The Death Penalty and the Eighth Amendment Admin
advertisement

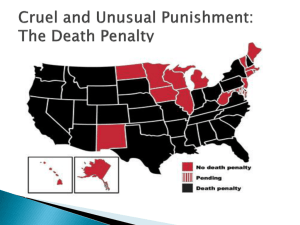
The Death Penalty and the Eighth Amendment Admin Opportunity to participate, be on the news! 2:00, Thursday, Room 117 Wooten – – First 60 students Line up at 1:50 Need a FERPA waiver – cross off “1050.001” and write in “1040.002” Admin Workbook 6-6, Question 14, Answer “A” has a typo (it should say “20%” instead of “10%”) 6-5 asks for information about women in particular jobs . . . If the information for a particular job is not available, don’t worry about it . . . Use the information on the website the best you can. Admin Exam Make-up If you want to retake (as opposed to make up) exam, you need to e-mail me (wwatson@unt.edu) Why you shouldn’t do it . . . – – – Retake score will be final, even if it is lower Gap since you learned material Format Eighth Amendment Prohibits cruel and unusual punishment “evolving standards of decency that mark the progress of a maturing society” Modern History of Death Penalty Furman v. Georgia (1972) Responses: – Death penalty for everyone! – Rejected by Supreme Court in Woodson v. N.C. (1976)) Aggravating and mitigating factors Accepted by the Supreme Court in Gregg v. Georgia (1976)) Death Penalty Today 37 states, the federal government, and the U.S. military have capital statutes Number of inmates on death row = 3,350 – – 393 death row inmates in Texas 660 in California, but CA is slow to carry out sentences Lethal injection available everywhere except Nebraska (electrocution) Public Opinion (All May 2006, Gallup) Are your for or against DP? – – Which is better penalty, DP or LWOP? – – 65% For 28% Against 47% DP 48% LWOP Is DP imposed fairly? – – 60% Fairly 35% Unfairly 8th Amendment Is death penalty per se cruel and unusual? – Only Justices Marshall and Brennan have advocated this position Is death penalty as applied cruel and unusual? – – – Method of execution Proportionality with crime (Coker v. Georgia (1977)) Certain classes of defendants Classes of Defendants Mentally ill (Ford v. Wainwright (1986)) Mentally retarded (Atkins v. Virginia (2002)) Juveniles (Roper v. Simmons (2005)) Close-up on Roper Simmons 17 at time of crime 1989, Supreme Court held that 16-18 year olds could be executed What changed? Justice Kennedy’s Opinion What evidence is there that standards of decency now prohibit execution of 16- and 17year olds? – – – – Steady (though slow) trend toward abolition 5 states abolished juvenile dp after 1989 Even in states that allow it, juvenile dp rare U.S. only country that still had juvenile dp (not controlling, but telling) Justice Kennedy’s Opinion DP reserved for most serious crimes, most culpable defendants Why are juveniles less culpable than adults? – – – Less mature, more given to impulsive behavior More susceptible to bad influences Character of juveniles not yet fixed (hope for rehabilitation) Purpose of dp: retribution and deterrence