Celestial Sphere 9-23-12
advertisement

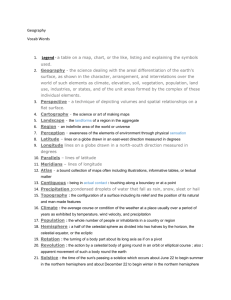
The Celestial Sphere (The sphere should really be rotating, not Earth) An Ancient Greek Idea • Imagine the universe to be a hollow sphere with the Earth at the center – The Celestial Sphere appear • Idea based upon how things _________ to be –The pattern of stars in the sky does not change ________________ • Stars ‘embedded’ on the _________ inside –Pretend the stars are painted on a giant ‘bubble’ around Earth • Geocentric (________________) model Earth centered Celestial Sphere: Extension of the Earth’s Coordinate System Celestial sphere • N/S celestial poles N/S Poles •____________ • Celestial equator •____________ Equator •Declination Latitude •____________ •Right Ascension Longitude •____________ Like a clear bowl over your head! The Celestial Sphere NCP Earth’s spin axis The celestial sphere Earth Celestial equator SCP NCP Celestial Sphere SS Path of Sun during the year AE Earth WS e SE Celestial equator Ecliptic SCP Ecliptic (2) == apparent _____________________________________________ annual path of Sun on the CS North Ecliptic East Sun’s Path Celestial Equator Declination (degrees) South Right Ascension (hours) Key terms • Celestial sphere: Apparent sphere of the sky (what it looks like) – _________ • Celestial poles joined by line that runs through the Earth’s north and south poles (this line is, in fact, the Earth’s spin axis) Earth’s North Pole • NCP is directly above _______________ – Point about which the stars appear to rotate • Celestial equator: Projection of Earth’s equator onto the CS – ___________ Apparent motion: Earth’s rotation • As Earth ________, rotates it looks as if the celestial sphere is _________ rotating around us • In the north, the center of the rotation is the _______________________________ North Celestial Pole - Polaris • In the south, the center of the rotation is the _______________________________ South Celestial Pole – No pole star • The celestial sphere appears to rotate once 24 hours every _________ Where on Earth • Definition: –Latitude (l): The angle between the Observer, the center of the Earth and the Earth’s equator (Measured in degrees) l = 0o (Equator) l = 90o (North pole) l = -90o (South pole) (l = 90o) North pole observer Equator l Earth South pole (l = -90o) horizon (l = 0o) The latitude of an observer is equal to the altitude of the visible celestial pole • latitude of observer = l • altitude of NCP = A To NCP zenith A B l B= -l A + B = 90o 90o l Earth To CE horizon The final steps: (hold tight) • By definition: angle A + angle B = 90o But, angle B = 90o - l, so A + 90o - l = 90o And hence, A=l The Celestial Sphere Precession In addition to its rotation and revolution, the earth’s axis also __________ precesses (wobbles) like a top. The angle between the ecliptic and the equator remains at 23.5°, but the direction changes. The period of this precession of the equinoxes is about ____________. 26,000 years Because of precession: • Polaris won’t always be the North Star • Orion won’t always be a winter constellation • Horoscopes are all wrong!