Medical terminology and applied kinesiology Anatomical Position
advertisement

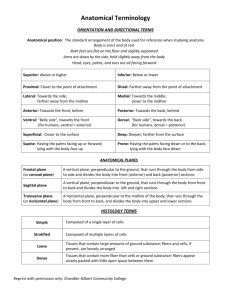
REVIEW: • What is the definition of Sports Medicine? • Who is involved in the Sports Medicine team? • What are the roles and responsibilities of the ATC? • What are the different settings that ATC’s can work in? MEDICAL TERMINOLOGY AND APPLIED KINESIOLOGY 1/23/13 ANATOMICAL POSITION Anatomical Position: • Person facing forward • Arms by side with palms up • Feet together PALPATION Palpation – to feel When palpating you are feeling for : Deformity Crepitus (noise) Warmth Abnormalities ANATOMICAL TERMINOLOGY • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • Anterior (Ventral)- front side in anatomical position Posterior (Dorsal) – back side in anatomical position Superior (Cranial) – closer to head Inferior (Caudal) – farther from head Proximal- closer to trunk Distal – father from trunk Medial – closer to midline Lateral – further from midline Superficial- closer to surface Deep- farther from surface Inferolateral – below and to the outside Inferomedial – below and toward the midline or inside Ipsilateral – on the same side Palmar- relating to palm or volar aspect of the hand Plantar – relating to the sole of the foot • • • • • • • • • • Posteroinferior – behind and below Posterolateral – behind and to one side specifically to the outside Posteromedial- behind and to one side specifically the inside Posterosuperior – behind and at the upper part Prone – face downward position (stomach lying) Supine – lying on back, face upward position of the body Superolateral – above and to the outside Superomedial – above and toward the midline or inside Ventral – relating to the belly or abdomen, on or toward the front, anterior part of Volar- Relating to the palm of the hand or sole of the foot BODY PLANES OF MOVEMENT Plane- A two-dimensional surface define by 3 points not on the same line (Motion occurs in a plane) SAGITTAL PLANE Sagittal- vertical plane that divides the body into RIGHT and LEFT parts - Flexion and extension activities occur in this plane - Axis runs medial to lateral FRONTAL PLANE Frontal – vertical plane that divides the body into ANTERIOR and POSTERIOR parts - Abduction, adduction (jumping jacks, and spinal lateral flexion - Axis runs anterior/posterior TRANSVERSE PLANE Transverse- horizontal plane that divides the body into CRANIAL and CAUDAL parts - Forearm pronation, supination, and spinal rotation - Axis runs superior/inferior PLANES MOVE ABOUT AN AXIS - Every where we go our body is moving in planes (frontal, sagittal, transverse). Sometimes we need to know in what plane we are moving - For example: - Which plane is this person moving in? BODY MOVEMENT TERMINOLOGY • • • • • • • • • • • • • Abduction – away from the body Adduction – towards the body Flexion – shortening Extension – lengthening Hyperextension – lengthening past neutral Dorsiflexion – Toes Up Plantarflexion – Toes down Elevation – move shoulder girdle up Depression – move shoulder girdle down Valgus – Knock kneed Varus – Bow-legged (Pigeon toed) Inversion – turning the sole of the foot inward or medially Eversion – turning the sole of the foot outward or laterally • • • • • • • • Trunk flexion – shortening the trunk Trunk extension – extending the trunk Lateral flexion – Bending side to side Lateral rotation – turning from side- side Circumduction –circular fashion Opposition – Thumb to pinky Thumb flexion – soda can Internal Rotation – rotation toward the midline of the body • External Rotation – rotating the bone away from the midline of the body • Pronation – internally rotating either the radius or foot • Supination – externally rotating either the radius or foot • Get together in groups of 2 or 3. • Fill in the anatomical movements that describe the position of these parts of the body: • Clavicle (collarbone) • Scapula • Olecranon Process • Cranium • Quadriceps • Gluteals • Ulna • Humerus in relation to trunk INJURY SPECIFIC TERMINOLOGY •Acute- sudden, immediate, just happened •Chronic – ongoing, gradual •Abrasion – any injury that rubs off the surface of the skin •Adhesion – scar tissue •Aerobic – exercise in which energy needed is supplied by oxygen •Anaerobic – exercise without the use of oxygen as an energy source • Anaphylaxis – severe allergic reaction, can be life threatening •Anatomy – study of the structures of the body •Anti-inflammatory – any agent which prevents inflammation •Inflammation- the body’s natural response to injury in which the injury site might display various degrees of pain, swelling, heat, redness, and/or loss of function (itis) •Asymptomatic- without symptoms •Symptomatic – with symptoms •Atrophy – to shrink •Hypertrophy – to grow TERMINOLOGY CONTINUED •Capsule – an enclosing structure which surrounds the joint and contains ligaments which stabilize t •Congenital – born with it •Concentric – shortening of the muscle •Eccentric – lengthening of the muscle •Cryotherapy – a treatment with use of cold •Cyst – abnormal sac containing liquid or semi-solid matter •Avulsion – the tearing away of a structure •Avascular necrosis – death of a part due to lack of circulation •Vascular – blood •Axilla – armpit •Cartilage – Smooth, slippery substance preventing two ends of bones from rubbing together and grating •Contusion (bruise) – a discoloration of the skin due to an compilation of blood into the underlying tissues •Ecchymosis – discoloration •Bursa- fluid filled sac that provides lubrication to joints TERMINOLOGY CONT… •Deformity – something out of place, unusual •Diagnosis – identification of a disease or disorder •Dislocation – complete displacement of joint surfaces •Dysfunction – unable to function normally •Disc – flat, rounded plate between each vertebrae of the spine (cushion, shock absorber) •Edema – swelling •Effusion – accumulation of fluid •Fascia – connective tissue sheath consisting of fibrous tissue and fat which unites the skin to the underlying tissue •Fracture – breach in community of a bone •Glenohumeral – shoulder girdle (glenoid capsule, head of the humerus and labrum) •Guarding – involuntary protective reflex (muscle contraction) MORE TERMINOLOGY… •Hematoma – tumor-like mass produced by a coagulation of blood in a cavity •Hemhorrage – to bleed •Interosseous Membrane – uniting membrane between tibia and fibula •Isometric contraction – tension is developed without the muscle lengthening or contracting •Isokinetic – active resistive exercise that puts a load on a joint or muscle at a fixed speed •Joint – the point of juncture between two or more bones where movement takes place •Lesion – wound or tumor •Ligament – band of fibrous tissue that connects bone to bone or bone to cartilage to help strengthen joints •Myositis – inflammation of a muscle •Necrosis – death to tissue •Neuron – a nerve cell •Paraesthesia – sensation of numbness, tingling •Pathology – study of the nature and cause of injury •Plica – fold of tissue in joint capsule MORE AND MORE •Radiating – pain that seems to travel from one point in the musculature to another •Referred Pain – pain felt in an undamaged area of body away from actual injury •Subluxation – Partial dislocation of a joint. •Synovial Fluid – lubricating fluid for joints and tendons, in inner lining of a joint • Thermotherapy - use of heat to treat a disease or disorder • Tendon - tissue that connects muscle to bone • Vasoconstriction – decrease of vessel diameter • Vasodilation – increase of vessel diameter NOW IS THE TIME TO ASK QUESTIONS? Any Questions? POP QUIZ 1. Name the three planes of movement. 2. What