FOCUS 10/25/06
advertisement

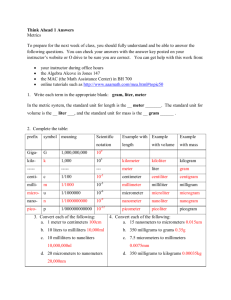
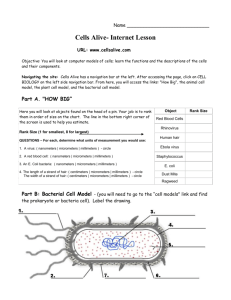
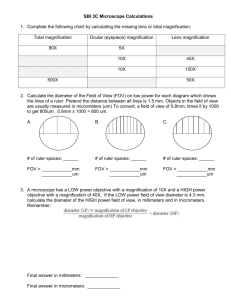
WarmUp 8/31/09 – Copy and answer in notebook 1. What is the name of the Red objective lens? Blue? Yellow? 2. What is the magnification of each? 3. What is the total magnification when looking through each of the following: scanner? Low Power? High Power? 4. How does what you see change as you increase in magnification? (2 ways) 5. How does the orientation of objects appear under the microscope compared to your naked eye? 6. What part of the microscope should never be used with the high power lens? 7. What term is used to describe the “circle of light” you see when looking through the ocular? Need to Know! – # of microns or micrometers in a millimeter – Volume of a block – Area of a circle – Volume of a cylinder 1000 µ L x W x H π r2 H π r2 CALCULATING SIZE OF MICROSCOPIC OBJECTS SCANNER OBJ. LENS 4X -------- > 40X __?____ = diameter of the field of view 4 mm DIAMETER 1 mm = 1000 micrometers 4 mm = 4000 micrometers 4000 micrometers = 4000 μ LOW POWER 100 X 2 mm 2000 micrometers (μ) LOW POWER 100 X 1/5 F.O.V. = 1/5 of 2000 μ 2000 μ / 5 = 400 μ HIGH POWER 400 X f.o.v.???? ? Low to high = 100x to 400x 4 times closer! See only ¼ as much! ¼ of 2000μ = 500 μ F.O.V. = 500 μ HIGH POWER 400 X Same Object 4/5 F.O.V. = 4/5 of 500 μ 400 μ ! Same object = Same Size! HIGH POWER 400 X 1/5 of 500μ = 100μ LOW POWER 1/10 of 2000μ = 200μ HIGH POWER 1/10 of 500μ = 50μ Mathematically! • 100x --- > 400 x increases by 4 times • But, you only see __________ as much! • One-fourth! So, f.o.v. or object on high power is ¼ that of low power! ocular = 10x low power objective = 20x high power objective = 40x The picture shows the low power field of view for the microscope with the lenses listed above. a) What is the approximate size of the cell in micrometers ? b) What would be the high power field of view ? c) How many cells like the one in the picture could fit in the high power field of view ? a). 500 micrometers First, we have to visualize how many of those cells could fit across the field --- about 4. So 2 mm (the width of the field) / 4 = .5 mm, which converts to 500 micrometers. b). 1000 micrometers The ratio of low to high power for this scope is 20/40, or 1/2. So we will see 1/2 of the low power field under high power. 1/2 x 2 mm = 1mm, which converts to 1000 micrometers. c). 2 cells Again the ratio of low to high power is 20/40, or 1/2. If we can see 4 cells across the low field of view we will see 1/2 as many in the high field of view. 1/2 x 4 = 2 cells.