 0 17 4137 165 111 Broad bed furrow system of planting in soybean in Krushakonnati weekly Agro news letter Increasing productivity in dry land pigeon pea by seedlings transplanting in Krushakonnati weekly Agro news letter Nimboli as a important component in pest management Weekly Krushakonnati Important five aspects in increasing productivity in soybean crop at Krushakonnati weekly Agro news letter 1 1 1 1 276 4 6 0 5 6 0 60 0 56 0 61 23 155 6 3 0 63 5 2 1 4 4 1 9 0 52 157 2 15991 6 1 1 3 2 5 21/07/2013 6 23/07/2013 7 27/07/2013 8 27/07/2013 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 4/9/13 Sakal 11/9/13 Lokmat 12/9/13 Sakal 26/11/2013 10/12/2013 7-13/1/14 Weekly Krushkonnti 11-17.02.14 Weekly Krushkonnti 16/5/2013,1 0/11/13,11/ 10/13,19/9/ 13 9/3/14 KVK Sagroli and ICRISAT working together in Sakal News paper Heavy snail infestation on soyabean in Daily Sakal Field day celebration at atkali on Green gram Field day celebration at atkali on Green gram in sakal Field day celebration at atkali on Bengal gram in sakal Field day celebration at Kedarwadgaon on Pigeon pea in sakal Field day at atkali Mexician beetle 1 Rabi sorghum seed production 1 Mini dal mill Watershed management/ Daily Sakal Ase kara wangyavaril kideenche niyantran 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 3 1 1 Sheteela purak VyavasayaMadhumaksheeka palan 01 Urea chi kimaya bhari nikrushta chara utkrishta kari,bhaktapur yethe shetkari mela ,shwan danshachi jakham panya khale dhuva ,pola sajarakara paramparik pan adunuk padhatine 4 रक्तक्षय व सोया पोहा लाडू – 1 कृशीकोन्नती 24 Radio talks 1 2 14/06/2013 14/06/2013 Bt cotton production technology Soybean production technology 1 1 3 4 14/06/2013 14/06/2013 5 14/06/2013 6 7 01/06/2013 01/06/2013 8 16/5/13 9 19/5/13 10 11 12 28/5/13 20/10/13 23/10/13 13 7/3/2014 14 7/3/2014 1 5/11/13, 2 7/11/13 Organic farming Sucking pest management in cotton Nanded Akashwani Nimboli as a important component in pest management In-situ soil and water 1.Raktkshayatil aahar margdarshan 2.shalkari mulancha aahar v aarogya Care and Management of animals during winter Importance of loose housing system indairy management Importance oc deshi cow Selection of dairy animals importance of colostrums 6)care and management of parturated animals Crop damages due to hailstorm and contingencies to be taken Soil and water testing through mobile soil testing van by KVK sagroli 1 2 Care and Management of animals during winter Importance of loose housing system indairy management 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 TV Talks 1 2 Advisory Services 181 Scientific visit to farmers field 41 984596 200 0 200 44 0 44 32 1 33 2 7 6 1 277 Farmers visit to KVK 50 207 15 222 76 0 76 8 0 8 2 8 8 0 288 Farmer Scientist interaction 7/3/2014 9/3/2014 15/3/2014 21/3/2014 22/3/2014 Dairy farming, Management of Milch animals, Importance of Vaccination, Feeding management of dairy animals Dairy farming, Management of Milch animals, Importance of Vaccination, Feeding management of dairy animals Dairy farming, Management of Milch animals, Importance of Vaccination, Feeding management of dairy animals Dairy farming, Management of Milch animals, Importance of Vaccination, Feeding management of dairy animals Dairy farming, Management of Milch animals, Importance of Vaccination, Feeding management of dairy animals 1 22 0 22 7 0 7 2 0 2 3 1 0 31 1 28 0 28 4 0 4 2 0 2 3 4 0 34 1 25 0 25 9 0 9 2 0 2 3 6 0 36 1 20 0 20 8 0 8 2 0 2 3 0 0 30 1 37 0 37 2 0 2 2 0 2 4 1 0 41 5 132 0 132 30 0 30 10 0 10 1 7 2 0 172 Diagnostic visits 10/08/2013 10/08/2013 10/08/2013 16/08/2013 24/09/2013 Weed infestation in Soybean crop Micronutrient deficiencies in Bt cotton Weed infestation in Cotton crop Yellowing in Cotton and soybean crop 1 1 2 2 0 0 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 3 0 0 2 3 4 5 0 0 4 5 1 1 2 6 0 0 2 6 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 4 0 0 2 4 0 0 4 10 Yellowing in Moong Reddening in cotton 1 1 2 2 0 0 2 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 2 0 0 2 2 4 1 0 4 4 0 0 4 4 03/09/2013 18/07/2013 Sucking pest management in cotton Sawli 20/07/2013 23/06/2013 Chainpur Rainwater harvesting 1 18 0 18 0 0 0 0 0 0 10/07/2013 De silting of Dam 1 130 0 130 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 2 0 2 0 0 0 1 0 1 3 0 3 2 44 0 44 13 0 13 2 0 2 5 9 0 59 1 8 1 3 0 0 18 0 130 17.2.14 18.02.14 7/3/2014 Sagroli shimpala 02 6 0 6 2 0 2 4 0 4 1 2 0 12 Hailstorm affected villages visit 10 118 0 118 42 0 42 3 0 3 0 163 28/3/2014 Micronutrient deficiencies management in summer groundnut 1 0 1 0 0 0 2 0 2 1 6 3 3 0 3 1 15 273 0 273 44 0 44 9 0 9 3 2 6 0 326 Exposure visits 2327/4/2013 Jain hills Jalgaon Dr.PDVK Akloa 1 38 0 38 27 0 27 3 0 3 18/04/2013 Pomegranate bag Udgir 1 18 0 18 5 0 5 2 0 2 09/04/2013 Polyhouse at Pimplgaon 1 42 0 42 16 0 16 2 0 2 23-27/4/13 Jalgaon and Dr. PDKV, Akola 1 38 0 38 27 0 27 3 0 3 09/04/2013 Vist to polyhouse and shed net at Pimpalgaon 1 42 0 42 16 0 16 2 0 2 18/04/2013 Visit to Pomegrante plantation at Udgir 1 18 0 18 5 0 5 2 0 2 06/09/2013 28-29 sept 13 Low cost Solar fencing Tech for Seva workshop 0 0 4 1 0 0 4 1 2 0 0 0 2 0 2 1 0 0 2 1 6 8 2 5 6 0 6 8 6 0 2 5 8 2 0 68 0 25 0 60 0 68 0 60 0 25 0 0 8 2 6 201 0 201 98 0 98 17 0 17 3 1 6 0 316 Soil health Camp 15/05/13, 10/07/13, 20/07/13, 7/09/13, 11/12/13, 16/12/13, 24/12/13 Entrepreneurship development 7 0 70 70 0 28 28 0 7 7 0 105 105 1 8 3 1 3 7 2 1 7 5 3 7 0 183 0 137 0 217 Soil test campaigns 01/04/2013 Adampur,Khatgaon 1 132 0 132 51 0 51 0 0 0 11/05/2013 Atkali,Wanali,Degloor 1 101 0 101 36 0 36 0 0 0 04/06/2013 Biloli,Sawali 1 164 0 164 53 0 53 0 0 0 3 397 0 397 140 0 140 0 0 0 0 537 Farm Science Club Conveners meet 22/06/2013 Farm science club meeting 1 20 0 20 0 0 0 0 0 0 2 0 0 20 2 0 25 25 0 3 3 0 2 2 0 30 30 1 0 1 2 0 101 163 410 Mahila Mandals Conveners meetings 4/7, 3/9 Ground nut decorticator, training needs of women Celebration of important days (specify) (26-31 Aug 2013) Parthenium awareness week celebration 1 82 0 82 13 0 13 6 0 6 20/10/2013 Health check up camp for elderly 1 97 88 185 150 75 225 0 0 0 population on the occasion of world senior citizen day 16/10/2013 08/02/2014 World food day Sagroli Food festival 1 1 4 Total 0 0 179 12 0 100 12 0 279 0 0 163 15 0 90 15 0 253 1 0 7 2 0 2 3 0 9 4 7 1 0 3 4 9 472 Categor y Crop/ enterpri se Thematic Area Date Name of the message No. of Messa ges No.of Farmers Other s Mal e Agronom y Crops Cotton ICM 9/4/2 013 बागायती बी.टी. कपाशी मध्ये अवास्तव वाढ थाांबवण्यासाठी Fe mal e SC/ST Tot al Ma le Fema le Total Tot al M ale Fe m ale Total 1 12607 3 60217 3 12607 3 60217 वाढ निरोधक म्हणूि सायकोसील (ललवोसीि) ६० पी.पी.एम.(१.२ लमली /१० लल.पाणी) ७५ दिवसाांिी फवारणी करावी ककां वा ७० ते ७५ दिवसाांिी शेंडा खुडावा - ववषय ववशेषज्ञ – वपकशास्र, के.व्ही.के, सगरोळी Agronom y Agronom y Agronom y Crops Crops Crops Cotton Cotton Cotton ICM ICM ICM 9/4/2 013, 9/7/2 013, 9/11/ 2013 बी.टी. कपाशीतील िैसर्गिक कारणामुळे होणारी पाते, फुले, 9/4/2 013, 9/5/2 013, 9/8/2 013 9/4/2 013 9/4/2 013 9/11/ 2013 बागायती बी.टी. कपाशी मध्ये अवास्तव वाढ थाांबवण्यासाठी बोंडे, याची गळ कमी करण्यासाठी एि.ए.ए. (प्लिोकिस) या सांजीवकाची ४० लमली प्रती एकर २०० लल.पाण्यातूि पात्या लागल्या तेव्हा पदहली फवारणी व त्यािांतर १५ ते २० दिवसाांिी िस ु री फवारणी करावी..ववषय ववशेषज्ञ – वपकशास्र, के.व्ही.के, सगरोळी वाढ निरोधक म्हणूि सायकोसील (ललवोसीि) ६० पी.पी.एम.(१.२ लमली /१० लल.पाणी) ७५ दिवसाांिी फवारणी करावी ककां वा ७० ते ७५ दिवसाांिी शेंडा खुडावा - ववषय ववशेषज्ञ – वपकशास्र, के.व्ही.के, सगरोळी बी.टी. कपाशीतील िैसर्गिक कारणामुळे होणारी पाते, फुले, बोंडे, याची गळ कमी करण्यासाठी एि.ए.ए. (प्लिोकिस) या सांजीवकाची ४० लमली प्रती एकर २०० लल.पाण्यातूि पात्या लागल्या तेव्हा पदहली फवारणी व त्यािांतर १५ ते २० दिवसाांिी िस ु री फवारणी करावी..ववषय ववशेषज्ञ – वपकशास्र, के.व्ही.के, सगरोळी 30 1500 2041 53454 Kisan Mobile Advisory Services Major Group 29 0 192 Agronom y Agronom y Crops Crops Rabi sorghum Cotton Varietal evaluation ICM 9/11/ 2013, 9/13/ 2013, 9/14/ 2013, 9/16/ 2013, 9/18/ 2013 9/12/ 2013, 9/13/ 2013 रब्बी ज्वारी लागवडीसाठी डुकरी/िगडी वािाचा वापर ि करता 5 33005 2 17543 2 19529 2 15465 5 24500 सुधाररत अर्धक उत्पािि िे णारे परभणी मोती ,परभणी ज्योती, अकोला क्ाांती ,फुले र्चरा ,फुले वसुधा ई. वािाचा वापर करावा …। ववषय तद्य -कृषी ववद्या, के .वी .के. सगरोळी, जज िाांिेड बी. टी. कपासीमध्ये वखराचा साहयािे लाकडी पट्टी ककवा पोते बाांधूि कपसीचा ओळीस माती चढूि घावी त्यामुळे मुलस्थािी जलसांधारण होते तचेस सरयाांचा वापर सांरक्षित पाणी िे ियासाठी होईल. प्रा. कवपल इांगळे ,ववषय ववशेषज्ञ – वपकशास्र, के.व्ही.के, सगरोळी. जज . िाांिेड Agronom y Crops Seed Varietal evaluation 9/19/ 2013, 9/21/ 2013 कृषी ववज्ञाि केंद्र, सगरोळी ता. बबलोली जज. िाांिेड कडे रब्बी वपकाचे खालील वाणाची बबयाणे ववक्ीसाठी उपलब्ध आहे त गहू - कुिरत-११, त्र्यांबक करडई - परभणी – ४० (बबिकाटे री), परभणी कुसुम (काटे री) रब्बी ज्वारी – परभणी मोती, परभणी ज्योती, अकोला क्ाांती, फुले रे वती, फुले माऊली, फुले पांचमी (लाह्या बिवणे), एस.जी.एस – ८-४ (हुरडा बिवणे) …. .... ववषय तज्ञ - कृषी ववद्या, के. जव्ह. के. सगरोळी, जज. िाांिेड Agronom y Crops Field day Field day 9/19/ 2013, 9/20/ 2013 सवि शेतकरी बाांधवािा सूचीत करणात येते की उद्या दििाक २० /९ /२०१३ शुक्वार सकाळी ११ वाजता कृषी ववज्ञाि केंद्र सगरोळी तफे "शेती दिि "आयोजजत केला आहे त्यामध्ये सोयाबीि वपकातील िवीि वाणाची ओळख ,कापूस लागवड तांरज्ञाि, कीड व रोग नियांरण, भात वपकातील ववववध लागवड पधती, भाजीपाला रोपवादटका या ववषयावर मागििशिि व वपक पहाणी होणार आहे आपली उपस्थीती प्राथििीय आहे . स्थळ : कृषी ववज्ञाि केंद्र ,सगरोळी Agronom y Crops Cotton IPM 9/23/ 2013, 9/25/ 2013, 9/26/ 2013, 9/28/ 2013, 9/30/ 2013 सध्या बी. टी. कापसात आकजस्मक मर (कारण-दिवसाचे तापमाि ३८ डडग्री . से . दिघेकाळ राहणे ,पाण्याचा ताण बसिे ,पाणी साचूि राहणे ) आढळू ि येत आहे . उपाय म्हणूि ववकृतीग्रस्त झाडाांिा १ .५ ककलो यरु रया +१ .५ ककलो पालाश+ २०० ग्रॅ म बाववस्टीि + २०० लमली हुलमक अलसड १०० लल . पाण्यात लमसळू ि १५० -२०० लमली पाणी प्रती ववकृतीग्रस्त झाडाांिा ियावे. त्यािांतर ८ -१ ० दिवसाांिी २ ककलो डीएपी +२०० ग्रॅम बाववस्टीि + २ ० ० लमली हुलमक अलसड १ ० ० लल . पाण्यात लमसळू ि १५० -२०० लमली पाणी प्रती ववकृतीग्रस्त झाडाांिा ियावे.. प्रा. कवपल इांगळे ,ववषय ववशेषज्ञ – वपकशास्र, के.व्ही.के, सगरोळी. जज . िाांिेड Agronom y Crops Rabi crops Seed trietmant 9/28/ 2013, 9/29/ 2013, 9/30/ 2013 पेरणीपूवी बीज प्रकक्या करूिच रब्बी वपकाची पेरणी करावी. 3 35035 5 37026 2 19163 हरभरा - मर व मुळकुज रोगाचा प्रतीबांधासाठी ट्रायकोडमाि @ ५ ग्रॅम / ककलो . त्यािांतर िर व स्फुरिासाठी रायझोबबयम @ २५ ग्रॅ म + पीएसबी @ २५ ग्रॅम /ककलो बीज प्रकक्या करावी . // रब्बी ज्वारी - कािी रोगाचा प्रतीबांधासाठी ३०० मेश गांधक ४ ग्रॅ म /ककलो व खोड माशी व्यावस्थापािा साठी थायोमेथोक्षिम ७० % ३ ग्रॅम /ककलो . त्यािांतर िर व स्फुरिासाठी आझोटोबाक्टर @ २५ ग्रॅम + पीएसबी @ २५ ग्रॅम /ककलो बीज प्रकक्या करावी . // करडई - बाववस्टीि @३ ग्रॅम / ककलो . त्यािांतर िर व स्फुरिासाठी आझोटोबाक्टर @ २५ ग्रॅ म + पीएसबी @ २५ ग्रॅम /ककलो बीज प्रकक्या करावी // गहू - थायरम @ ३ ग्रॅ म / ककलो. त्यािांतर िर व स्फुरिासाठी आझोटोबाक्टर @ २५ ग्रॅम + पीएसबी @ २५ ग्रॅम /ककलो बीज प्रकक्या करावी ……. प्रा. कवपल इांगळे , ववषय तज्ञ - कृषी ववद्या, के. जव्ह. के. सगरोळी, जज. िाांिेड. Agronom y Agronom y Crops Crops Bengal gram Bengal gram ICM INM 10/10 /2013 , 10/12 /2013 , 10/14 /2013 , 10/15 /2013 , 10/18 /2013 10/10 /2013 कोरडवाहू हरभऱा पेरणी १५ ऑक्टोबर पूवी करावी ,बागायती पेरणी २० ऑक्टोबर ते १० िोव्हें बर पयंत करावी. मर व मळ ु कुज रोगाचा प्रतीबांधासाठी ट्रायकोडमाि @ १० ग्रॅ म / ककलो , त्यािांतर िर व स्फुरिासाठी रायझोबबयम @ २५ ग्रॅम + पीएसबी @ २५ ग्रॅम /ककलो बीज प्रकक्या करावी . पेरणीसाठी खालील वाणाचा वापर करावा .// कोरडवाहू िे शी वाण -आकाश ,ववजय ,दिजववजय ,जाकी -९२१८. // बागायती िे शी वाण - ववशाल ,दिजववजय ,जाकी -९२१८ . // बागायती कबुली वाण - ववराट ,काक -२ ,कृपा ,ववहार,// फुटाणे बिवण्यासाठी -गुलक-१ ,डी -८ ,// पुलाव व उसळ बिवण्यासाठी -दहरवा चाफा …प्रा. कवपल इांगळे ,ववषय ववशेषज्ञ – वपकशास्र, के.व्ही.के, सगरोळी. जज . िाांिेड. कोरडवाहू हरभऱा खतमारा- शेणखत / कांपोस्ट खत २ टि प्रती एकर, युररया १८ ककलो + लसांगल सुपर फॉसफेट १०० ककलो, अथवा डीएपी ३५ ककलो + युररया ४ ककलो ,अथवा १२ :३२ :१६ ५० ककलो प्रती एकर पेरणीचा वेळेस वापरावे // ,बागायती हरभऱा खतमारा - शेणखत / कांपोस्ट खत २ टि प्रती एकर, युररया २२ ककलो + लसांगल सुपर फॉसफेट १२६ ककलो, अथवा डीएपी ४४ ककलो + युररया ५ ककलो ,अथवा १२ :३२ :१६ ६४ ककलो प्रती एकर पेरणीचा वेळेस वापरावे. तसेच झझांक ,फेरस आझण गांधक कमतरता असणाऱ्या जलमिीमध्ये १० ककलो झझांक सल्फेट,१० ककलो फेरस सल्फेट, ८ ककलो गांधक प्रती एकर पेरणीचा वेळेस दिल्यास उत्पािणात वाढ आढळू ि आली आहे …प्रा. कवपल इांगळे ,ववषय ववशेषज्ञ – वपकशास्र, के.व्ही.के, सगरोळी. जज . िाांिेड. Agronom y Crops Wheat ICM 11/13 /2013 बागायती गहू पेरणी १ ते १५ िोव्हें बर िरम्याि करावी . 1 19197 2 19340 2 15259 2 6271 2 6037 1 2 उशीरा घेण्यात येणाऱ्या गहू वाणाची पेरणी १५ डडसेंबर पूवी करावी . पेरणीपूवी बीज प्रकक्या थायरम / बाववस्टीि @ ३ ग्रॅम / ककलो. त्यािांतर िर व स्फुरिासाठी आझोटोबाक्टर @ २५ ग्रॅम + पीएसबी @ २५ ग्रॅम /ककलो करावी.…प्रा. कवपल इांगळे ,ववषय ववशेषज्ञ – वपकशास्र, के.व्ही.के, सगरोळी. जज . िाांिेड. Agronom y Crops Weeds IWM 11/20 /2013 गाजर गवत नियांरणाचे उपाय : गाजर गवत फुलावर येण्यापूवी मुळासगट उपटूि धीग करूि जाळू ि टाकावे ककां वा वलायफोसेट ४१% हे तणिाशक १०० लमली प्रती १० ली. पाण्यात लमसळू ि फुलावर येण्या पूवी फवारावे ककां वा २०% लमठाचे द्रावण करूि (२० ककलो प्रती १०० ली. पाणी) या प्रमाणात फुलावर येण्या पूवी फवारावे ककां वा जैववक पद्धतीिे नियांरणासाठी मेजक्सकि भुांगे @२०० प्रती एकर सोडावेत.…. प्रा कवपल इांगळे , ववषय तज्ञ - कृषी ववद्या, के. जव्ह. के. सगरोळी, जज. िाांिेड Agronom y Crops Bengal garm INM 12/13 /2013 हरभरा वपकास २% डीएपी (२०० ग्रॅम डीएपी प्रती १० ललटर पाणी ) ककां वा ३ % युररया (३०० ग्रॅम युररया प्रती १० ललटर पाणी ) पदहली फवारणी फुले येण्यापूवी आझण त्यािांतर १० १२ दिवसाांिी िस ु री फवारणी केल्यास िाणे चाांगले भरुि उत्पाििात वाढ होते… प्रा कवपल इांगळे , ववषय तज्ञ - कृषी ववद्या, के. जव्ह. के. सगरोळी, जज. िाांिेड Agronom y Crops Field day Field day 1/22/ 2014 दि२४/१/१४शुक्वार रोजी सकाळी १०वा हरभरा वपकातील जाकी ९२१८ या वाणाच्या प्रात्यक्षिका अांतगित"शेती दििाचे" आयोजि मौजे अटकळी ता बबलोली येथील शेतकरी श्री राम पापा पोलकमवाड याांच्या शेतावर(खांडोबा मांदिराजवळ)केले आहे तरी आपली उपजस्थती प्राथििीय प्रा कवपल इांगळे ,केव्हीके सगरोळी Agronom y Crops Summer soybean Varietal evaluation 1/29/ 2014 उन्हाळी सोयाबीि लागवडीसाठी एमएांयए ु स-१६२(यांराद्वारे काढणीस उपयुक्त)एमएां यए ु स-१५८,एमएांयए ु स-८१ या वाणाची बबयाणे उपलब्ध आहे इच्छुकाांिी सांपकि साधावा.... के. जव्ह. के. सगरोळी, जज. िाांिेड Horticultu re Vegetabl e Nursary Plant protection 24072013 अनतपावसामुळे िसिरी तील रोपे वपवळी पडत असतील तर ताबडतोब १०.युररया व %०५ % काबेिडीझम ची फवारणी करावीित्रा म्हे रे .डा ., केसगरोळी .के .वव . Horticultu re Horticultu re Vegetabl e Nursary Plant protection Acid lime Plant protection Horticultu re Turmeri c Plant protection Horticultu re Sweet orange Plant protection 25072013, 26072013, 28072013 06082013, 10082013, 12082013 26082013 अनत वष्ृ टीमुळे मर रोगाची लागण लागण होवू िये म्हणूि 06092013 3 21502 3 23689 हळिीमध्ये हुमणी अळीचा प्रािभ ु ािव झाल्यास फोरे ट ककां वा काबोफुरोि ४ ते ५ ककलो एकरी मुळाजवळ पडेल असे 1 202 मोसांबी फळरस शोषण करणाऱ्या पतांगाच्या प्रभावी 1 175 3 55068 1 1247 फळबागेतूि तसेच भाजीपाला शेतातूि चर काढूि पाण्याचा निचरा करावाके वव के सगरोळी . पावसाळ्यात ललांबू झाडावर खैरया रोगाचा प्रािभ ु ािव होतो त्यासाठी रोगग्रस्त फाांद्याांची छाटिी करूि फाांद्या जाळू ि टाकाव्यात व झाडावर १ ग्रामस्टे पटोसायक्लीि . अर्धक ३० ग्राम कॉपर ऑस्कीक्लोराईड प्रती १० ललटर पाण्यात लमसळू ि एक मदहन्याच्या अांतरािे तीि फवारण्या कराव्यात .एस( . व .के )पीक सांरिण .एस .एम्हीसगरोळी .के . वापरावे)सगरोळी .के .व्ही.उद्यािववद्या के .एस .एम .एस( . नियांरणासाठी बागेत प्रकाश सापळे , रिक सापळे नतच्या फोडी )फेरोमेि( बागेत गळालेली फळे गोळा करूि .लावावेत बागेत एका कोपऱ्यात साठ्वाव्यात व त्यावर आकवषित झालेली पतां गे कीटक िाशकाांच्या सहाय्यािे मारावीत .वव( . सगरोळी .कें .वव.उद्यािववद्या कृ .त .वव, िाांिेड) Horticultu re Horticultu re Onion Guava Plant protection Plant protection 23102013, 25102013, 28102013 24102013 रब्बी काांद्याच्या लागवडीसाठी एकरी ३ टे ३ककलो बबयाणे ५. ट्रायकोडेमाि ककां वा काबेन्डॅझझम ककां वा कॅप्टि ५ ग्राम प्रती ककलो बबयाण्यास चोळू ि रोपे गािी ककां वा सपाट वाफ्यावर तयार करावीतित्रा म्हे रे .डॉ . पेरू फळबागेतील कीड नियांरणासाठी १फळमाशीच्या ) नियांरणासाठी लमथील युजेिोल व डायकलोरोवोस चे सापळे एकरी ८ फळे )२बागेत झाडाला बाांधावेत १०-पोखरणाऱ्या अळीसाठी म्यालर्थओि ककां वा मोिोक्ोटोफोस ककां वा ट्रायझोफोस १५ लमली १० ललटर पाण्यातूि फवारावे ३ खोड ) १०पोखरणाऱ्या अळीच्या नियांरणासाठी डायकलोरोवोस चे लमली १००लमली ीषध पाण्यात लमसळू ि त्यात कापसाचे बोळे लभजवूि नछद्रे बांि करूि घ्यावीत डॉित्रा . म्हे रे Horticultu re Onion Plant protection 30102013 काांिा वपकात करपा रोगाचा प्रािभ ु ािव आढळल्यास मेटाललकझील ८ %६४म्यािकोझेब १९:ग्राम 1 96 1 1247 3 16712 1 1248 2 22546 3 18245 + %२० ग्राम १० लल . १००पाण्यातूि फवारावे सोबत १९हे खात १९: लमसळल्यास उत्रम डॉित्रा म्हे रे ., Horticultu re Guava Plant protection 30102013 पेरू फळबागेतील कीड नियांरण १ फळमाशीच्या ) नियांरणासाठी लमथील युजेिोल व डायकलोरोवोस चे सापळे एकरी ८फळे पोखरणाऱ्या )२बागेत झाडाला बाांधावेत १०- अळीसाठी म्यालर्थओि ककां वा मोिोक्ोटोफोस ककां वा ट्रायझोफोस १५ लमली १० ललटर पाण्यातूि फवारावे ३खोड ) १०पोखरणाऱ्या अळीच्या नियांरणासाठी डायकलोरोवोस चे लमली १०० लमली ीषध पाण्यात लमसळू ि त्यात कापसाचे बोळे लभजवूि नछद्रे बांि करूि घ्यावीत डॉित्रा . म्हे रे Horticultu re Tomato, Onion and potato Plant Protection Horticultu re Vegetabl es general Cultural methods Horticultu re Geneeral Informatio n training Horticultu re Fruit crop Mango PLnat protection 21112013, 23112013, 25112013 25112013 06122013, 12122013, 15122013 10012014, 12012014, 1701- सध्या थांडीचे वातावरण चालू आहे तें व्हा अधूि मधूि ढगाळ वातावरणात धुके पडते तें व्हा अश्या वेळी काांिा, टमाटे , बटाटा या वपकावर करपा रोगाचा परीणाम दिसूि येतो तें व्हा तात्काळ काबेिडीझम म्यान्कोझेब अशे घटक असलेले + -१०बुरशीिाशक १५ ग्राम प्रती १० ललटर पाण्यात लमसळू ि फवारावेित्र .डॉ .्ा म्हे रे थांडी वाढण्या अगोिर शेतात भाजीपाला रोपाांची लागवड ( लमरची, काांिा, वाांगे व टोमाटो) पूणि करूि घ्यावी कृषी ववज्ञाि केंद्र सगरोळी येथे ववववध कृषी निगडीत ववषयावरील मागििशििासाठी ट्रे निांग कायिक्म आयोजजत केले जातात अर्धक मादहतीसाठी कायिक्म समन्वयक ., कृ . वव -०२४६५सगरोळी याांिा भेटावे अथवा ललहावे सांपकि .के. २२७७५७ आांबा बागाईतिारािो मोहोर फुटण्याच्या अवस्थेत बाग असेल तर कडूनिांब अकि ककां वा तत्सम कीटकिाशक १५लमली ( तसेच पोट्यालशम िायट्रे ट१३१०ग्राम प्रती ललटर पाणीनिघाल्यावर २०- १००( %१ )०:४५: लमसळू ि फवारावे मार मोहोर ) तुडतुडे व भुरी रोगाच्या रिणाकररता इलमडाक्लोवप्रड ४ लमली अर्धक गांधक ग्राम ककां वा काबेन्डॅझझम २० )%८०( प्रती १० ललटर पाण्यातूि मोहोरावर तसेच पािावर िे खील फवारावे. 2014 Horticultu re Fruit crop Mango Plant protection 10012014 आांबा बागाईतिारािो मोहोर फुटण्याच्या अवस्थेत बाग असेल तर कडूनिांब अकि ककां वा तत्सम कीटकिाशक १५लमली ( तसेच पोट्यालशम िायट्रे ट१३ १०ग्राम प्रती 1 14794 1 14844 1 3541 २०- १०० )०:४५: ललटर पाण्यात लमसळू ि फवारावे मार मोहोर निघाल्यावर तुडतुडे व भुरी रोगाच्या रिणाकररता इलमडाक्लोवप्रड ४ लमली अर्धक गांधक ग्राम ककां वा काबेन्डॅझझम २० )%८०( १० ग्राम प्रती १० ललटर पाण्यातूि मोहोरावर तसेच पािावर िे खील फवारावे Horticultu re Fruit crop Mango Plant protection 21012014 आांबा बागाईतिारािो मोहोर फुटण्याच्या अवस्थेत बाग असेल तर कडूनिांब अकि ककां वा तत्सम कीटकिाशक १५लमली २०- ललटर पाणीलमसळू ि फवारावे मार मोहोर निघाल्यावर ) ( तसेच पोट्यालशम िायट्रे ट१३१०ग्राम प्रती १००( %१ )०:४५: तुडतुडे व भुरी रोगाच्या रिणाकररता इलमडाक्लोवप्रड ४ लमली अर्धक गांधक ग्राम ककां वा काबेन्डॅझझम २० )%८०( प्रती १० ललटर पाण्यातूि मोहोरावर तसेच पािावर िे खील फवारावे. Horticultu re General Training informatio n 22012014 कृषी ववज्ञाि केंद्र सगरोळी एस एम एस सेवेचा लाभ घ्या व आपले कृषी ज्ञाि अद्यावत ठे वा तसेच वेळोवेळी ववववध मागििशिि कायिक्मासाठी व वपकाांच्या अर्धक मादहतीसाठी कृषी ववज्ञाि केंद्रास अवश्य भेट िया-०२४६५सांपकि Plant Protection Fruit crop Citrus IPM/IDM 06/08 /13 .२२७७५७ पावसाळ्यात ललांबू झाडावर खैरया रोगाचा प्रािभ ु ािव होतो 1 त्यासाठी रोगग्रस्त फाांद्याांची छाटिी करूि फाांद्या जाळू ि टाकाव्यात व झाडावर १ ग्राम ३०स्टे पटोसायक्लीि अर्धक ललटर पाण्यात लमसळू ि . 187 १०ग्राम कॉपर ऑस्कीक्लोराईड प्रती .एक मदहन्याच्या अांतरािे तीि फवारण्या कराव्यात Plant Protection Plant Protection Kharif crop Kharif crop Cotton Sybean IPM IPM 13/8/ 13, 15/8/ 13, 18/8/ 13 20/8/ 13 कापूस वपकात सध्या मावातुडतुडे व पाांढरी माशीचा प्रािभ ु ािव , झाला असूि त्याांच्या नियांरणासाठीअॅलसफेट ७५ टक्के २० ग्रामललटर पाण्यात लमसळू ि पदहली फवारणी १०प्रती पदहली फवारणी केली असल्यास या ककडीांच्या .करावी . 3 20541 1 203 नियांरणासाठीअॅलसटालमप्रीड २० टक्के ४ ग्रामलमसळू ि िस ु री . फवारणी सोयाबीिचे पीक फुलधारणा अवस्थेत असताांिा सोयाबीि वपकात तांबाखूवरील पािेखाणारी अळी व चक्ी भुांवयाचा प्रािभ ु ािव असल्यास क्लोरोपायरीफॉस २० टक्के प्रवाही २० लमली३.ककां वा इमामेक्त्रीि बेन्झोएट .५ ग्राम प्रती १० ललटर पाण्यात लमसळू ि फवारणी करावी. Plant Protection Plant Protection Kharif crop Kharif crop Tur Tur IPM IPM 20/8/ 13, 23/8/ 13, 26/8/ 13 30.8.1 3 तुर वपकात २० टक्के २५ लमलीललटर पाण्यात लमसळू ि Plant Protection Kharif crop Kharif crop Cotton Soybean IPM 3.9.13 , 4.9.13 , 7.9.13 IPM/IDM १०प्रती . 3 206 1 206 . 3 210 ऑस्कीक्लोराईड २५ ग्राम प्रती १० ललटर पाण्यात लमसळू ि 1 249 1 1820 3 430 2 14970 .फवारणी करावी तुरीवरील पािे गुांडाळणाऱ्या अळीच्या नियांरणासाठी डायमेथोएट ३० टक्के प्रवाही १० लमली .प्रती १० ललटर पाण्यात Plant Protection पािे गुांडाळणाऱ्या अळीच्या नियांरणासाठी डायमेथोएट ३० टक्के प्रवाही १० लमली ककां वा क्लोरोपायरीफॉस. ललटर पाण्यात लमसळू ि फवारणीकरावी. कापसावरील रस शोषणाऱ्या व पाांढरी ,तुडतुडे ,फुलककडे( ककडीांच्या नियांरणासाठी )माशीअॅलसटालमप्रीड २० टक्के ४ ग्राम ककां वा कफप्रोिील ५ टक्के प्रवाही २० लमली १०प्रती .ललटर पाण्यात लमसळू ि फवारणी करावी सोयाबीि वपकात पािाांवरील दठपके व शेंगावरील करपा 6.9.13 रोगाांच्या नियांरणासाठी मैन्कॉझेब २५ ग्राम ककां वा कॉपर १० दिवसाांच्या अांतरािे िोि वेळा फवारणी करावी. Plant Protection Kharif crop Tur IPM 18.9.1 3 Plant Protection Plant Protection Vegetabl e Kharif crop Chilli Tur IPM/IDM IPM 12.9.1 3, 14.9.1 3, 17.9.1 3 28.9.1 3, 29.9.1 3 तुर वपकात पािे गुांडाळणाऱ्या अळीच्या नियांरणासाठी डायमेथोएट ३० टक्के प्रवाही १० लमली .प्रती १० ललटर पाण्यात लमसळू ि फवारणी करावी. लमरची वपकावरील फुलककडयाांच्या नियांरणासाठी कफप्रोिील ५ टक्के प्रवाही २० लमली.लमली ३ ,टक्के ४५ककां वा जस्पिोसैड . प्रती १० ललटर पाण्यात लमसळू ि फवारणी करावी. तुर वपकात पािे गुांडाळणाऱ्या अळीच्या नियांरणासाठी डायमेथोएट ३० टक्के प्रवाही १० लमली ककां वा क्लोरोपायरीफॉस. २० टक्के २५ लमलीललटर पाण्यात लमसळू ि .फवारणी करावी १०प्रती . Plant Protection Vegetabl e Chilli IPM/IDM 28.9.1 3 लमरची वपकावरील फुलककडयाांच्या नियांरणासाठी कफप्रोिील ५ टक्के प्रवाही २० लमली.लमली ३ ,टक्के ४५ककां वा जस्पिोसैड . प्रती १० ललटर पाण्यात लमसळू ि फवारणी करावी Plant Protection Kharif crop Cotton IPM 8.10.1 3 1 490 1 628 3 1244 1 100 1 1244 1 100 2 354 कपाशी वपकावर धुरयाकडील ओळीांवर वपठ्या ढे कणाचा प्रािभ ु ािव आढळू ि आलेला आहे वपठ्या ढे कणाचे नियांरणासाठी क्लोरोपायरीफॉस ३० लमली .लमली २०ककां वा ट्रोयझोफॉस . ककां वाअॅलसफेट ३० ग्राम प्रती १० ललटर पाण्यात लमसळू ि फवारणी करावी. Plant Protection Plant Protection Kharif crop (Spices) Turmeri c Kharif crop Cotton IDM IPM 17.10. 13, 19.10. 13, 21.10. 13 29.10. 13 हळिीवर करपा रोगाचा प्रािभ ु ािव आढळू ि आल्यास कॉपर ऑस्कीक्लोराईड २५ ग्राम ककां वा काबंडेझीम १० ग्राम प्रती १० ललटर पाण्यात लमसळू ि फवारणी करावी कपाशी वपकावर धुरयाकडील ओळीांवर वपठ्या ढे कणाचा प्रािभ ु ािव आढळू ि आलेला आहे वपठ्या ढे कणाचे नियांरणासाठी क्लोरोपायरीफॉस ३० लमली .लमली २०ककां वा ट्रोयझोफॉस . ककां वाअॅलसफेट ३० ग्राम प्रती १० ललटर पाण्यात लमसळू ि फवारणी करावी. Plant Protection Plant Protection Kharif crop (Spicees) Turmeri c Kharif crop Cotton IDM 17.10. 13 हळिीवर करपा रोगाचा प्रािभ ु ािव आढळू ि आल्यास कॉपर ऑस्कीक्लोराईड २५ ग्राम ककां वा काबंडेझीम १० ग्राम प्रती १० ललटर पाण्यात लमसळू ि फवारणी करावी IPM 29.10. 13 कपाशी वपकावर धुरयाकडील ओळीांवर वपठ्या ढे कणाचा प्रािभ ु ािव आढळू ि आलेला आहे वपठ्या ढे कणाचे नियांरणासाठी क्लोरोपायरीफॉस ३० लमली .लमली २०ककां वा ट्रोयझोफॉस . ककां वाअॅलसफेट ३० ग्राम प्रती १० ललटर पाण्यात लमसळू ि फवारणी करावी. Plant Protection Kharif crop Safflowe r IPM 17.12. 13, 19.12. 13 करडी वपकात मावा ककडीचा प्रािभ ु ािव दिसूि येत आहे . १०टक्के प्रवाही ३०माव्याच्या नियांरणासाठी डायलमथोएट .ललटर पाण्यात लमसळू ि फवारणी करावी १०प्रती .लमली पॉवर स्प्रेसाठी वरील ककटकिाशकाची मार नतप्पटकरावी. Plant Protection Plant Protection Fruit tree Rabi Vegetabl e Mango Chilli IPM/IDM IPM/IDM 17.1.1 4, 18.1.1 4, 22.1.1 4 1.2.14 सध्या आांबा वपकात फुलककडेतुडतुडे व भुरी रोगाचा प्रािभ ु ािव / २०दिसूि येत आहे तरी या ककडीच्या नियांरणासाठी कफप्रोिसल लमली ललटर १०ग्रॅम काबेन्डाझीम प्रती १०+पाण्यात 3 लमसळू ि फवारणी करावी. काांिा व लसूि वपकावरील फुलककडे व करपा नियांरणासाठी काबोसल्फाि १० लमली ककां वा प्रोफेिोफॉस १० लमलीअर्धक 1 . २५मॅन्कॉझेब ग्रॅ म प्रती १० ललटर पाण्यात लमसळू ि फवारणी 3398 करावी. Rainwate r harvestin g In-situ soil conervat ion Soil and Water Conservati on 120613, 1406-13 Use insitu soil conservation method 2 Post Harvest Technolo gy Green Gram Post Harvest Technolog y Use of Neem oil 5 mili/kg for grain storage 3 Agri. Engg. Water managem ent Drip irrigatio n Micro irrigation Agri. Engg. Post Harvest Technolo gy Soybean Post Harvest Technolog y 200813, 220813, 2508-13 13-913, 14-913, 16-913 18-913 Agri. Engg. Rainwate r harvestin g 031013, 41013, 71013, 11- Agri. Engg. Agri. Engg. Rainwater harvesting 414 731 15016 Benefits of drip irrigation 3 6298 Grain storage 1 19361 Conservation of water in farm pond 4 19659 10-13 Agri. Engg. Post Harvest Technolo gy Soybean Post Harvest Technolog y 8-1013 Care taken during storage 1 19701 Agri. Engg. Post Harvest Technolo gy Pulses Post Harvest Technolog y 071113, 81113, 101113, 131113, 1511-13 11/10 /13 Information about mini dal mill 5 19213 Health checkup camp 3 21083 Home Science Farm women and farmer Health Home Science Farm women Training 12/10 /13 World food day 3 800 Home Science Farm women Health 11/11 /13 Importance of amla 1 477 Nutrition Home Science Farm women Vet. Sci. Awarene ss Vet. Sci. Vet. Sci. Other enterpris es Livestoc k Awarene ss Tantradny an mahotsav 20/12 /13 Tantradnyan mahotsav 9 800 Disease manageme nt 9/4/2 013 12:47 :28 PM 1:21: 54 PM 1:27: 07 PM 1:31: 11 PM 2:58: 50 PM 9/12/ 2013 11:05 :32 AM 11:13 :34 AM 11:31 :19 AM 3:02: 51 PM 3:07: 55 PM 3:59: 42 PM 9/13/ 2013 4:03: 09 PM 4:06: 22 PM 4:13: 43 PM बैलाच्या लशांगाला वाणीस लावल्यािे त्याांिा लशांगाचा कॅन्सर 5 21152 6 13256 3 13302 Disease manageme nt Other enterpris es Nutrition होऊ शकतो वाणीस लावण्या ऐवजी लशांग रे गमल पेपर िे घासूि त्यावर खोबरे ल तेल लावावे. बैलाच्या अांगावर रां ग लावल्यािे त्याांिा अल्लेजी होऊि कातडीचे आजार होऊ शकतातरां ग लावण्या ऐवजी गोचीड.,गोमाशी िाशक ीषधाची फवारणी करूि घ्यावी. अांडी,तेल पाजण्या ऐवजी जन्त्िाशाकाची गोळी िे वूि जांत िाशि करूि सवि जि आिांिािे पारां पररकच पण शास्रीय पद्धतीिे आरोवय िायी पोळा सि साजरा करूयात. पोळा सणानिलमत्र सवि पशुपालक बांधूिा कृषी ववज्ञाि केंद्र, सगरोळी तफे हादिि क शुभेछा. डॉगजा.िि ढगे, ववषयकृषी )पशुवैद्यक शास्र( ववशेषज्ञ- ववज्ञाि केंद्र, सगरोळी जजल्हा िाांिेड. वप्रय पशप ु ालक बांधुिो, आपल्या पशध ु िाचे गाय(,म्है स ,बैल,शेळी ,में ढीपायखुरी आजारापासि ू /तोंडखरु ी) सांरिण करण्यासाठी त्याांिा वषाितूि िोि वेळेससप्टें बर व माचि( मदहन्यातपायखुरी प्रनतबांधक लस टोचूि /तोंडखुरी) लसीकरणापूवी तज्ञ.घ्यावी पशुवैद्यकाच्या मितीिे जिावराांचे जांतिाशि करवूि घ्यावे. डॉगजािि ढगे., ववषय ववशेषज्ञ- )पशुवैद्यक शास्र( कृषी ववज्ञाि केंद्र, सगरोळी जजल्हा िाांिेड. वप्रय पशुपालक बांधुिो, जिावराांचा गोठा आझण पररसरात मलमूर व अस्वच्छता असल्यास त्या दठकाणी ववववध आजारास कारणीभूत ठरणाऱ्या जांतूांचा प्रािभ ु ािव होऊि जिावरे आजारी पडू शकतात तसेच त्याचा जिावराच्या िध ु उत्पाििावर व पैिास िमतेवरही वाईट पररणाम होतो. कृपया जिावराांचा गोठा स्वच्छ)१(, कोरडा व मलमूराचा वास रदहत ठे वा. (२गोठ्यात हवा खेळती असावी यासाठी उपाय योजिा ) .करा (३गोठा आझण पररसरात परजीवी िाशक ीषधी तज्ञ ) पशु वैद्यकाच्या सल्ल्यािे फवारा. डॉगजािि ढगे., ववषय- )पशव ु ैद्यक शास्र( ववशेषज्ञ कृषी ववज्ञाि केंद्र, सगरोळी जजल्हा िाांिेड. Vet. Sci. Disease manageme nt 9/14/ 2013 4:43: 11 PM 11:29 :37 AM वप्रय पशुपालक बांधुिो, िवु धव्यवसाय व्यावसानयकदृष्ट्या 2 1516 2 20272 3 33786 फायिे शीर होण्यासाठी गाई व म्हशीां व्याल्यािांतर त्या २ ते ३ मदहन्यात माजावर येणे व गाभण रहाणे क्मप्राप्त ठरतेकृबरम रे ति केलेल्या ककां वा िैसर्गिकरीत्य.्ा फळवलेल्या गाई व म्हशीांच्या गभिधारणेची तपासणी व खारी जिावरे फळवल्या िांतर ३ मदहन्याांिी तज्ञ पशुवैद्यकाकडूि करूि घ्यावी तरच आपणास प्रत्येक जिावरापासूि वषािला एक वासरू लमळे ल आझण आपला िवु ध व्यवसाय फायिे शीर ठरे ल. डॉगजािि ढगे., ववषयपशुवैद्यक शास( ववशेषज्ञ-्र.) कृषी ववज्ञाि केंद्र,शारिािगर, सगरोळी जजल्हा िाांिेड. Vet. Sci. Livestoc k Other enterpris es 9/16/ 2013 4:08: 48 PM 9/18/ 2013 12:09 :02 PM वप्रय पशुपालक बांधुिो, सकस आहार हा सुदृढ प्रकृती आझण अर्धक उत्पाििाचा पाया आहे यासाठी शेतीकाम करणाऱ्या आझण िभ ु त्या जिावराांिा दहरवा चारा वषिभर उपलब्ध करणे गरजेचे आहे . दह गरज पूणि करण्यासाठी सांकरीत िेवपअर वाणाचे बहुवावषिक-८ एका वषाित(९ कापण्या होणारे पदहली / ते २५व्या दिवशी आझण त्यािांतरच्या कापण्या ६०कापणी ३० दिवसािे होणारे फुले जयवांत" चारापीक),फुले यशवांत आझण सांपूणाि ची ठोंबे " ववक्ीसाठी)रुपया प्रती ठोंब १(आमच्याकडे उपलब्ध आहे त. डॉगजािि ढगे., ववषयपशुवैद्यक ( ववशेषज्ञ)शास्र कृषी ववज्ञाि केंद्र,शारिािगर, सगरोळी जजल्हा िाांिेड. Vet. Sci. Awarene ss Other enterpris es 9/18/ 2013 1:32: 27 PM 2:52: 32 PM 2:57: 34 PM वप्रय पशुपालक बांधुिो, जिावराांच्या अांगावरील बाह्यपरजीवीगोचीड(,गोमाश्यारक्त शोषणा लशवाय इतरही) अिेक प्राणघातक आजार पसरवतात त्याचा जिावराांची कायििमता आझण िध ु उत्पािि िमतेवरही वाईट पररणाम होतो, यासाठी ललजक्वड बुटोक्सककां वा)डेल्टामेल्ीि( जक्लणारीषधी जिावराांवर तसेच गोठ्यात )सायपरमेल्ीि( आठवडयातूि एकवेळेस याप्रमाणे मदहन्यातूि सतत तीि वेळेस फवारल्यास बह्यापजीववांचा समूळ िायिाट करणे शक्य आहे या कररता. (१जिावरावर )डेल्टामेल्ीि(ललजक्वड बुटोक्स) ललटर पाण्या १फवारतािा त २ लमली आझण गोठ्यात फवारतािा १ ललटर पाण्यात ५ लमली या प्रमाणात फवारावे. (२ १जिावरावर फवारतािा )सायपरमेल्ीि(ललजक्वड जक्लणार) ललटर पाण्यात1 लमली आझण गोठ्यात फवारतािा १ ललटर पाण्यात3 लमली या प्रमाणात फवारावे. डॉगजािि ढगे., ववषय)पशुवैद्यक शास्र( ववशेषज्ञ- कृषी ववज्ञाि केंद्र,शारिािगर, सगरोळी जजल्हा िाांिेड. Vet. Sci. Other enterpris es Nutrition 9/19/ 2013 8:13: 41 PM 8:16: 22 PM वप्रय पशप ु ालक बांधुिो, जिावराांचे खाद्य ओल्या ,कोणिट 2 6084 3 14374 1 947 2 2099 जागेवर ठे वल्यािे त्यावर बुरशीची वाढ होऊि जिावरास बाधा होऊ शकतेखुराक/जिावराांचे खाद्य. कोरडया हवेशीर जागेवर ठे वावे तसेच जिावरास पुरवण्यात येणाऱ्या सुक्या चाऱ्यावरकडब्यावर बुरशीची/ वाढ झाली िसल्याची खारी वेळोवेळी करूि घ्यावीकडबा पाण्यािे/सुका चारा. लभजणार िाही यासाठी खबरिारी घ्यावी. डॉगजािि ढगे.,ववषय- )पशुवैद्यकशास्र(ववशेषज्ञ कृषी ववज्ञाि केंद्र,सगरोळी जजल्हा िाांिेड. Vet. Sci. Disease manageme nt 9/23/ 2013 3:06: 12 PM 3:09: 41 PM 4:28: 43 PM वप्रय पशुपालक बांधुिो िमस्कार , सविसामान्यपणे सवि जिावराांत जांताचा प्रािभ ु ािव होतो पोटात.जांत होणे हे अिेक आजाराांचे मुळ कारणही आहे पण शेळी,में ढी व त्याांची करडे याांिा जांताचा प्रािभ ु ािव अर्धक प्रमाणात होतो त्यामुळे त्याांची वाढही खुांटते आझण ते अिेक आजाराांिा बळी पडतातकृपया.,आजच आपण तज्ञ पशुवैद्यकास भेटूि सवि जिावराांिा जांत िाशकाची मारा िे वूि त्याांचे प्राणसांरिण करागजािि ढगे.डॉ., ववषय)पशुवैद्यकशास्र( ववशेषज्ञ-,कृषी ववज्ञाि केंद्र, सगरोळी जजल्हा िाांिेड. Vet. Sci. Other enterpris es Disease manageme nt 9/28/ 2013 1:24: 18 PM वप्रय पशुपालक बांधुिो, िमस्कार जिावराचे पोट अनततीव्र स्वरुपात फुगणे हे अचािक तडकाफडकी मत्ृ यूचे कारण ठरतेपोट फुगीकडे िल ि करू िका व गोडतेल िध ु ि ु असे . घरगुती वापरातले पिाथिही पाजू िकात्याऐवजी ललजक्वड . ब्लोटोसील टायरे ल ककां वा ललजक्वड सारखी ीषधी १०० ते २०० लमली पाजूि जिावराच्या तोंडात कडू ललांबाची जाडसर काडी आडवी बाांधावी आझण ताबडतोब तज्ञ पशव ु ैिकास पाचारण करावेगजािि ढगे.डॉ., ववषय ववशेषज्ञ- )पशुवैद्यकशास्र(,कृषी ववज्ञाि केंद्र,सगरोळी जजल्हा िाांिेड. Vet. Sci. Livestoc k 9/28/ 2013 1:41: 17 PM 1:46: 11 PM वप्रय पशुपालक बांधुिो, िमस्कार आज जगभरात .जागनतक रे बीज दिि साजरा केला जात आहे जिावरास रे बीज. होणे म्हणजे ते जिावर वपसाळणेवपसाळलेला कुरा चावल्यािे पसरणाऱ्या या रोगािे भारतात िरवषी २५ ते ३० हजार . माणसे व जिावरे मत्ृ युमुखी पडतातया. रोगाववषयी जिजागरण करणे हा या दिवस साजरा करण्या मागचा उद्येश असूि या निलमत्र आज सायांकाळी ठीक ७वाजता ३०: आकाशवाणी केंद्र, िाांिेड ककसािवाणी या कायिक्मातूि या ववषयावर " जिावराती वपसाळणे करणे आझण उपाय" घेतलेली माझी मुलाखत प्रसाररत करणार आहे सवांिी लाभ . गजािि ढगे.डॉ..घ्यावा, ववषय)पशुवैद्यकशास्र( ववशेषज्ञ-,कृषी ववज्ञाि केंद्र,सगरोळी जजल्हा िाांिेड. Vet. Sci. Livestoc k Nutrition 10/3/ 2013 11:17 :04 AM 11:43 :39 AM वप्रय पशप ु ालक बांधुिो, िमस्कार पायखुरीिे बार्धत/तोंडखरु ी. 2 20588 1 19677 5 1077 3 27735 तोंडातील.जिावराांचा उपचार लवकर करूि घ्या जखमाांिा लोणी व हळि सम प्रमाणात लमसळू ि लावावे खुरािा.झालेल्या जखमा पोट्यालशयम परम्याांविेट च्या द्रावणािे स्वच्छ धुवूि घ्यावे व त्यावर टोपीकुर ककां वा दहमाक्स मलम रोज िोि वेळेस जखमा पूणि भरे पयंत लावावेता अर्धक आजाराची तीव्र. .असल्यास तज्ञ पशुवैद्यकाशी सांपकि साधावा डॉगजािि ढगे., ववषयपशुवैद्यकशास्त( ववशेषज्ञ-्र),कृषी ववज्ञाि केंद्र,सगरोळी जजल्हा िाांिेड. Vet. Sci. Disease manageme nt 10/5/ 2013 3:38: 40 PM 3:48: 06 PM वप्रय पशुपालक बांधुिो, िमस्कार िभ ु त्या जिावराांचा १०० ककलो खुराक तयार करतािा त्यात मका+ ज्वारी ५५( )ककलो,शेंगिाणा पें ढ)ककलो२५( सरकीची पें ढ+,मुगाची चुिीउडिाची+ चुिीगव्हाचा +ताांिळाचे तौड+ )ककलो२०(भुसाघेऊि त्यात १ ककलो मीठ टाकूि या लमश्रणाचा भरडा करूि घ्यावाजिावराच्या िै िांदिि गरजासाठी िीड. ककलो व प्रती ललटर िध ु उत्पाििासाठी अधाि ककलो प्रमाणे वरील खुराख रोज िोि वेळेस ववभागूि द्यावाग.डॉ .जािि ढगे, ववषय)पशुवैद्यकशास्र( ववशेषज्ञ-,कृषी ववज्ञाि केंद्र,सगरोळी जजल्हा िाांिेड.. Vet. Sci. Livestoc k Nutrition 10/7/ 2013 3:13: 22 PM वप्रय पशुपालक बांधुिो, िमस्कारिवजात वासरे .,करडे व वराहाांची वपले याांिा जन्मजातच जांताची बाधा होत असतेपोटात जांत होणे हे अिेक आजाराांचे मुंय कारण . असूि यामुळे िवजात वपलाांची वाढही खुांटतेवासराांच्या निकोप . वाढीसाठी व त्याांिा निरोगी ठे वण्यासाठी िवजात वासराांचे जन्मलेल्या दिवशीच ककां वा िस ु रा दिवशी तज्ञ पशव ु ैद्यकाच्या सल्ल्यािे जांत िाशि करूि घ्यावेगजािि ढग.डॉ .्े, ववषय)पशुवैद्यकशास्र( ववशेषज्ञ,कृषी ववज्ञाि केंद्र,सगरोळी जजल्हा िाांिेड. Vet. Sci. Awarene ss 3/19/ 2014 4:35: 58 PM 4:38: 01 PM 3/28/ 2014 12:51 :50 PM वप्रय पशप ु ालक बांधुिो राम राम अवकाळी पाउस व गारपीट िांतर जिावराांिा घटसपि फयाि तीवा निमोनिया आजाराांचा प्रसार होऊ शकतो जिावरे सुस्त असल्यास त्याांिा ताप आला असल्यास ताबडतोब पशुवैद्याकािा भेटा डॉ गजािि ढगे Vet. Sci. Awarene ss 3/28/ 2014 12:54 :00 PM वप्रय पशप ु ालक बांधुिो रामराम जिावराांिाकोणतीही द्रव 1 10422 181 984596 ीषधी िाकावाटे कधी पाजू िका असे केल्यािे जिावराांिा निमोनिया होऊ शकतो काही वेळेस जिावर िगाऊ शकते द्रव ीषधी तोंडावाटे पाजातािाही ववशेष काळजी घ्यावी ककां वा गुळात लमसळू ि द्यावे डॉ गजािि ढगे के व्ही के सगरोळी Details on Technology Week Celebrations Types of Activities Title/topic/technology Date No. of Activities /quantity No. of participants/beneficiaries Male Fem Total ale Gosthies Lectures organized Water management in Sustainable Agriculture and Experiments in cropping pattern of Gram and soyabean Group Farming:A Properious Business 28 December 2013 28 December 2013 28 December 2013 28 December 2013 29 December 2013 29 December 2013 29 December 2013 29 December 2013 29 December 2013 29 December 2013 29 December 2013 Our Agriculture and Our Farmer Amrut Pattern: A cotton Production Technology Importance of NABARD in Agricultural development Protected cultivation (Polyhouse/Shadenet) Woman Nutrition and Child care Women Entrepreneurship and Woman Power Integrated Farming system and new experiments in agriculture Success story in Apple Ber Cultivation Success story in Milk Production Exhibition 3 2650 675 3225 7 1500 1800 3300 10 4150 2475 6525 27 stalls of the agri inputs and farm machinery Film show Fair Farm Visit Diagnostic Practical’s Distribution of Literature (No.) Distribution of Seed (q) Distribution of Planting materials (No.) Bio Product distribution (Kg) Bio Fertilizers (q) Distribution of fingerlings (No) Distribution of Livestock specimen (No.) Visit to KVK crop cafeteria of vegetable, fodder and vegetable Rabi crop and cash crop folders 5000 33 Crop cafeteria kharif-2013 PLAN OF LAYOUT Crops : Soybean, Pigeon pea, Deshi cotton, Hybrid cotton, Green gram, Black gram Plot size : Gross: 70 x 1 m Method of sowing : line sowing Total No. of plots : 36 Variety /Hybrids : Pigeon pea: BSMR-853, BDN-708, BDN-711 , Vipula, ICPL-87,Kudrat Deshi Cotton: Phule JLA-47, Soybean: MAUS-47 (Parbhani sona), MAUS-81(Shakti), MAUS-32 (Prasad), MAUS-71, MAUS-158, JS-335, MAUS-162 Niger:( Local) Green gram: BM_4, Kopargaon,BPMR-145,BM-2002-1, BM-2003-2, Black gram: BDU-1,TAU-1 Cowpea:Sadabhar Spacing: Recommendations by MAU Parbhani in each crops Fertilizers : Recommendations by MAU Parbhani in each crops No of farmers visited : 1020 Crop cafeteria rabi-2013-14 PLAN OF LAYOUT Crops : Chick pea, Safflower, Linseed, Mustard, Sunflower, Wheat Rajma,Pea,Rabi grain sorghum Plot size : Gross: 30 x 1 m Method of sowing : line sowing Total No. of plots : 40 Variety /Hybrids : Chick pea (12 varieties) Deshi : Harita,Akash,Jaki-9218,Gulak,Digvijay,Saki 9516,Vijay,Vishal, Kabuli:Virat, PKV-4,PKV-2,Kripa Safflower: Sharda, PBNS-12, PBNS-40 Linseed: PKV NL-260 Mustard: Local Sunflower: Sunbreed Maize::Sunbreed Rajma:Local Pea:Local Wheat:Kudrat-11.Kudrat-17,Navratna,LOK-1.Shever,Triambak. Rabi Jawar (13 varieties) :PhuleVasuda,PhuleYashoda,PhuleRavati,Phulechitra,Phulemauli,Phulepanchami,Phuleanura dha,CSV-22,PKV kranti,ParbhaniJyoti,Parbhani moti,Maldandi,SGS-8-4 Spacing : Recommendations by MAU parbhani in each crops Fertilizers : Recommendations by MAU parbhani in each crops No of farmers visited: 80 Fodder crops cafeteria 2013-14 PLAN OF LAYOUT Crops :Lucerne,Berseem,oat,Foddermaize,cowpea,FodderjawarMpchari,kadwal,Hybridnappier-phuleyashwant, phulejayawant,sampurna(DHN-6),and Hybrid bajara-nutrifeedetc Plot size : Gross: 70 x 1 m Method of sowing : line sowing Total No. of plots : 13 Variety /Hybrids : Spacing : Recommendations by MAU Parbhani in each crops Fertilizers : Recommendations by MAU Parbhani in each crops No of farmers visited: 1023 3.5 Production and supply of Technological products SEED MATERIALS Major group/class CEREALS Crop Rabi Sorghum Wheat OILSEEDS Safflower Soybean Variety Parbhani Moti Parbhani Jyoti SGS-8-4 PKV Kranti Phule Vasudha Phule Chitra Phule Revati Phule Yashoda M 35-1 Phule Panchami Kudrat 11 Kudrat 17 Trimbak PBNS 40 PBNS 12 MAUS 71 MAUS 162 MAUS 158 MAUS 81 Quantity (kg.) 189 30 9.5 42 64 11 46 17 8 1 205 270 80 361.5 50 820 1247 166 5 Value (Rs.) 5670 900 285 1260 1920 330 1380 510 240 30 8200 10800 3200 18075 2,500 41000 87290 9960 300 Provided to No. of Farmers 12 4 8 9 8 2 6 6 1 1 11 14 1 39 10 19 39 13 1 BSMR 853 BDN 708 Vipula BDN 711 BDNG 797 Virat 14 10 100 6 165 2 980 700 7000 420 8250 100 4 2 15 2 10 1 PhuleJLA 794 RGS 936 27.5 5 3 0.5 12 4125 500 150 20 360 21 1 1 1 5 PULSES Pigeon pea Gram VEGETABLES FLOWER CROPS OTHERS FIBRE CROP DESICOTTON INDUSRIAL CROP Guar gum FODDER CROPS Sweet sorghum Fodder jowar Fodder Bajra MP Chari Gaint Bajra SUMMARY Sl. No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 Major group/class CEREALS OILSEEDS PULSES VEGETABLES FLOWER CROPS OTHERS TOTAL Quantity (qtl.) Value (Rs.) 972.5 kg 2649.5 kg 297 kg 0 0 48 kg 34725 159125 17450 0 0 5155 0 Provided to No. of Farmers 83 121 34 0 0 29 216455 PLANTING MATERIALS Major group/class Crop Quantity (Nos.) Variety Value (Rs.) Provided to No. of Farmers FRUITS SPICES Brinjal seedlings Tomato seedlings VEGETABLES Phule Arjun Abhinav US 618 Onion Bhima Shubhra Bhima Kiran Chilli Parbhani Tejas Cauliflower US 178 8446 4293=00 47 1280 1926 519.5 Sq.ft. 1664.5 Sq.ft. 4354 278 640=00 963=00 10390=00 33290=00 4078=20 222=40 8 16 19 24 33 8 1760=00 50=00 16 1 FOREST SPICES ORNAMENTAL CROPS Marigold Gillardia Orange double red 1760 50 PLANTATION CROPS OTHRS Hybrid Napier FODDER CROPS Phule Jaywant Phule Yashwant DHN -6 29612 29612=00 24769 24769=00 148850 148850=00 203231 55 78 180 313 SUMMARY Sl. No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Major group/class FRUITS VEGETABLES SPICES FOREST SPECIES ORNAMENTAL CROPS PLANTATION CROPS OTHERS TOTAL Quantity (Nos.) 0 16284 546125 0 1810 0 203231 767450 Value (Rs.) 0 10196 43680 0 1810 0 203231 258917 Provided to No. of Farmers 0 172 43 0 17 0 313 545 3.6. Literature Developed/Published (with full title, author and reference) (A) KVK News Letter ((Date of start, Periodicity, number of copies distributed etc.) (B) Literature developed/published Item Research papers Title Oesophageal obstruction and its surgical removal in non descript cow –a case report Authors name Dr gajanan dhage Number of copies Not applicable Nimboli as a important component in pest management Weekly Krushakonnati Ase kara wangyavaril kidenche niyantran. Weekly Krushakonnati Amla ek amrut fal , in Krushi Panan Mitra (December 2013) Soyabean prakriya ek aarogydai udyog – godva sheticha – march 2014 1. Dudhal janavaranchi nivad 2. Urea chi kimaya bhari nokrushta chara utkrushta kari 3. Hivalyat janavaranchi ghyavayachi kalaji 4. Rabies ek pranghatak aajar 5. Shelya mendhyanchi ghya kalaji 6. Janavaranchi Pavsalyatil aajar 7. Deshi gowanshache samvardhan kalachi gara 8. Mukta sanchar gotha aani dugdha vyavsay Mr. Pravin P. Deshpande Mr. Pravin P. Deshpande Prof. Madhuri Revanwar 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Control of sucking pest of cotton IPM in soybean Control and identification of pest on redgram Neemark for control of pest Control of milibug in cotton Mr. Pravin P. Deshpande 6. 7. Ann tayar kartana ghyavayachi kalji Shalapurv balkancha aahar Mrs. Revanwar MS 500 copies each 8. Dudhal janavaranchi nivad 9. Urea chi kimaya bhari nokrushta chara utkrushta kari 10. Increasing productivity in dry land pigeon pea by seedlings transplanting. 11. Broad bed furrow system of planting in soybean. 12. Reddening in bt cotton and its management. 13. Important five aspects in increasing productivity in soybean crop 14. Bio fertilizers for sustainable agriculture 15. Parthenium weed control Dr Gajanan Dhage Mr. Kapil Ingle 1000 copies each 16. Custard Apple Production (Marathi) 17. Kitchen Garden (Marathi) Dr. Dattu A. Mhetre 2000 2000 18. Mini Dal mill small enterprise 19. In-situ soil and water conservation Mr. Vaijanath Bomble 2000 Technical reports Popular articles Leaflets/folders Total Grand TOTAL Dr Gajanan Dhage 1000 copies each 2000 1000 copies each 20500 N. B. Please enclose a copy of each. In case of literature prepared in local language please indicate the title in English (C) S. No. Details of Electronic Media Produced Type of media (CD / VCD / Title of the programme DVD / Audio-Cassette) NIL Number 6.7. Success stories/Case studies: 1. Upliftment of livelihood following buffalo farming by adopting loose housing system Shri madhav gundure a small scale farmer holding only 0.2 hectares of land was running a general store at his village Borgan sangavi tq Degloor Dist Nanded(MS)The income from general store was inadequate to run his life and he was not satisfied with its income hence he had decided to rear buffalo and adopt the new business dairy farming.as initial capital investment was very less with him he had purchased only two marathwadi buffaloes and started selling milk getting out of it.by selling quality milk in a very short span of time he has got very good name and fame in degloor market and peoples got attracted towards his product and demand of milk is increased, to suffice the need of the consumer he had planned to increase the number of buffalo but the land was a constraint. With these problem he has approached to KVK SAGROLI TQ BILOLI DIST NANDED to get a technical advice.kvk advised him regarding loose housing system,napier fodder crop,azola unit,etc. Shri gundure immediately followed the advice given by the Kvk and stared rearing 7 buffaloes.he have planted the napier in 0.018 hectare of land as a fodder crop, in 0.01hectare of land established low cost azola production unit and in rest of the area that is in 25x30 loose housing system is adopted by using gabion mesh.now he has 4 buffalos in lactation and rest of the 3 buffaloes are pregnanat milking animals are giving 30 litres of milk per day.the price of buffalo milk in local market is Rs 50 per lit likewise he is getting Rs 1500 per day out of sell of milk.by deducting the expenses on the ration and fodder and labor he is earning Rs1000 per day. 3.8 Give details of innovative methodology/technology developed and used for Transfer of Technology during the year: As per the PRA survey, different farming groups are identified, as SHG, FIGs and innovative farmers in the selected villages, a group discussion, group meetings, and participation of the farmers in the KVK activities was increased by giving Mobile Advisory Service to farmers. Regular meeting with the farmers and farm women was conducted. Give details of indigenous technology practiced by the farmers in the KVK operational area which can be considered for technology development (in detail with suitable photographs) 3.9 S. No. 3.10 Crop / Enterprise ITK Practiced Purpose of ITK Indicate the specific training need analysis tools/methodology followed for - Identification of courses for farmers/farm women: PRA survey was conducted in the jurisdiction area of KVK by using different tools to identify technology gap, training needs, enterprises and different natural resources available in the villages and jurisdiction area. Group discussion with the line departments, monthly workshops and in the extension activities conducted to the farmer and farm women. Rural Youth: PRA survey and a thorough discussion with the DIC, group discussion with the youths in the villages. Inservice personnel: A discussion with the extension functioneries at the District monthly workshop of the agriculture department, personel discussion with the extension functioneries. 3.11 Field activities i. ii. iii. 3.12. Number of villages adopted: 3 No. of farm families selected: 450 No. of survey/PRA conducted: 3 Activities of Soil and Water Testing Laboratory Status of establishment of Lab : Soil testing lab given by Manav Vikas Mission (RKVY), Nanded 1. 2. Year of establishment : 2012 Jan, 2013 List of equipments purchased with amount : No purchase of equipment. Sl. No 1 2 3 Name of the Equipment Qty. Cost Mobile Van received from Hon. Dist. Magistrate and Collector, under Manav Vikas Mission, Nanded, in Jan, 2013 Total 3. Details of samples analyzed so far : Details Soil Samples Water Samples Plant Samples Petiole Samples Total 3.13. Date No. of Samples 934 12 --948 No. of Farmers 934 12 --948 No. of Villages 38 8 --46 Amount realized 27920 1200 -28080 Activities under rainwater harvesting (for those KVKs Nature of Activity Title Clie nt (PF/ RY/ EF) No. of Cour ses No. of Participants including SC/ST Fe Ma Tota ma le l le No. of SC/ST Participants M al e Fem ale Tot al Total Participants Ma le Fe ma le Tot al 4.0 IMPACT 4.1. Impact of KVK activities (Not to be restricted for reporting period). Name of specific technology/skill transferred Change in income (Rs.) Before After (Rs./Unit) (Rs./Unit) Use of fertilizer in split doses in cotton 22 35000 46000 Replacement of varieties in safflower 15 23000 27000 Varittal replacement in okra 20 42000 55000 Use of balanced diet to milch animal 26 4200 5600 Us of improved variety in bengalgram 26 32000 48000 NB: Should be based on actual study, questionnaire/group discussion etc. with ex-participants. 4.2. No. of participants % of adoption Cases of large scale adoption Celebration of pola festival in scientific way Pola festival is selebrated on a large scale in Maharashtra .farmers involved almost all animals like working bullocks ,bulls calves in this festival.whilse celebrating the festival applying a varnish to the horns of the animals ,drenching the sweet oil to animal colouring the animal offering the chapatti etc is common traditional practice which is very harmful to the animals but farmers are practicing due to lack of scientific knowledge .application of varnish can cause horn cancer ,drenching the sweetoil can cause pneumonia and application of colours causes allegic reaction to animals and chapatti or puran poli can cause acidic indigestion and gastric disturbances in animals .such things are disclosed amongs the farmers by adopting the kisan goshti and meetings in village Sagroli .peoples they have realize the seriousness of the wrong practices done by them .and followed the kvks advice.onthe day of pola 90% of the farmers they have followed the advice and stopped their routine practice. 4.3 period Details of impact analysis of KVK activities carried out during the reporting 5.0 LINKAGES 5.1 Functional linkage with different organizations Name of organization 1) Vasantrao Naik Marathwada Agriculture University, Parbhani 2) Dept Of Agriculture, Govt Of Maharashtra 3) NABARD. Nanded 4) MAHABEEJ, Nanded 5) Department of Animal Husbandry, Nanded 6) Almost All Questions Answered (aAqua.org) as a crop doctor, software designed by IIT pawai 7) Rallies India Pvt. Ltd, Mumbai 8) Dhanuka Agri tech Ltd, New Delhi 9) Dhan foundation, Chennai 10) Manav Vikas Mission (RKVY) 11) ICRISAT, Hyderabad 12) Doordarshan Kenndra,Mumbai 13) Mahila Arthik Vikas Mandal 14) DRDA 15) Integrated Chield Devleopment Scheme (ICDS) 16) ATMA Nature of linkage Participation of advanced training programmes for the SMS, Action plan meeting, Participation of scientists and officials from different departments in training programmes, melas and other extension activities. Organization of joint training programs as TOF, field activities and extension activities. Participation in SAC meeting and a as guest in programme organized by KVK. Organization of seed production programme with farmers and at KVK farm. Organization of joint training and other extension activities for farmers and extension functionaries of LSS. Worked SMS as an Expert (crop doctor) and partner of aAqua.org for answering the questions asked by farmers To work as PPP, for working to farming community by organizing training to the farmers of their interest. Organization of demonstrations. Collaborative training programme organization. Mobile soil testing van to fulfill the need of soil testing of the jurisdiction area at village level. Demonstrations of sorghum and seed production of sorghum. Memer of the programme planning for rural development of Sahyadri channel Participation in training programme and tehnology week of KVK Participation in training programme and tehnology week of KVK Participation in training programme and tehnology week of KVK Participation in meeting and joint organsiaton of training programme NB The nature of linkage should be indicated in terms of joint diagnostic survey, joint implementation, participation in meeting, contribution received for infrastructural development, conducting training programmes and demonstration or any other 5.2 List special programmes undertaken by the KVK, which have been financed by State Govt./Other Agencies Date/ Month of initiation Name of the scheme 5.3 Programme Training programmes 5.4 S. No. Amount (Rs.) Details of linkage with ATMA a) Is ATMA implemented in your district S. No. 1. Funding agency Yes Nature of linkage Remarks Training preogrammes are being conducted by KVK of Self Help Group and Farmers Commodity Groups Give details of programmes implemented under National Horticultural Mission Programme Exposrure visits under NHM Nature of linkage Joint organization of training cum exposure visits Constraints if any 5.5 Nature of linkage with National Fisheries Development Board S. No. Programme Nature of linkage Remarks NIL 6. PERFORMANCE OF INFRASTRUCTURE IN KVK 6.1 Performance of demonstration units (other than instructional farm) 2013 1 2013 1 75,000 1 Mini Dal mill Fruit Grader Azola Amount (Rs.) Cost of Gros inputs incom 62,000 2 Fodder 2013 6.2 Performance of instructional farm (Crops) including seed production 1 2 Demo Unit Name Of the crop Details of production Year of estt. 2013 Area 4 pits of size1x3x9ft 1hectare Date of sowing Date of harvest 08-032013 08-122013 13/11/201 3 29/11/2 013 12-072013 04-012014 Area (ha) Sl. No. Variety Produce Qty. Azola 70kg 70kg Rs3000 Rs 5700 1)Phule jaywant 2)phule yashwant 3)sampurna 4)gajraj Rs 320000 buds 320000 buds Rs 2000 Rs 320000 Details of production Variety Type of Quantity Produce / qtl Amount (Rs.) Cost of Gross inputs income Cereals Rice Wheat 280 sq.m. 300 sq.m. 0.2 0.2 Pulses Pigeon pea 21/7/2013 02-072014 1.2 2.8 2 0.4 Gram 25/10/201 3 14/2/20 14 3.4 0.2 0.4 0.6 Oilseeds Soybean 16/6/2013 29/6/2013 07-05- 21/10/2 013 28/10/2 013 11-07- 1.4 0.4 0.8 27P31 Grain 1.07 qt. 600 1391 Grain 1.21 qt. 800 1875 Kudrat 11 Kudrat 17 Grain 3.79 qt 2870 6822 Grain 3.78 qt 2870 6804 BDN 708 BDN 711 Vipula BSMR 853 Jaki 9218 Digvija y Vishal BDNG 797 Grain 7.7 qt. 6994 28490 Grain 26.99 qt 16303 110659 Grain Grain 15.06 qt 6.5 qt 11645 3494 55722 31600 Grain 50.2 qt 30762 123124 Grain 0.74 qt 600 1628 Grain Grain 3.68 qt 5.19 qt 1800 5429 9568 13494 MAUS 162 MAUS 158 MAUS Grain 33 qt 21487 112200 Grain 2.5 qt 6150 8500 Grain 5 qt 12300 16500 Remar ks 2013 13/11/201 3 10-092013 2013 04-032014 04-032014 Fibers BT cotton 13/6/2013 0.8 Desi cotton 15/6/2013 Nov.201 3 Nov.201 3 Vegetables Brinjal 17/8/2013 0.2 ha Onion 30/8/2013 30/10/2 013 25/11/2 013 Tomato 30/8/2013 0.1 ha Bhindi 08-062013 08-032013 08-032013 25/10/2 013 23/8/20 13 10-102013 11-062013 Safflower Cauliflower Cabbage 81 PBNS 12 PBNS 40 0.2 Grain 3.8 qt 3564 10640 Grain 7.5 qt 6683 21000 Ajit 155 Phule JLA 794 Fiber 12 qt 19175 60600 Fiber 3.5 qt 3000 17675 Phule Arjun Bhima shubhr a US 440 Fruit 34.75 qt. 11.12 qt. 6623 104250 2050 33360 6823 159210 PBN OK CFC 1522 BC-79 Fruit 4996 40170 Fruit 53.07 qt. 13.39 qt. 0.88 qt. 1200 2640 Leaves 0.60 qt. 1200 1800 1.5 0.2 0.1 ha 0.3 ha 5R 5R Bulb Fruit 6.3 Performance of production Units (bio-agents / bio pesticides/ bio fertilizers etc.,) -Nil 6.4 Sl. No. 6.4 Sl. No Amount (Rs.) Name of the Product Qty Cost of inputs Remarks Gross income Performance of instructional farm (livestock and fisheries production) Name of the animal / bird / aquatics Details of production Breed Type of Produce Amount (Rs.) Qty. Cost of inputs Gross income Remarks 6.5 Rainwater Harvesting Training programmes conducted by using Rainwater Harvesting Demonstration Unit Date Title of the training course Client (PF/RY/E F) No. of Courses No. of Participants including SC/ST Male Femal Total e No. of SC/ST Participants Male Female Total NIL 6.6 Utilization of hostel facilities Accommodation available (No. of beds): Months Title of the training course/Purpose of No. of trainees Trainee days Reason for short fall (if any) stay stayed (days stayed) April 2012 Total May 2012 Total June 2012 Total July 2012 Total August 2012 Total September 2012 Total October 2012 Total November 2012 Total December 2012 Total January 2013 Total February 2013 Total March 2013 Total Grand total 7. FINANCIAL PERFORMANCE 7.1 Details of KVK Bank accounts Bank account With Host Institute With KVK 7.2 Location Sagroli Sagroli Account Number 20243943959 60083823533 Utilization of funds under FLD on Oilseed (Rs. In Lakhs) Item Inputs Name of the bank Bank of Maharashtra Bank of Maharashtra Released by ICAR Kharif Rabi 2012-13 2012-13 --- Expenditure Kharif Rabi 2012-13 2012-13 --- Unspent balance as on 1st April 2013 Extension activities TA/DA/POL etc. TOTAL 7.3 NIL Utilization of funds under FLD on Pulses (Rs. In Lakhs) Item Released by ICAR Kharif Rabi 2012-13 2012-13 Expenditure Kharif Rabi 2012-13 2012-13 Inputs Extension activities TA/DA/POL etc. TOTAL 7.4 NIL Utilization of funds under FLD on Cotton (Rs. In Lakhs) Item Released by ICAR Kharif 2012-13 Inputs Extension activities TA/DA/POL etc. TOTAL 7.5 Unspent balance as on 1st April 2013 Expenditure Kharif 2012-13 Unspent balance as on 1st April 2013 Nil Utilization of KVK funds during the year 2011-12 and 2012-13 (upto Sep. 2012) (yearwise separately) (current year and previous year) 2011-12 Year S. Particulars No. A. Recurring Contingencies 1 Pay and Allowances 2 Traveling allowances 3 Contingencies A Stationery, telephone, postage and other expenditure on office running, publication of Newsletter and library maintenance (Purchase of News Paper and Magazines) B POL, repair of vehicles, tractor and equipments C Meals/refreshment for trainees (ceiling upto Rs.40/day/trainee be maintained) D Training material (posters, charts, demonstration material including chemicals etc. required for conducting the training) E Frontline demonstration except oilseeds and pulses (minimum of 30 demonstration in a year) F On farm testing (on need based, location specific and newly generated information in the major production systems of the area) G Training of extension functionaries H Maintenance of buildings I Establishment of Soil, Plant and Water Testing Laboratory J Library TOTAL (A) B. Non-Recurring Contingencies 1 Works Sanctioned Released Expenditur e 250000 50000 250000 50000 138750 52204 170000 -- 170000 -- 194896 27245 -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- -- ---- ---- ---- --470000 --470000 --413095 A Admin Building 500000 500000 520471 B Farmers Hostel Building 400000 400000 392662 2 Equipments including SWTL and Furniture A Digital Camera 25000 25000 24720 B LCD Projector 100000 100000 30250 C Furniture 100000 100000 119529 D Xerox Machine 100000 100000 45811 E Computer and Accessories 100000 100000 104725 F Fax Machine 20000 20000 19550 G Tractor with Implements 700000 700000 700840 3 Vehicle (Four wheeler/Two wheeler, please specify) 650000 650000 658882 Library (Purchase of assets like books and journals) TOTAL (B) C. REVOLVING FUND -2695000 -2695000 23508 2640948 100000 100000 100000 3265000 3265000 3154043 4 GRAND TOTAL (A+B+C) 2012-13 Year S. Particulars No. A. Recurring Contingencies 1 Pay and Allowances 2 Traveling allowances 3 Office Contingencies A Stationery, telephone, postage and other expenditure on office running, publication of Newsletter and library maintenance (Purchase of News Paper and Magazines) B POL, repair of vehicles, tractor and equipments Sub total 4 Technical Programme A Meals/refreshment for trainees (ceiling upto Rs.40/day/trainee be maintained) B Training material (posters, charts, demonstration material including chemicals etc. required for conducting the training) C Frontline demonstration except oilseeds and pulses (minimum of 30 demonstration in a year) D On farm testing (on need based, location specific and newly generated information in the major production systems of the area) E Training of extension functionaries F Maintenance of buildings G Establishment of Soil, Plant and Water Testing Laboratory H Library I Publication of extension literature for famers and extension functionaries J Honorarium for trainers K Kissan Melas (at KVK Farm) Sanctioned Released Expenditure 4100000 125000 4100000 125000 4085422 87282 450000 0 450000 450000 0 450000 336014 113612 449626 -- -- 14415 -- -- 26100 -- -- 23750 ------ ------ 49262 1300 12191 -11112 ---- ---- 27000 3000 31805 Sub total TOTAL (A) B. Non-Recurring Contingencies 1 Works 200000 4875000 200000 4875000 199935 4822265 1000000 1000000 999718 2 Equipments including SWTL and Furniture -- -- -- 3 Vehicle (Four wheeler/Two wheeler, please specify) -- -- -- Library (Purchase of assets like books and journals) TOTAL (B) C. REVOLVING FUND -1000000 -1000000 -999718 -- -- -- 5875000 5875000 5821983 4 GRAND TOTAL (A+B+C) 2013-14 Year S. Particulars No. A. Recurring Contingencies 1 Pay and Allowances 2 Traveling allowances 3 Office Contingencies A Stationery, telephone, postage and other expenditure on office running, publication of Newsletter and library maintenance (Purchase of News Paper and Magazines) B POL, repair of vehicles, tractor and equipments Sub Total 4 Technical Program me A Meals/refreshment for trainees (ceiling upto Rs.40/day/trainee be maintained) B Training material (posters, charts, demonstration material including chemicals etc. required for conducting the training) C Frontline demonstration except oilseeds and pulses (minimum of 30 demonstration in a year) D On farm testing (on need based, location specific and newly generated information in the major production systems of the area) E Training of extension functionaries F Maintenance of Farm G Establishment of Soil, Plant and Water Testing Laboratory H Library I Publication of extension literature for famers and extension functionaries J Honorarium for trainers K Kiss an Melas (at KVK Farm) Sub Total Sanctioned Released Expenditu 6000000 200000 6000000 200000 591 15 500000 -500000 500000 -500000 28 21 49 -- -- 2 -- -- -- -- 5 ------ ------ 4 ---200000 ---200000 3 2 19 5 A B C Technology Demonstration On Pulses Red gram 30 Demon, Under kharif@ Rs-4000/-Demo Green gram 30 Demon .under Kharif @ Rs-2000/-/Demo Bengal gram 30 Demon. under Rabi @ Rs-4000/- Demo. Sub Total TOTAL (A) B. Non-Recurring Contingencies 1 Works 300000 7200000 300000 7200000 29 706 449 4500000 4500000 2 Equipments including SWTL and Furniture -- -- 3 Vehicle (Four wheeler/Two wheeler, please specify) -- -- Library (Purchase of assets like books and journals) TOTAL (B) C. REVOLVING FUND -4500000 -4500000 -- -- 11700000 11700000 4 GRAND TOTAL (A+B+C) 7.6 Status of revolving fund (Rs. in lakhs) for the three years Year April 2010 to March 2011 April 2011 to March 2012 April 2012 to March 2013 April 2013 to March 2014 8.0 Opening balance as on 1st April --187584 -70619 Income during the year Expenditure during the year -208503 711473 1622055 -20919 969676 1674217 Net balance in hand as on 1st April of each year -187584 -70619 -122781 Closing balance of farm produce Net balance -222169 447475 187584 151550 324994 Please include information which has not been reflected above (write in detail). 1. DAMAGES DUE TO HAILSTORM IN NANDED DISTRICT AND EFFORTS BY KVK SAGROLI th From 26 feb, 2014, Nanded dist was suffered from the Hail storms particularly, Biloli, Degloor, Kandhar, Loha, Naigaon, Hadgaon, Umari, Himatnagar , Kinwat, Mahur, affected by hailstorms with the area of 62000 ha.It destroyed the rabi standing crops as Bengal gram, Jowar, safflower, wheat and Kharif crops as irrigated cotton, sugarcane up to 90 to 100%. A fruit drop in mango, collapse of banana plants, and vegetable gets affected up to the mark of 70 to 80 percent. Livestock also get injured and in some part sheep and goats lost their lives, destroyed the houses, cottages and farm sheds in varying intensity. Name of Affected Tahsil No. of villages affected Total area affected 9loss above 50 %) Total area affected 9loss below 50 %) 1.Nanded 2.Ardhapur 3. Loha 4.Biloli 5.Hadgaon 6. Kinwat 7.Dharmabad 8.Mahur 9.Umari 10 H. Nagar 76 22 9 68 41 77 6 11 7 3 31 143 466 4375 7093 3205 350 11 343 218 9527 2160 156 2713 4470 2224 0 554 312 0 449 1156 11Kandhar 12Naygaon 13Degloor 14Mudkhed Total 66 15 7 20 5422 3050 1484 90 26281 0 1540 100 1980 25736 KVK scientist visited to the affected area of Biloli (Shewala, Shelgaon, Kesrali, Rampur, Adampur, Khadgaon, thadisawali, Minky and Mutnyal), Degloor (Shewala, Shelgaon, Kotekallur), and Naigaon (Kedarwadgaon) block of Nanded district. Found total destructions of houses, tins, cottages, total lodgeing of the Jowar, and total loss of Bengal gram, Wheat, Safflower, Cotton, sugarcane and vegetable. Also found the fruit drop in mango, also some plots of banana. To get awareness among farmers, KVK scientists given the radio talk on the Nanded akashwani under head 1. Crops damages due to hailstorm in Nanded dist and contingencies to be taken (dated-7/3/2014) 2. Health care and disease management of the animals in hailstorm affected area (dated-8/3/2014) 3. News paper coverage in agro one news paper (Dated 10/3/2014) written under title “Hailstorm predisposes the animals for different life threatening diseases and its management” 4. Organized animal health camps, group discussions, etc. 5. KVK has given the forecasting regarding storm and rains for near future at regular interval by sending SMS on Kisan Port on mobile. It cannot be evaluated loses due to death of animals, poultry birds and destructions in houses which depends on the situation and entity. 8.1 Constraints (a) (b) (c) Administrative Financial Technical Annexures District Profile - I Include the details of 2. General census : Population data Sr. No. 01 02 03 04 05 Particulars Total Population Male Female Rural Urban Number 28,76,000 14,81,000 13,95,000 21,87,000 6,89,000 Population of the Schedule Caste/Schedule Tribes Sr. No. 01 02 Particulars Schedule Caste Schedule Tribes Number 4, 98,000 (17.25%) 2, 53,000(8.8 %) Literacy: Sr. No. 1. 2. 3. Particulars Total Literacy rate Male Female Percentage to total population 68 81 55 Soil Types: Sr. No. 1. 2. 3. Particulars Deep black soil Medium deep black soil Shallow black soil Area (‘000’ ha) 394.65 101.12 576.26 Percentage to total land 36.81 9.43 53.75 Irrigation facilities and area covered: Sr. No. Particulars 01 Major rivers Godavari, Lendi, Manyad, Manjra, Painganga Kayadhu Manyad, Lendi, Babhli 02 Major irrigation Project Vishnupuri, 03 Medium Projects Kardkhed, Barul, 04 Net irrigated area 1, 12,000 ha (12.16%) 05 Gross irrigated area 1,25,000 ha Climate profile: Sr. No Particulars 01 Rainfall 02 Temperature 03 Humidity 993.1 mm(46rainydays) 28.3oCto45.9oCMaximum,10.3oCto27.6oCMinimum 70-87%-Morning and41-68%Evening 1. Agricultural and allied census Sr. No. Particulars Number 01 Geographical area 10,33,100 ha 02 Cultivable area 8,08,700 ha 03 Forest area 85,000 ha 04 Land under non-agricultural use 35,000 ha 05 Permanent pasture 50,000 ha 06 Cultivable waste land 35,000 ha 07 Land under miscellaneous trees crop 6,000 ha 08 Barren and uncultivable land 19,000 ha 09 Current fallows 73,000 ha 10 Other fallows 24,000 ha Land Use pattern: Particulars Net sown area Area sown more than once Gross cropped area Cropping intensity (%) Number 7,11,000 ha 1,00,000 ha 8,11,000 ha 114 2. Agro-climatic zones Sr. No Agro-climatic Zone Characteristics 1 Central Maharashtra Plateau Zone /Assured Rainfall Zone (VII) Climatic condition- Maximum temp. 41 C Minimum temp. 21 C. Average annual rainfall- 700 to 900 mm 75 % rains received Soil type- Soil colour ranges from black to red. Type- 1) vertisols 2) entisols and 3) incept sols PH 7-7.5. Crops and cropping pattern- In kharif Rainfed cotton(32.24%) ,soybean (25.40%), Kharif Jawar (17.77%), Pigeon pea(7.8%), Black gram(7.38%), Greean gram (6.06%) are predominant crops .In Rabi sesson Bengal gram(44.87%), Rabi Jawar (37.39%),Wheat(10.12%), Safflower(5.72%) Sugarcane and summer groundnut are taken on availability of irrigation. 3. Major and micro-farming systems Major crops grown in district: Major Kharif crops:Soybean, rain fed cotton,Kharif Jawar, pigeon pea, black gram,green gram Major Rabi crops:Chick pea,Rabi Jawar,Wheat,Safflower. Major summer crops: Summer groundnut. Cash crops: Sugarcane,Irrigated cotton,Banana,Turmeric Minor crops: Maize,Rice,Sesamum,Niger,Sunflower, Castor. Cropping systems: Intercropping systems:Cotton+Pigeon pea(6:1/8:2),Soybean+Pigeon pea(9:1/12:3),Cotton+Black gram/Green gram/soybean (1:1),Kharif Jawar+Pigeon pea(9:1/12:3),Turmeric+Castor(6:1/8:1). Mixed cropping:Soybean+Jawar,Chick pea+Rabi Jawar,Chick pea+Safflower, Wheat +Mustard. Cropping pattern: Single crop rain fed: Cotton,Kharif Jawar. Double crop rain fed: Soybean-Chick pea/Safflower, Double crop Irrigated: Irrigated Cotton +summer groundnut,Soybean/Kharif Jawar-Wheat, Soybean-Chick pea Multi crop Irrigated: Soybean-Chick pea- Summer Groundnut, Soybean – Wheat-summer vegetables Integrated farming systems: 1. Crops+ 1 to 2 milch non-descriptanimals+ compost 2. Crops+Vegetable production, Crops +Fruit production 3. Crops+Back yard poultry 4. Crops + Goatery 4. Major agriculture and allied enterprises Sr. No. 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Farming system/enterprise Only Agriculture (most of the farmers) Agriculture + Animal Husbandry (1-2 Deshi milch animals) Agrilculture + Poultry (10-20 deshi birds) Agriculture + Goatery (2-3 goats) Agriculture+ Horticulture (Mango, Guava, Sapota, Sweet orange etc few plants) Agriculture + Vegetable production on small scale. Nonfarm enterprises – sewing and stitching, Rope making bamboo sheets. Agro-ecosystem Analysis of the focus/target area - II Include 1. Names of villages, focus area, target area etc. Krishi Vigyan Kendra, Sagroli, is established in October 2011 (Vide Sanction Letter No. F.N0. 5-2/2009-AE II, dated 4/10/2011, ICAR, New Delhi-12), but actual works started in July 2012. It is located at Shardanagar, Sagroli and about 80 km away from Nanded head quarter. 2. Survey methods used (survey by questionnaire, PRA, RRA, etc.) 3. Various techniques used and brief documentation of process involved in applying the techniques used like release transect, resource map, etc. 4. Analysis and conclusions 5. List of location specific problems and brief description of frequency and extent/ intensity/severity of each problem Major Problems identified in operational area: 1. Agronomy a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. Unavailability of seeds of improved variety. Problematic soils. Unawareness of improved technology in cultivation of agronomical crops. Very less area under micro irrigation in cash crops. Unavailability of bio fertilizers. Unawareness about soil testing and lack of soil testing facility. Unavailability of timely and quality agriculture inputs. Lack of market facilities and linkages. i. Un- organized farmers. j. Lack of location specific meteorological predictions. 2. Horticulture a. Low attraction towards cultivation of fruit and vegetable crops. b. Unawareness about flower crops cultivation. c. Lack of proper nutrition and water management d. Limited area under spices and medicinal crops. e. Low yield in vegetable production. f. No use of poly house technology for vegetable and flower production. 3. Plant Protection a. Unawareness about IPM, and IDM technology to increase productivity of the crops. b. Injudicious use of pesticides and fungicides to control pest and diseases. c. Less awareness about to use of bio-fertilizer for seed treatment and use of biopesticide, bio-fungicide. d. Less awareness about technical knowledge regarding insecticidal and fungicidal formulation e. Less awareness about use of Need based bio pesticides 4. Animal Science a. Unawareness about the importance of mineral mixture in lactating animals. b. Anoestrous, emaciation and hypogalactia in livestock. c. Lack of marketing facilities for livestock products and by products. d. Lack of expert veterinary services. e. Less fodder production coupled with low quality grasses. f. Increasing feed cost. g. Imbalanced feeding practices. h. No supplementary diet. i. Poor animal husbandry practices. j. High mortality in new born kids and calves. 5. Home Science a. Heavy Drudgery work for farm women. b. Protein Energy Malnutrition (PEM) among preschool children c. Anemia and Bone problems in women d. Lack of knowledge regarding processing of food. e. Lack of knowledge regarding processing and consumption of soybean f. No economic empowerment among women g. Unaware about preservation of nutrition while cooking. h. No knowledge about value addition. i. Early marriage with early pregnancy. 6. General Problems a. Unavailability of the communication media, market information. b. Unawareness about use of mass media. c. Lack of knowledge about the use of credit facilities. d. Poor record keeping of self help group. e. Improper functioning of the self help groups. f. Improper management of budget of the farm enterprises. g. Lack of linkages between the farmers, bankers and development department. h. Unawareness about information & communication technology, i. Lack of extension material for the reading. Lack of farmer’s organisations in villages. 6. Crop Matrix ranking of problems Problems Ranking Agronomy Cotton Soybean Kharif Jawar Urad / Mung Pigeon pea Bengal Gram Safflower Rabi Jawar Low Productivity under rain fed condition. Wrong selection of verities/Hybrids as per soil type, farming situation (Rain fed/Irrigated) Inadequate use of fertilizers, Do not apply fertilizers in split doses specially N. Yield losses due to weed infestation. No use of micronutrients & organic fertilizers in INM Crop spacing and plant population problem No seed treatment Lack of improved high yielding varieties especially nonShattering type. Low productivity. Inadequate use of fertilizers and no use of Sulphur containing fertilizers. Yield losses due to weed infestation. No seed treatment Low productivity. Inadequate use of fertilizers. Lack of in situ soil moisture conservation measures. Lack of improved high yielding varieties . Improper crop spacing ( Overcrowding plant population) Yield losses due to weed infestation. No seed treatment Lack of improved high yielding varieties. Low Productivity. Inadequate use of fertilizers. Improper sowing time. Yield losses due to weed infestation. No seed treatment. Lack of improved high yielding varieties specially early under rain fed condition. Inadequate use of fertilizers or very less use of fertilizers. No seed treatment Traditional method of sowing. Pod borer infestation. Lack of improved high yielding verities. Low productivity. Inadequate use of fertilizers. Traditional sowing methods. Mostly rain fed crop and if irrigated irrigation at improper stages. No seed treatment. Nipping practice not followed. Lack of improved & high yielding varieties especially non spiny resistance to aphids, leaf spot. Inadequate use of fertilizers. Low productivity. Yield losses due to weed infestation. Lack of in situ soil moisture conservation measures. Sucking pest problem specially aphids Lack of improved & high yielding varieties. I II III IV V VI VII I II III IV V I II III IV V VI VII I II III IV V VI I II III IV V I II III IV V VI VII I II III IV V VI I Wheat Summer Groundnut Low productivity. Lack of in situ soil moisture conservation measures. Inadequate use of fertilizers. Traditional sowing methods and improper crop spacing. Yield losses due to weed infestation. No seed treatment & crop lodging. Lack of improved & high yielding varieties. Low productivity. Inadequate use of fertilizers, less awareness about INM. Improper sowing time. Yield losses due to weed infestation. Irrigation at improper stage of growth and less no of irrigations. Less awareness about seed treatment. Lack of improved & high yielding varieties Inadequate use of fertilizers, less awareness about INM No use of Gypsum in nutrient management. Irrigation at improper stage of growth and less no of irrigations. Yield losses due to weed infestation. Less aware about improved cultivation practices like poly mulching, bed system of planting etc. II III IV V VI VII I II III IV V VI VII I II III IV V VI Horticulture Mango Sweet Orange Banana Custard Apple Papaya Guava Chilli Brinjal Tomato Low yield More fruit drop Irregular fruiting Fruit Drop Dieback Irregular bearing Micronutrient deficiency Irregular fruit harvesting Imbalance use of fertilizers Low bunch weight Insect pest attack Low yield Unawareness about other high yielding varieties Uneven shape and size of fruits Market unavailability Unavailability of storage facilities Nutrient deficiency in orchards Leaf curl virus Traditional method of planting Irregular bearing and low yield Micronutrient deficiency. Low yield Imbalanced fertilizer management Disease and pest attack and heavy cost management Fruit and shoot borer Pest attack Medium to lower yield Traditional method of planting Disease attack problems and fruit rotting Nutritional deficiency and imbalanced fertilizer management I II III I II III IV I II III IV I II III IV V I II III I II I II III I II I II III Turmeric Gaillardia Marigold Nutrient deficiency Uneven plant growth Storage problems High cost of cultivation Pest attack Disease problems Low yield No new varieties Traditional planting I II III IV I II III I II Aphids Jassids Thrips Mealy bug Spodoptera Pink bollworm Spodoptera Girdle beetle Semilooper Anthraxnose Pod fly Helicoverpa armigera Wilt Helicoverpa armigera Cutworm BPH WBPH Stem borer Shoot borer Stem borer Pyrilla Wooly aphid Rhizome fly Leaf spot of turmeric Wheat stem borer Termite Loose smut Grain smut Stem fly Tikka disease Thrips Aphids stem borer mango hopper root and stem rot Little leaf. Fruit fly Mealy bug Fruit sucking moth Die back Nematodes Citrus canker High High High Nil High Low High low High High High High Low High Medium High Medium High Medium Medium Low High Medium Low Medium Low High Medium Medium Low Medium Medium High Medium Medium Medium Low High Medium Low Medium Plant Protection Cotton Soybean Red gram Bengal gram/Chickpea Paddy Sugarcane Turmeric Wheat Rabi sorghum Ground nut Mango Papaya Banana Guava Sweet orange Citrus Brinjal Okra Chilli Cruciferous Vegetables Lemon butterfly Wilt Shoot and Fruit borer White fly Little leaf Nematodes Fruit borer Jassids Yellow vein mosaic Thrips Fruit borer Damping off Diamond Back MothAphids Cut Worm Cabbage butterfly Damping off- Medium High High High Medium Low High High Low High Medium low High Medium Low High Medium Home Science Health and nutrition Anaemia in women and malnourishment in children Negligence for women health No knowledge about value addition for better health. Early marriage with early pregnancy. Reproductive health problem of girls and women. Drudgery Unaware about new agricultural technologies while doing agri. Related tasks. Unavailability of small Agril hand tools Economic Unaware about the small scale enterprise empowerment Unavailability of credit facilities to farm women Lack of technical know-how about small scale enterprise. I II III IV V I II I II III Veterinary Science Poultry Goats /sheep Cattle / buffaloes 7. Lack of technical knowledge High cost of feed and fear of infectious diseases Lack of marketing facilities nearby. Fluctuations in selling prices Poor quality of grasses, mortality in new born kids No supplementary diet No breeding strategies Scarcity of green fodder, mortality in new born calves Imbalanced feeding formulations. Unavailability of dairy and market for milk and milk products. Lack of knowledge about animal husbandry practices List of location specific thrust areas Crop/Enterprise Thrust area Agronomy Cotton Integrated Nutrient Management Integrated weed management Water management I II III IV I II II I II III IV Soybean Kharif Sorghum Pigeon pea Black gram/Green gram Bengal gram Rabi Jawar Wheat Safflower Summer groundnut Integrated pest management Use of Improved varites /Hybrids Integrated Nutrient Management Integrated pest management Integrated Nutrient Management Integrated weed management Integrated pest management Integrated Nutrient Management Integrated weed management Integrated pest management Use of Improved varites/Hybrids. Integrated Nutrient Management Integrated weed management Integrated pest management Use of Improved varites/Hybrids Integrated Nutrient Management Integrated weed management Integrated pest management Use of Improved varieties/Hybrids Integrated Nutrient Management Soil and water conservation. Integrated pest management Use of Improved varieties/Hybrids Integrated Nutrient Management Integrated weed management Integrated pest management Water Management. Use of Improved varieties/Hybrids Integrated Nutrient Management Soil and water conservation. Integrated pest management Integrated pest management Integrated Nutrient Management Integrated weed management Water Management. Horticulture Integrated nutrient management in fruit crops. Value addition of fruit and vegetable Entrepreneurship development in rural youths. Promotion of hi-tech horticulture. Seed and seedling production of vegetable and fruits. Avail marketing to farmers through group activity. Increase productivity of vegetable, fruits and flower crops by adopting advance production technology. Plant Protection Use of IPM, and IDM technology to increase productivity of the crops. Create awareness about to use of bio-fungicide for seed treatment. Building judgement about selection of insecticide and insecticide fungicide formulation. Implementation of bio pesticide use. Home Science Improvement in nutritional status of women and children Increasing self-employment by value addition through agro based small scale enterprises. Reduce drudgery by popularizing hand operated agricultural tools among farm women. Balanced diet through kitchen gardening and available food items. Awareness about importance of hygiene and sanitation. Awareness of consequences of early marriage. Veterinary Science Increase in area under fodder crop and productivity of livestock. Feed cost reduction through exploiting nutrient efficient local resources. Self-employment generation through income generating activity. To increase productivity and to reduce metabolic diseases through proper feeding and balanced diet. Corrective measures for various common ailments in livestock. Better profitability through market driven production. 8. List of location specific technology needs for OFT and FLD Sr. No. Agronomy Technology Intervention Varietal evaluation of improved and non spiny verities in Safflower. a) PBNS-40 (Parbhani-40) Varietal evaluation of improved varieties in Bengal gram. 2. b) Digvijay Weed management through post emergence herbicides in wheat. 3. a)PoE-Metasulphuraonmetyl 20 WP@20 gml/ha. Horticulture OFT Fruit set management in mango through fertilizer management Varietal assessment in okra (PBN-OK-1) Plant Protection OFT OFT 1 Management of shoot and fruit borer on brinjal (Assessment) 2 Management of okra fruit borer. Home Science OFT FLD 1. FLD FLD 1 Assessment of Revolving milking stool and stand to increase work efficiency of women at the time of milking the animals. 2 To control anemia in adolescent girls by using Iron rich roosted rice flakes chiwda Demonstration of Smokeless Chulla to improve work efficiency of 3. women while cooking. To demonstrate Vaibhav sickle, MKV sickle, Lakshmi sickle to 4. improve work efficiency of women while weeding Veterinary Science Use of hormonal preparations to regulate estrus in cattle and buffalo Assessment of Bordeaux mixture to cure dermatophytosis in cattle Better forage yield by cultivating jaywant napier fodder crop Increase in milk yield by using mineral mixture in milch animals Enhancing the quality of dry grasses /straw by Urea treatment 1 2 3 4 5 9. List of location specific training needs Agronomy Importance of soil testing in fertilizer application. In situ soil moisture conservation measures. Use improved verities/hybrids rather than local one. Integrated nutrient management. Integrated weed management especially chemical weed control. Integrated crop management. Use of bio fertilizers in nutrient management. Importance of micronutrients and their management. Cropping system management. Seed production programs in different crops. Irrigation management especially at critical stages of crop growth. Horticulture Preparation to turmeric cultivation Dryland fruit production in custard apple and ber Vegetables nursery management in Brinjal, Tomato and Chilli planting of jasmine and tuberose Marigold flower production INM in cole crops Nutritional care in papaya and banana Vegetables growing under protected cultivation Pre and post harvest management in chilli, bhendi Bahar management in sweet orange Care of indoor and outdoor ornamental plants Vegetables growing under protected cultivation Plant Protection Use of IPM, IDM technology. Use of Bio-Pesticide and Bio-fungicide Use of organic inputs i.e. NSKE Use of Pheromone Traps to monitor and mass trapping of moths. Employment generation (Apiculture/ Lac culture) Home Science Care and development of preschool children Soybean processing Fruits processing for entrepreneurship development Use of user- friendly equipments to reduce the drudgery. Fuel saving devices in kitchen OFT OFT FLD FLD OFT OFT FLD FLD FLD Income generation through masala processing Care and development of preschool children Store grain problems at household level Care to be taken while cooking to save nutrient losses Low cost nutritious diet for adolescent girls personal hygiene in girls for good health Anemia in girls and women Cereal processing Vegetable processing to control the losses Veterinary Science 1. Cattle and buffalo urea treatment to straw to increase its nutritive value Increase the productivity of milch animals. Care and management of new born kids and calves. Silage making. Scientific milking methods for men and women farmers. Awareness about use of mineral mixture in dairy animals. Care and management of sick animals. Importance of deworming and vaccination in animals. Prevention and care of HS, FMD. Common ailments and its cure. First aid of commonly observed ailments in animals. 2. Sheep And Goats 3. Income Generating Activity (Poultry, Goatry, Dairy and Vermi composting) Use of concentrate for weight gaining in bucks. Care and management of sick animals. Deworming and vaccination schedule for sheep and goat. Bacterial and viral diseases and its first aid in sheep and goat. Poultry Scope and importance of poultry farming. Poultry diseases and its prevention. Hands on practice of poultry vaccination. Feed formulations for broiler poultry. Backyard poultry farming for rural women. Technology Inventory and Activity Chart - III Include 1. Names of research institutes, research stations, regional centres of NARS (SAU and ICAR) and other public and private bodies having relevance to location specific technology needs Inventory of latest technology available * 2. Sr. No Technology Crop/enter prise Year of release or recommendatio n of technology Safflower -- MAU, Parbhani MAU/MPKV Krishi dainandani Bengal Gram -- MPKV Rahuri,MAU Parbhani MAU/MPKV Krishi dainandani Wheat -- MPKV Rahuri MPKV Rahuri Source of technology Reference/citation Agronomy 1. 2. 3. Varietal evaluation of improved and non spiny verities in Safflower. b) PBNS-40 (Parbhani40) Varietal evaluation of improved varieties in Bengal gram. c) Digvijay Weed management through post emergence herbicides in wheat. a)PoEMetasulphuraonmetyl 20 WP@20 gml/ha. Horticulture 4. mango -- MKV Parbhani MKV Parbhani chilli -- MKV, Parbhani MKV Parbhani China aster Chilli --- MPKV, Rahuri TNAU, Periyakulam MPKV, Rahuri TNAU, Periakulam Plant Protection IPM 8. IPM 9. Home Science Brinjal Bengal gram -- MPKV, Rahuri MKV Parbhani 10. Soya poha laddu Health 11. 12. 13. Smokeless Chula Kitchen Garden Revolving milking stool and stand Health Health Drudgery 5. 6. 7. Use of scheduled fertilizer at proper time Varietal assessment in chilli China aster introduction Paired row planting of Chilli -College of home sci., MAU, Parbhani AARTI,Pune -College of home sci., MAU, Parbhani Krishi Diary Krishi Diary Folder, College of home science MAU Parbhani AARTI, Pune Folder, College of home science MKV, Parbhani Folder, College of home science MAU Parbhani MPKV, Rahuri MAFSU, Nagpur MAFSU, Nagpur Krushi dainandini-2012 MAFSU, Folder - 2000 MAFSU, Folder - 2000 AARTI, Pune Folder, College of home science MKV, Parbhani Veterinary Science 14. 15. 16. Better forage yield Disease Management Oestrus Management 3. Cattle Cattle Cattle Activity Chart 2010 2000 2005 Crop/Animal/E nterprise Problem Cause Solution Activity Reference of Technology Agronomy A) Kharif Crops Wrong selection Unawareness about Cotto of selection of n verities/Hybrids var/Hybrids as per as per soil type, soil type, farming farming situation situation. (Rainfed/Irrigated ) Low productivity Yield losses by weed infestation. Inadequate use of fertilizers. Do not apply fertilizers in split doses specially N. Make awareness among farmers regarding different types of verities/hybrids and its use as per soil type, farming situation through training. Mostly rain fed crop INM. Inadequate use of Proper selection fertilizer and do not of var/Hyb as per apply fertilizers in farming situation, split doses especially soil type. N. Weed Management No use of Micronutrients, through Herbicide. Weed infestation. Lifesaving Problem in varietal irrigation at selection as per proper stages. farming situation, soil type. IPM for sucking complex. Sucking complex problem. Use of micronutrients for Reddening different phenomenon. deficiencies especially reddening. Soil test based fertilizer application in split doses. Only depend on Weed manual weeding management through herbicide Availability of labor as cheapest as costly operation. method. Less awareness about herbicide use. Make awareness among farmers about new herbicides and its use. Imbalanced INM. fertilizers Soil test based application fertilizer Less awareness application in about soil test based split doses. fertilizer application. Training FLD OFT MAU, Parbhani FLD OFT Training Radio talk Newspap er coverage Field days MAU, Parbhani OFT FLD Training MAU, Parbhani OFT FLD Training. MAU, Parbhani Crop spacing and plant population problem Only use of NPK fertilizers. No use of micronutrients. Most of the farmers fallow traditional spacing. Unawareness about recommended crop spacing. No seed treatment Unawareness. Unavailability of Bio fertilizers Soyb Lack of improved Use of only JS-335 ean varieties Non availability especially on other improved var scattering type. other than JS-335. Low productivity. Use of traditional var(JS-335) Inadequate use of fertilizer and no use of sulphur containing fertilizers. Mostly rain fed crop Weed infestation. Insect pest problem. Yield losses by weed infestation Only depend on manual weeding Availability of labor as costly operation. Less awareness about herbicide use. Training to farmers about recommended crop spacing. Recommended crop spacing trails through FLD/OFT. Awareness through training. Make available bio-fertliizers. Make aware to farmers regarding improved var through trainings. Make available seed to farmers through FLD/Seed production programs especially non scattering type like MAUS-71, 81. INM. Introduction of Improved var. Weed Management through herbicide. Lifesaving irrigation at proper stages. IPM Application of sulphur containing fertilizers. Weed management through herbicide as cheapest method. Make awareness among farmers about new FLD OFT Training. MAU, Parbhani Training. FLD MAU, Parbhani FLD* Training. Training FLD OFT FLD OFT* Training. MAU, Parbhani MAU, Parbhani MAU, Parbhani No seed treatment Unawareness. Availability of bio fertilizers Khari Lack of improved f varieties Unawareness about Jawar improved var. Unavailability of improved seeds. Low productivity Use of traditional var. Inadequate use of fertilizer Mostly rain fed crop No in situ soil moisture conservations measures. Weed infestation. Insect pest problem Use of traditional seed drill. Sowing of crop 30*10 cm results in overcrowding plant population. No seed treatment Less awareness and availability problem Use of modern seed drill. Sowing of crop on recommended spacing i.e. 45*15 cm. Seed treated with 300 mesh sulpher @ 4 gm/kg + Azectobacter @ 25 gm /kg. Lack of improved Unawareness about Make awareness varieties. improved var and among farmers only use of local var. regarding improved verities Non Availability of through trainings. improved seeds. Make available seed to farmers through FLD and Seed production Improper crop spacing. Gree n gram and black gram herbicides and its use. Awareness through training. Make available bio-fertilizers. Make awareness among farmers regarding improved verities through trainings. Make available seeds of improved Var/Hyb to farmers through FLD and Seed production programs. INM. Introduction of Improved var. In situ moisture conservation measures. Weed Management through Herbicide. Lifesaving irrigation at proper stages. Training. OFT. FLD OFT Training. MAU, Parbhani MAU, Parbhani OFT FLD Training. MAU, Parbhani OFT FLD Training. MAU, Parbhani OFT Training. MAU, Parbhani FLD OFT MAU, Parbhani Low productivity. No seed treatment Pigeo Lack of improved n pea & high yielding varieties Inadequate use of fertilizers or very less use of fertilizers. No seed treatment B) Rabi crops programs. Use of traditional INM. verities. Introduction of Improved var. Inadequate use of fertilizer. Weed Improper sowing Management time through Herbicide.. Weed infestation. Seed treatment of Late sowing results rhizobium in more pest problem especially Proper sowing sphingid moth and time. PM No seed Control measures treatment for Sphingid moth and Powdery mildew. Timely sowing before 8 July Unawareness. Use of rhizobium @ 25 gm/kg of Unavailability of bio seed. fertilizers Make available bio fertilizers. Unawareness about Make awareness improved var and among farmers only use of local var. regarding improved Non Availability of verities through improved seeds. trainings. Make available seed to farmers through FLD and Seed production programs. Imbalanced INM. fertilizers Soil test based application fertilizer application in Less awareness about soil test based split doses. fertilizer application. Only use of NPK fertilizers. No use of micronutrients. Unawareness. Use of rhizobium @ 25 gm/kg of Unavailability of bio seed. fertilizers Make available bio fertilizers. FLD OFT Training MAU, Parbhani Training. OFT. MAU, Parbhani FLD* OFT MAU, Parbhani OFT FLD Training. MAU, Parbhani Training. OFT. MAU, Parbhani Beng al gram Lack of improved Unawareness about varieties improved var. Non Availability of improved seeds. Low productivity. Use of traditional verities. Inadequate use of fertilizer Mostly rain fed crop Weed Infestation. Pod borer problem Yield losses by weed infestation Only depend on manual weeding Availability of labour as costly operation. Less awareness about herbicide use. Inadequate use of Roughly fertilizers fertilizers application Less awareness about soil test based fertilizer application. Only use of NPK fertilizers. No use of micronutrients. Irrigation to crop Less awareness at improper stage about critical stages of crop growth of irrigations. No use of life saving irrigation. Awareness among farmers regarding improved verities through trainings. Make available seed to farmers through FLD/Seed production programs. INM. Introduction of Improved var. Weed Management through Herbicide. Life saving irrigation at proper stages. IPM. Weed management through herbicide as cheapest method. Make awareness among farmers about new herbicides and its use. INM. Soil test based fertilizer application FLD* Training Training FLD OFT Radio talk MAU, Parbhani Training FLD OFT MAU, Parbhani Training FLD OFT MAU, Parbhani Irrigation at Critical stages of crop. Sowing of gram under irrigated condition instead rain fed. Use of micro irrigation methods like Sprinkler for efficient use of Training FLD OFT MAU, Parbhani MAU, Parbhani Indigenous implement use . Less awareness about modern methods of sowing like sowing on Beds and use of improper spacing spacing. No seed treatment Unawareness. Availability of Biofertilizers Traditional methods of sowing Saffl Lack of improved ower varieties Unawareness about especially non improved verities.. spiny. Non Availability of improved/ non spiny verities. Spiny verities difficult to harvest. Low productivity. Use of traditional var. Inadequate use of fertilizer Mostly rain fed crop Weed Infestation. Pod borer problem Inadequate use of Roughly fertilizers fertilizers application Less awareness about soil test based fertilizer application. Only use of NPK fertilizers. No use of micronutrients. Yield losses by Only depend on weed infestation manual weeding Availability of labor as costly operation. Less awareness about herbicide use. water. Use of improved seed drill. Adopt proper spacing. Sowing on beds. Awareness through training. Make available bio-fertliizers. Make aware to farmers regarding improved var through trainings. Make available seed to farmers through FLD/Seed production programs. INM. Introduction of Improved var. Weed Management through Herbicide. Life saving irrigation at proper stages. IPM. INM. Soil test based fertilizer application Weed management through herbicide as cheapest method. Make awareness among farmers about new herbicides and its Training FLD OFT MAU, Parbhani Training. FLD MAU, Parbhani OFT* MAU, Parbhani Training Training Field day Training FLD OFT MAU, Parbhani Training FLD OFT MAU, Parbhani MAU, Parbhani Sucking pest Use of susceptible problem specially verities. aphids. Less use of plant protection measures. Rabi Lack of improved Jawar varieties Unawareness about improved var. Non Availability of improved seeds. Low productivity. Use of traditional var. Inadequate use of fertilizer Mostly rain fed crop No in situ soil moisture conservations measures. Weed Infestation. Insect pest problem Lack of in situ soil conservation measures. Unawareness about these measures. Inadequate use of Roughly fertilizers fertilizers application Less awareness about soil test based fertilizer application. Only use of NPK fertilizers. No use of micronutrients. Traditional Use of traditional use. Use of resistance var. Apply plant protection measures especially for aphids. Make awareness among farmers regarding improved verities through trainings. Make available seed to farmers through FLD/Seed production programs. Training FLD OFT MAU, Parbhani Training FLD MAU, Parbhani Training FLD OFT MAU, Parbhani Make awareness about different measures. Make basins (10*20 sq.m) in fields before sowing of crop for rain water harvesting. INM. Soil test based fertilizer application Training FLD OFT MAU, Parbhani Training FLD OFT MAU, Parbhani Use of modern Training MAU, INM. Introduction of Improved var. In situ moisture conservation measures. Weed Management through Herbicide. Life saving irrigation at proper stages. sowing method and improper crop spacing. Yield losses by weed infestation. seed drill. Sowing of crop 30*10 cm results in overcrowding plant population. Only depend on manual weeding Availability of labor as costly operation. Less awareness about herbicide use. No seed treatment Less awareness and availability problem Whe at Lack of improved varieties Unawareness about improved var. Non Availability of improved seeds. Low productivity. Use of traditional verities. Inadequate use of fertilizer Rain fed crop, If irrigated less no of irrigations and at improper stages. Gamble of temp. Sowing time. Weed Infestation. Rust problem. Inadequate use of Roughly fertilizers fertilizers application Less awareness about soil test based fertilizer application. seed drill. Sowing of crop on recommended spacing i.e 45*15 cm. Weed management through herbicide as cheapest method. Make awareness among farmers about new herbicides and its use. Seed treated with 300 mesh sulpher @ 4 gm/kg + Azectobacter @ 25 gm /kg. Make awareness among farmers regarding improved verities through trainings. Make available seed to farmers through FLD/Seed production programs. INM. Introduction of Improved var. Weed Management through Herbicide. Grown under irrigated condition and irrigation at proper stages. Proper sowing time. IPM. INM. Soil test based fertilizer application FLD OFT Parbhani Training FLD OFT MAU, Parbhani Training FLD MAU, Parbhani Training FLD* OFT MAU, Parbhani Training FLD OFT MAU, Parbhani Training FLD OFT MAU, Parbhani Wrong sowing time Yield losses by weed infestation Only use of NPK fertilizers. No use of micronutrients. Less awareness. Temp play imp role in germination, growth finally yield. Only depend on manual weeding Availability of labor as costly operation. Less awareness about herbicide use. Irrigation at Unawareness about improper stage of critical stages of growth and less crop growth in no of irrigations. wheat. Lack of water. Horticulture Mango Low yield Sweet Orange More fruit drop Irregular fruiting Fruit Drop Dieback Irregular bearing Low and improper nutrition Pest and disease attack Nutrient deficiency Alternate year bearing habit Mono cropping No new varietal introduction Old planting method Old neglected orchards Poor drainage Nematodes Imbalance nutrition management Poor nutrition Bahar treatment practices Rain fed crop sown Irrigated crop sown Awareness through training. Weed management through herbicide as cheapest method. Make awareness among farmers about new herbicides and its use. If irrigated training to farmers about critical stages of crop growth at which irrigation to be given. FLD Training Video show . MAU, Parbhani FLD MAU, Parbhani Training Video show Training Use of balanced fertilizers and hormones OFT FLD Training INM OFT Training FLD Training FLD Training Use of cultar Improved variety New technique of planting Proper nutrition management Good irrigation and drainage management FLD Training Proper nutrition New bahar management FLD Training Study MAU, Parbhani MAU, Parbhani Micronutrien t deficiency Banana Custard Apple Guava Irregular fruit harvesting Poor nutrient management Low bunch weight Nutrient and water management Insect pest attack Low yield Unawareness of pest and disease attack Improper nutrition and water management Unawareness about other high yielding varieties Naturally planting only, no commercial planting Uneven shape and size of fruits Irregular bearing and low yield Improper fruit growth and canopy management Negligence about bahar treatment and nutrition No addition of micronutrient fertilizers of FYM to orchard Poor method of planting No irrigation and nutrient management Micronutrien t deficient orchards Chilli Unawareness about soil testing Improper nutrient management Low yield Area goes on decreasing due to disease incidence Risk of crop failure and canopy management practices Soil testing including micronutrient Addition of micronutrient fertilizers Use of recommended dose of fertilizers Water management and nutrient supplements Use of IPM module in banana Balanced nutrition as per recommendatio n and soil health Growing of high yielding varieties on commercial basis Irrigation management and canopy load Water management and nutrient supplements Addition of recommended micronutrients Integrated nutrient management and change in cropping pattern New method of planting adoption tour OFT Training OFT Training FLD Training FLD Training FLD Training FLD Training FLD Training OFT/FLD Training OFT Training FLD Training OFT Training MAU, Parbhani Brinjal Pest attack and heavy cost management No idea of crop pest and disease management Fruit and shoot borer Pest attack Plating time responsible to heavy attack Repetition of crop on same field Lack of proper nutrition and high yielding varieties Tomato Turmeric Gaillardia Marigold Medium to lower yield Traditional method of planting Disease attack problems and fruit rotting Deficiency symptoms Not use of recommended fertilizer Uneven growth Storage problems Imbalanced fertilizer management Unawareness of storage treatment High cost of cultivation Pest and Disease problems Low yield No use of high yielding varieties and improper nutrition No new varieties Traditional planting Unawareness of new varieties No commercial view toward crop growing Proper time management of pest and diseases with IPM Integrated pest management Use of balanced dose of fertilizers and manures No use of modern Use of modern method like planting staking use of drip method liked method of row or paired irrigation row method No use of staking Modern method or disease resistant of planting and varieties staking Heavy dose of inorganic fertilizers and plant protection measures Unawareness of pest and diseases OFT Training FLD Training OFT Training MAU, Parbhani OFT Training FLD Training Use of recommended balanced fertilizers FLD Training FLD Training Storage treatment with insecticide and fungicide Balanced nutrition and good plant protection schedule Use of schedule pesticides and fungicides Introduction to high yielding varieties and nutrition management Introduction of new varieties Standard method and spacing of FLD Training OFT FLD Training FLD Training FLD Training FLD FLD Training MAU, Parbhani planting Plant Protection Cotton Soybean 1) Incidence of Low sucking pest productivity 2) Incidence of of cotton reddening. under rain 3) Incidence of wilt fed and para wilt. medium black soil Low yield of Soybean 1) Occurrence of Leaf eating caterpillars. 2) No use of Biofertilizer. Incidence of pod borer complex. Red gram Low yield in Redgram due to pod borer complex Paddy Repeated use of insecticides is ineffective during crop growth and reproductiv e stage for control of BPH and WBPH Brinjal Sweet orange 1. Resurgence of BPH and WBPH 1.Spraying of Incidence of insecticides after shoot and heavy incidence of fruit borer shoot and fruit borer Incidence No management of of of fruit fruit sucking moth at sucking proper stage moth Rabi sorghum 1.Incidance of grain smut Low yield Bengal Incidence of 1. No seed treatment 1)Proper management for 1.FLD reddening 2.Training on 2) IPM for control IPM /IDM of sucking pest 3.Video show and reduced cost of production 3) Disease Management. 1)Integrated Pest 1)Training Management programme 2) Seed treatment on pest and with Bio-fertilizer. disease management 2) Training on Biofertilizer seed treatment 4. IPM for pod 1)Training bor programme er on pest and Complex. disease management 2) Training on Biofertilizer. 3) FLD MKV Parbhani MKV Parbhani MKV Parbhani 1. OFT for assessment on use of bio pesticide Metarhizium anasoplae @ 2.5 kg/ha Dr. PDKV, Akola 1) Use of Pheromone Traps 2) Use of neem oil OFT FLD Training programme MPKV, Rahuri Use of NCIPM trap OFT 1. Use of bio pesticide Metarhizium anasoplae @ 2.5 kg/ha 1) Seed treatment at time of sowing. 2)Use of 300 mesh sulphur 1)Use of seed FLD Training programme FLD NCIPM, New Delhi MKV Parbhani MKV gram/ Chickpea wilt and pod 2. No use of IPM borer practices treatment 2) IPM technology Chilli Incidence of 1.Spraying of Powdery fungicides after heavy mildew incidence of disease Timely Spraying Sugarcane Incidence of 1) Incidence of shoot, various pest top shoot and stem Injudicious borer use of 2) Incidence of pyrilla insecticides and wooly aphid 1) Use of bio agents and bio pesticides. 2) Judicious use of insecticides. Training programme FLD Training programme OFT FLD Training programme Parbhani MKV Parbhani MKV Parbhani Home Science Health Drudgery Economic Empower ment 1.Unavailability of 1. Iron and folic Nutritious food for acid rich foods women like soyapoha 2. Lack of knowledge. laddu (soybean, 1.Low Hb 3. Early marriage. level among rice flakes, 4. Early pregnancy. girls & Bengal gram women flour, Jaggery) . 2. bone 2. Populerising problems new soybean 3.Malnutriti recipes. on among children 3. kitchen garden 4. Awareness campaigns 1. OFT & FLD Trainings 1.Finger pain 2.Backache 3.Body pain 4.weakness 5.Uncomfor table conditions while doing work. 1. OFT & FLD 1. Low economic status. 1. Traditional methods of farming 2.Unawareness about new agril tools 3. multiple responsibilities. 1. Introducing new agril tools like Revolving milking stool & stand, Smokeless Chula, 2.Extension activity (group meeting, lectures, Melava ) Green fodder scarcity 1.Unawareness about 1. Introducing small-scale enterprises small scale 2. Lack of technical enterprises. knowledge. 3. Lack in time and resource management. 1. Trainings on Soya processing for development of small scale business Unavailability of improved seed, FLD of green fodder Providing knowledge about Tech inventory sr.no.7 and 5 2. Trainings on improved agril tools Veterinary Science Cattle Tech inventory sr.no.1, 6 - Imbalanced diet and low milk yield Mortality in new born calves Disease management Less profitability High mortality seedling and knowledge for fodder crop Lack of knowledge regarding balanced diet and mineral mixture latest varieties and source of seed and seedling Use of cost effective local resources for preparing balanced feed, use of different mineral mixture Umbilical abscess, hernia, pneumonia, joint ill, diarrhoea 1. Lack of knowledge 2. Poor nutrition 3. Anoestrus Providing knowledge about disease management and preventive measures and medication Increasing feed cost Use of local resources as part replacement 1. Unawareness about Disease contagious diseases management and like RD, IBD,fowl adopting cholera etc preventive 2. Epidemic fear of measures like bird flu vaccination. 3. poor management Poultr y Goats No supplementary diet No breeding strategy Low productivity Mortality in new born kids low cost supplementation Lack of knowledge Local goats Lack of knowledge Lack of knowledge low cost supplementation Up gradation of local goats Proper herd management 1. Providing knowledge 2.Disease Napier varieties FLD Trainings MAU, Parbhani Trainings Animal Health camp OFT on oestrus management FLD Vaccination camp of FMD and HS Training FLD 1. OFT on antibacterial feed supplements 2. FLD on additional income generation activity 3. Trainings on prevention of contagious diseases 4. Standard management practices about feeding, vaccination and hygiene. Trainings FLD and Trainings Trainings Trainings MAU, Parbhani management and preventive measures 3.medication 1. Details of each of the technology under Assessment, Refinement and demonstration a. Detailed account on varietal/breed characters for each of the variety/breed selected for FLD and OFT Sr. No. 1 Safflower 2 Gram b. Crop Verities used in OFT/FLD PBNS-40 ((Parbahni-40) Duration (Days) 135 Digvijay 105-110 Rainfed-15-16 Irrigated-20-22 Rainfed-14-15 Irrigated-30-35 Varietal features Non spiny variety, Suitable for rainfed,Irrigated conditions, tolerant to wilt , leaf spot Reddish yellowish bold grains, Resistance to wilt, Suitable for rainfed, Irrigated and late sowing. Details of technologies that may include formulation, quantity, time, methods of application of nutrients, pesticides, fungicides etc., for technologies selected under FLD and OFTs Sr. No. Crop Name of herbicide 1 Gram Pendimethalin (panida) 2 Wheat Metasulphuronmethyl (algrip) c. Yield (Qt/ha) Active ingredient (kg) 30% EC Rate of application (lit/ha) 2.5 20 WP 20 gm Applicable for weeds Time of application Broad leaved and annual grassy weed control Broad leaved weed control Pre emergence application (Before germination ) Post emergence 3035 DAS. Details of location/area specificity of recommended technology viz., for each of the variety/breed/technology selected for FLD and OFT Mango kesar Selected from Gujarat region Saurashtra For pulp industries and home based juice making Irrigated as well as dryland horticulture Regular bearer attractive oblong fruit with saffron pulp color with pleasant aroma Regular bearer Having average good price less than alphonso in Market 10-15 cm long 5-7 cm breadth and 250300gm weight Okra PBN OK1 New research variety from VNMKV Prabhani High yielding and faint green in colour Brinjal Phule Arjun Research variety from MPKV Rahuri High Yielding and little resistan to fruit and shoot borer Irrigated Bottle gourd Samrat Research variety from MPKV Rahuri High Yielding and atrative fruits with good shape and size Irrigated and dryland Medium long fruits having 30% higher productivity then prabhani kranti and Arka anamika Resisant to YMV More marketable fruits Medium green fruits with viloat strip Medium Long fruits Resisant to little leaf More marketable fruits Firm fruit pulp More marketable fruits 8 to 9 cm long 2 to 3 cm thick and 9 to 10 gram in weight 7 to 8 cm long and 5 to 6cm thick and 20 to 30 gram weight 30 to 35 cm long 7 to 8 cm thick and 500 to 600 gram in weight Irrigated