Conducting an Industry Analysis
advertisement

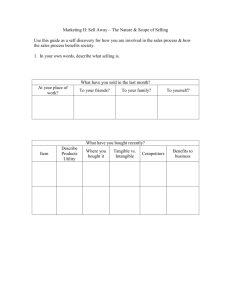
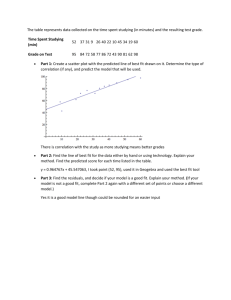
Conducting an Industry Analysis Seven Questions for Industry Analysis 1. What are the industry dominant economic traits? 2. What competitive forces are at work in the industry and how strong are they? 3. What are the forces of change in the industry and what impact will they have? 4. Which companies are in the strongest/weakest competitive position? 5. Who’s likely to make what competitive moves next? 6. What key factors will determine success or failure? 7. How attractive is the industry in terms of its prospects for above average profitability? Q1. What are the industry dominant economic traits? Market size (Small markets don’t attract big fish) Scope of competitive rivalry Market/industry growth rate (life cycle) – Fast growth breeds new entry; slowdowns lead to increased competition. Number of rivals and their size Number of buyers and their size Level of backward and forward integration Technological change (rate and scope) Level of differentiation between firms’ products Opportunities for economies of scale Ease of entry and exit Capital requirements Q1: Industry’s Dominant Economic Traits Market – – – – – Size Scope Growth rate Growth cycle # & size of competitors – Distribution channels – Structure Forward Integration Backward Integration Product – Differentiation – Potential for economies of scale – Learning effects – Entry / exit costs – Technological change Q2. What competitive forces are at work in the industry and how strong are they? Porter’s Five Forces. Forces influencing industry and competitive advantage: – – – – – Competitive Intensity (Rivalry Among Sellers) Barriers to Entry (Potential for New Entrants) Bargaining Power of Suppliers Bargaining Power of Customers Threat of Substitute Products pg. 33 in Applegate Q2. What competitive forces are at work in the industry and how strong are they? The rivalry among sellers – Greater the rivalry, lower the avg. profitability – What causes rivalry to be strong or weak? # of competitors Size / capability of competitors Financial status of competitors Slow growth Cost of exit barriers Switching costs for customers Variability in demand Q2. What competitive forces are at work in the industry and how strong are they? Potential new entrants – Barriers to entry Economies of scale Learning curve effects Customer loyalty / brand preferences Resource / investment Access to distribution Regulation Patents, proprietary technology – Level of industry profits Q2. What competitive forces are at work in the industry and how strong are they? The relative power of suppliers – – – – Importance of component Switching costs Backward integration threats Substitutes The relative power of buyers – – – – – Switching costs % market share / size # of suppliers Product standardization Potential for backward integration Q2. What competitive forces are at work in the industry and how strong are they? Substitute products – – – – Place a ceiling on prices and profits of industry Invite comparison shopping E.g., eyeglasses vs. contact lenses E.g., sugar vs. artificial sweeteners Q3. What are the forces of change in the industry and what impact will they have? The most dominant forces the cause the industry to change are called driving forces Task 1 - identify the driving forces Task 2 - assessing their impact on the industry (few are important, generally) Common Driving Forces Changes in long term industry growth rate Changes in who buy the products and for what reason Product innovation Technological change Marketing innovation Increasing globalization Regulatory changes Changing societal concerns, attitudes and lifestyles Environmental scanning Q4. Which companies are in the strongest/weakest competitive position? Using the strategic group mapping: two dimensional representation according to the competitive characteristics of the competitors in the industry Axes should not be correlated Size of circles proportional to combined sales The closer the circles, the stronger the rivalry See http://i.i.com.com/cnwk.1d/html/b/305,1,Competitive and http://www.quickmba.com/strategy/pest/ for more information. Product line/merchandise mix Q5. Who’s likely to make what competitive moves next? In order to outmaneuver your competition you have to evaluate the competitors’ future moves. Identify competitors strategies Evaluate who are the major players-- now Who will be the major players Evaluate what the major players are going to do Q6. What key factors will determine success or failure? Key success factors (KSF) are crucial elements that lead to success. What are they now? What will they be? In beer production KSF can be brewing skills In retail apparel KSF can be low cost, superior service, superior design In your industry, KSF=???? Q7. How attractive is the industry in terms of its prospects for above average profitability? Growth potential Driving forces Entry/exit Stability of demand Competitive forces Risk and uncertainty Competition and its impact on the industry’s future 7 Questions 1. What are the industry dominant economic traits? 2. What competitive forces are at work in the industry and how strong are they? 3. What are the forces of change in the industry and what impact will they have? 7 Questions 4. Which companies are in the strongest/weakest competitive position? 5. Who’s likely to make what competitive moves next? 6. What key factors will determine success or failure? 7. How attractive is the industry in terms of its prospects for above average profitability?