PPT Version
advertisement

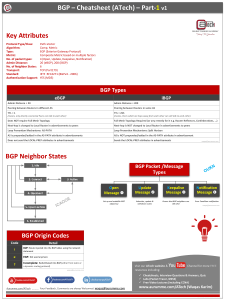
Internal BGP as PE-CE Protocol Pedro Marques roque@juniper.net Robert Raszuk rraszuk@cisco.com Dan Tappan tappan@cisco.com Luca Martini luca@level3.net Problem AS 65001 AS 65001 AS 10458 Provider CE-1 PE-1 PE-2 CE-2 Route Advertisement as-path 65001 as-path 10548 65001 When BGP is used as PE-CE protocol, it uses External BGP rules: as-path perpending, etc. Accept looped routes in CE-1 Rewrite customer AS# with provider AS# Continued When CE connections are not isolated islands and exchange BGP routes with any other party, it just gets messier. Customer island peers with the service provider (for Internet service, for instance). Customer islands exchange routes with outside world: Provider AS# appears in the path. Never ending requests for as-path rewrite hacks. Rent-a-core Core CE-1 RR-1 RR-2 CE-2 Traditional network design: Core distributes routing information to sites. Pop/Site routers receive routing information from their respective RRs. Reflectors participate in top level iBGP mesh. IGP may be stub area if there are no backdoor links. These are often managed independently. Proposed model PE routers are route reflectors to each CE site location. Customer network attributes are pushed into an “attribute stack” at ingress. This deals with interference on localpreference, communities, MEDs, etc. At egress “attribute stack” is poped. cluster is perpended when advertising to CE side. cluster-list performs loop avoidance. IGP interaction Shouldn’t require a single IGP between distinct sites. Even if an IGP is running between all sites it may not be able to compare inter-site metrics (Provider assigned) and intra-site. Perform implicit “next-hop self” on the PE/RR when advertising to CE. when advertising to other PEs. PE/RR makes decisions by taking inter-cluster metrics always higher than intra-cluster. Deployment Mix and match of eBGP and iBGP in the same VPN. Proposed attribute (ATTR_SET) consists of customer AS# plus attributes in original path. This allows a PE to know what to advertise to a given CE. origin peer iBGP eBGP internal if same as# use pop and apply internal rules external rules external advertise as-is existing rules Summary Using iBGP between PE and CE requires a few extra considerations: non-interference of customer attributes in provider network. IGP/next-hop dependencies. apply external rules when crossing as boundaries. iBGP interaction can provide transparency to customer network. as-path manipulation hacks only get you so far. Thank You For more details see: draft-marques-ppvpn-ibgp-00.txt