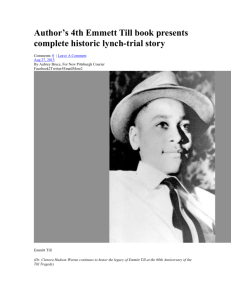
KWON US History Unit 7 Week 3 2014
advertisement

LCD Screen Isabella K Gerardo G Eleanor H Reyna C Maynard S Marcus L Pierce Riola Tinashe C Chris M Daniel C Aliana Tsai Jenna C Brooke V Owen O’keeffe Corinna Lee Wendy S Sam H Daniel V Tomas LunaHerrera Cailin Lin Mackenzie D Arlynda H Kalvin G Bradley W Computer Desk Jenna A Jackie Melo Table White Board Windows White Board Closet Trezhur R Bookshelf LCD Screen Samantha C Natalie D Alyssa F Fernando T Luis Ortega Joseph P Morgan M Natalie D Sebestian P Jimi W Peter S Athena B Diana C Reese W Heather W Mikaela H Brandon G Reanna L Marissa F Nic L Reagan M Windows White Board Closet Hanna P Genesis A Computer Desk Vanessa V Elaine J Lucy X Jodi D Mia C Table White Board Bookshelf US HISTORY Unit 7, Week 3 Homework for the Week • Tuesday, 2/25 • Study for the Test! • Prepare Checklists • Wed/Thursday, 2/26-2/27 • Paper due on Friday • Friday 2/28 • Finish Emmett Till activity Agenda, Monday, 2/24 • Unit 7 checklist • HOT ROC- poverty in the 1950s • Chapter 43 – Lesson planning • Debrief/compare HOT ROC: poverty in the 1950s Use Ch 43 • How is poverty defined (then and now)? • Why was poverty “invisible”? (3 reasons) • Which were the poorest groups in America? Why were they poor? • Compared to 1950’s, how is the problem of poverty today? • Currently, what is the difference between “middle class” and lower class? • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UAJHp89BInE • (~4:14) • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=GO5b_FwR5HU Lesson Plan Activity: How would you teach Ch. 43? Objective: Draft a PowerPoint presentation that would help students to understand and remember the key ideas from Ch. 43. • Step 1 - Break up into groups of 3-5 people • Step 2 – Review the content. • Organize/divide up info • Make notes on key info • Step 3 - Create a HOT ROC that goes with your content. It can be a question or an activity. • Step 4 – Choose PPT graphic/layouts • Example: • Slide 1 – HOT ROC • Slide 2-4 Key information from the chapter • Slide 5 (and 6) - What activity can help students engage with the content? (compare/contrast, cause and effect, connect to prior knowledge, simulation) • Would you want to add a video clip? What would an ideal video clip be? What pictures would you include? Tuesday, 2/25 • Agenda • Finish Unit 7: Review key ideas and terms • Review questions for Unit 7 • Add new vocabulary: inner city (ignore escalate) • Homework • Study for the Test Tomorrow! • Prepare Checklists • Add “inner city” to vocab list 1950’s poverty: summary • Poorest groups according to The Other America: 1. Colored minorities (inner city Blacks, Indian tribes**) 2. People in certain rural areas (farmers*, miners) **termination policy *agribusiness Lesson Plan Activity: How would you teach Ch. 43? Objective: Draft a PowerPoint presentation that would help students to understand and remember the key ideas from Ch. 43. • Step 1 - Break up into groups of 3-5 people • Step 2 – Review the content. • Organize/divide up info • Make notes on key info • Step 3 - Create a HOT ROC that goes with your content. It can be a question or an activity. • Step 4 – Choose PPT graphic/layouts • Example: • Slide 1 – HOT ROC • Slide 2-4 Key information from the chapter • Slide 5 (and 6) - What activity can help students engage with the content? (compare/contrast, cause and effect, connect to prior knowledge, simulation) • Would you want to add a video clip? What would an ideal video clip be? What pictures would you include? Best ideas for HOT ROC & activity • HOT ROC: period 5 • Draw picture of the rich and poor. Factor in poverty but mask it. • Show the first visual in chapter 43 and ask students if this family is poor and how • Divide the class into four different classes and give them money to spend in a month and give them buying options • Crossword puzzle on vocab words from chapter • Picture/cartoon that shows how poverty is hidden • Short video on state of the economy then and now • Activity: period 5 • Choose a card (has character of different social class). Talk to people from differences classes (they will be masking their class) try to find the poor person • Compare/contrast different problems • Q. how did this help understand poverty in the 50’s? (divide and spend money activity) • Everyone will get specific classes and people will stand up to show the percentage of those in poverty visually • Cause/effect in rural area. Struggles of poverty video • Divide into 10 students and give them pennies according to their social class. See what happens when union raises minimum wage, etc. • HOT ROC: 6th period • Political cartoon analysis (poor should be invisible) • How did poverty increase/decrease through the years? How to solve poverty? • In what ways would you be different if you were poor in the 50’s vs. now? • Describe your experience with (someone in) poverty? What is the impact of poverty? • Compare/contrast between 1920s, 1950s, 2000s rich/poor • How did the termination policy help/not help native Americans? • Activity: 6th period • Simulate what it is like to live in poverty household. • Compare/contrast T chart with 1950s and 2013 • Ask for creative solutions for poverty in 50’s vs now • 6-7 min documentary of homelessness. Ask questions related to the video. 1) how to solve the issues. What are some of the programs? 2) how modern day homeless different from 50s? 3) make a T-chart between you and the homeless person • A three-way venn diagram between 20’s, 50’s, 2000s • Compare/contrast poverty then and now Use your textbook and partners to make sure you know these terms • NATO • Alger Hiss • Marshall Plan • Levittown • Warsaw Pact • Baby Boom • Brinksmanship • Life for women in the • Mutual Assured 1950s • Polio vaccine • Other America • Termination policy for Native Americans • Agribusiness Destruction • Federal Civil Defense Administration • Hollywood Ten • Julius and Ethel Rosenberg Review: Unit 7 essential ideas and details • GI Bill • 3rd world country • Women’s work after WWII • Rosenberg trial • Stalin and USSR buffer • Review station activity • • • • • • • zone Iron Curtain Goal of Marshall Plan Outcome of Korean War Berlin Blockade and Airlift NATO, Warsaw MAD McCarthyism debrief questions (week2) • Why were the poor invisible in the 1950’s? • Planned obsolescence • Agribusiness Block Day, 2/26-2/27 • Agenda • Turn in your checklist • Unit 7 Test: Time to show what you know! • Intro to Unit 8 civil rights HW: Research paper – hard copy with you to class and also submit a copy to turnitin.com by 5pm on Friday. Reconstruction • Reconstruction (1865-1877): rebuilding the South post-Civil War and healing the nation’s wounds • 13th Amendment: abolishes slavery • 14th Amendment: blacks are citizens and equal before the law • 15th Amendment: “The Great Betrayal” • Compromise of 1877: disputed Presidential election of 1876 • Hayes (Northern Republican) vs. Tilden (Southern Democrat) • Hayes given Presidency, agrees to end Reconstruction and the north’s military occupation of the south. • Known as the “Great Betrayal” Failures of Reconstruction • Southern Democrats aim to save South by “returning it to the white man’s rule” • Poll Taxes and Literacy Tests stop blacks from voting • Jim Crow Laws create segregation • Ku Klux Klan terrorizes blacks through lynching Literacy Test Practice (Alabama: 1965) 1. Which of the following is a right guaranteed by the Bill of Rights? _____Public Education _____Employment _____Trial by Jury _____Voting 2. The federal census of population is taken every five years. (True or False?) 3. If a person is indicted for a crime, name two rights which he has. 4. A U.S. senator elected at the general election in November takes office the following year on what date? 5. A President elected at the general election in November takes office the following year on what date? 6. Which definition applies to the word “amendment?” _____Proposed change, as in a Constitution _____Make of peace between nationals at war _____A part of the government 7. A person appointed to the U.S. Supreme Court is appointed for a term of __________ ? 8. When the Constitution was approved by the original colonies, how many states had to ratify it in order for it to be in effect? 9. Does enumeration affect the income tax levied on citizens in various states? 10. Person opposed to swearing in an oath may say, instead: (solemnly) _______________________________________ Literacy Test Practice (Alabama: 1965) 11. To serve as President of the United States, a person must have attained: _____25 years of age _____35 years of age _____40 years of age _____45 years of age 12. What words are required by law to be on all coins and paper currency of the U.S.? 13. The Supreme Court is the chief lawmaking body of the state. (True or False?) 14. If a law passed by a state is contrary to provisions of the U.S. Constitution, which law prevails? 15. If a vacancy occurs in the U.S. Senate, the state must hold an election, but meanwhile the place may be filled by a temporary appointment made by _________________________ 16. A U.S. senator is elected for a term of _____ years. 17. Appropriation of money for the armed services can be only for a period limited to _____ years. 18. The chief executive and the administrative offices make up the ___________________ branch of government. 19. Who passes laws dealing with piracy? 20. The number of representatives which a state is entitled to have in the House of Representatives is based on________? Answers 1. Which of the following is a right guaranteed by the Bill of Rights? _____Public Education _____Employment __X___Trial by Jury _____Voting 2. The federal census of population is taken every five years. (True or False?) 3. If a person is indicted for a crime, name two rights which he has. Habeas Corpus (immediate presentation of charges); lawyer; speedy trial. 4. A U.S. senator elected at the general election in November takes office the following year on what date? January 3 5. A President elected at the general election in November takes office the following year on what date? January 20 6. Which definition applies to the word “amendment?” __X___Proposed change, as in a Constitution _____Make of peace between nationals at war _____A part of the government 7. A person appointed to the U.S. Supreme Court is appointed for a term of ____Life (with good behavior) ______ ? 8. When the Constitution was approved by the original colonies, how many states had to ratify it in order for it to be in effect? 9 9. Does enumeration affect the income tax levied on citizens in various states? Yes 10. Person opposed to swearing in an oath may say, instead: (solemnly) Affirm Literacy Test Practice (Alabama: 1965) 11. To serve as President of the United States, a person must have attained: _____25 years of age ___X__35 years of age _____40 years of age _____45 years of age 12. What words are required by law to be on all coins and paper currency of the U.S.? In God We Trust 13. The Supreme Court is the chief lawmaking body of the state. (True or False?) 14. If a law passed by a state is contrary to provisions of the U.S. Constitution, which law prevails? US Constitution 15. If a vacancy occurs in the U.S. Senate, the state must hold an election, but meanwhile the place may be filled by a temporary appointment made by ? The Governor 16. A U.S. senator is elected for a term of ___6__ years. 17. Appropriation of money for the armed services can be only for a period limited to ___2__ years. 18. The chief executive and the administrative offices make up the _________Executive__________ branch of government. 19. Who passes laws dealing with piracy? Congress 20. The number of representatives which a state is entitled to have in the House of Representatives is based on_____Population___? BOILING POINTS What led to the Civil Rights Movement? Fundamental Reasons • WWII • Veterans were discriminated against upon their return to the US. • An increase in black activism during WWII A Philip Randolph’s organized protest of workplace discrimination • Blacks in the Urban North • Making gains socially, politically, and economically as well as having voting rights unlike those in the south. • Strength of the NAACP • The organization was attracting support, funding, and new, young members as well as the support of many lawyers (white & black) Section 44.2 No public busing • Copy the spoke diagram below into your notebook. • In each of the six ovals around the center oval, list one area of life discussed in Section 44.2 in which blacks experienced segregation. • Near each of those six ovals, list as many examples as you can that show how segregation affected Americans during this era. Schools Aspects of life affected by segregation Friday, 2/28 • Collect papers • Finish spoke diagram • The Story of Emmett Till The Story of Emmett Till • Emmett Till was a 14 year old black boy from Chicago. He came to Money, Mississippi to visit relatives. On August 28, 1955 Emmett Till was brutally murdered for “whistling” at a white woman. Despite overwhelming evidence, his killers were set free after a short trial. The case galvanized the nation. • http://www.youtube.com/watc h?v=MGqqOMTreNA • How did Southerners justify the brutal murder of Emmett Till? Mamie Till’s reaction • Emmett’s mom had grown up in the south and moved to • • • • • Chicago. She refused to let Emmett’s death be just another forgotten lynching. She held an open casket funeral in Chicago that was attended by thousands from the community and got national attention. The trial to convict his murderers also got national news coverage. When his murderers were found not guilty by an all-white jury, she tried to appeal the case. Once found innocent, the murderers sold the story of how they did it to Look Magazine. Mamie Till then appealed to President Eisenhower to take action against the confessed killers, but he refused. The Murder of Emmett Till • As we analyze the circumstances of Emmett Till’s murder, it is important to also reflect on who we are as individuals and how we are viewed in society. 1.Using markers and colored construction paper, draw the outline of your hand. 2.Inside the hand, write or draw things that shape your identity, such as gender, names, religion, physical features, languages, family, political beliefs, etc. You should not put anything on this chart you’re not willing to share. 3.Outside of the hand outline, write or draw examples of how other people identify or "label" you (both positive and negative labels). How did Southerners justify the brutal murder of Emmett Till? • Historians and sociologists today still argue over how people are able to justify such disgusting acts of racial violence in their minds. Today we seek to answer that question looking at the case of Emmett Till. How did Southerners justify the brutal murder of Emmett Till? 1. Read through Documents A-D and collect evidence supporting the THREE HYPOTHESES at the top of your graphic organizer 2. You need to find TWO PIECES OF EVIDENCE for each hypothesis. Be sure to record both the SOURCE information and a QUOTATION