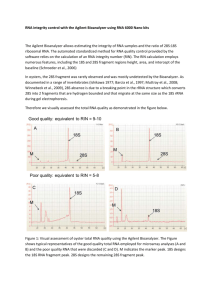
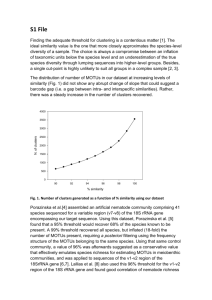
GluR 5,6,7
advertisement

HARVARD BRAIN TISSUE RESOURCE CENTER An NIH National Resource A National Repository for the Acquisition and Distribution of High Quality Postmortem Brain Tissue to the Neuroscience Community Neuropathological Assessment Microscopic Evaluation Alzheimer’s Disease Tangles Distributive Diagnoses Cases Collected 2002-March, 2007 Diagnosis Intake Distributive Controls (Normal) 282 197 Alzheimer’s Disease Alzheimer’s D., Lewy Body Variant Diffuse Lewy Body Disease Frontotemporal Dementia 411 356 21 38 30 Huntingtington’s Disease Huntington’s Disease (Grades 3,4) Huntington’s Disease (Grades 1,2 Huntington’s “at risk” 202 Parkinson’s Disease Progressive Supranuclear Palsy 107 2 62 6 *Tourette’s Syndrome 11 11 Schizophrenia Bipolar Disorder Depression , Unipolar *Autism 85 66 0 41 35** 34** 0 6 Total 114 59 2 1207 971 *Must get approval from appropriate tissue use committee. **Diagnosis pending on approximately 20 cases. Standards of Practice Brain banks must conform to the Uniform Anatomic Gift Act of 1987 Informed consent for brain donation is critical, particularly as it relates to genomics research Irreversible anonymization may eliminate ethical/legal issues regarding genomics research. Distribution of brain tissue is ethical when the tissue or its bioderivatives are serving the common good i.e. they help to identify the causes and new therapies of brain disorders. Standards of Practice Assembling cohorts of cases with a brain disorder and matching with healthy controls with respect to age, postmortem interval (PMI), gender, hemisphere, pH and cause of death Ruling out substance abuse with careful family history and toxicology is essential Learning about all the psychotropic and other medications that each donor was taking prior to death Determining the correct psychiatric diagnosis of the individual using medical records and family questionnaires Obtaining a careful neuropathological assessment to rule out the presence of neurodegenerative disease, tumors, strokes or trauma is essential Table 1aS The McLean 66 Cohort and Quality Control Parameters for RNA Integrity Brain Number 3498 3688 3699 3706 3732 3806 3814 3817 3898 3902 3927 3933 4069 4113 4156 4157 4158 4190 4198 4237 4238 4240 4256 4337 4375 4403 4435 4462 4464 4469 4496 4545 4586 Diagnosis Age PMI Schizophrenia Control Bipolar Control Control Control Bipolar Bipolar Control Schizophrenia Bipolar Schizoaffective Bipolar Bipolar Schizophrenia Schizophrenia Schizophrenia Schizoaffective Schizophrenia Bipolar Schizophrenia Schizophrenia Schizophrenia Control Schizophrenia Bipolar Schizoaffectiv e Bipolar Bipolar Schizophrenia Schizophrenia Bipolar Control 66 66 51 40 69 70 29 64 78 83 38 84 80 42 44 35 42 78 46 78 26 42 47 36 31 76 48 50 74 80 49 74 37 22.1 18.7 31.0 28.0 15.3 15.0 10.7 11.0 14.1 23.2 41.5 25.7 12 15.8 19 28.0 18.1 13.4 18.5 30.2 16.0 27 19 24.5 29.0 22.8 33.7 30.5 24.8 10.9 19.0 7.2 18.7 Hemisphere Gender Rt Rt Lt Rt Rt Rt lt Rt Rt Rt lt Rt Lt lt Lt Lt Lt Lt Lt rt Rt Rt Rt Lt Rt Lt Lt Rt Lt Lt Lt lt Rt M M M m m f F F F F M F F F M M M F M M M M M M M F F M M M M M M Brain pH 18/28s rRNA ratio 3'/5' ratio GAPDH 3'/5' ratio B-Actin Percent Present Calls 6.43 6.76 7.02 6.50 6.88 6.59 6.70 6.69 6.22 5.91 6.52 6.14 6.51 6.26 6.05 6.25 6.26 6.81 6.31 6.30 6.75 6.64 6.57 6.26 6.46 6.60 6.63 6.35 6.53 6.44 6.60 6.70 6.68 1.80 1.50 0.95 0.55 1.50 1.35 1.30 1.30 1.26 0.25 1.45 0.50 1.00 1.30 0.94 0.96 1.00 1.20 1.04 0.70 1.60 1.20 1.90 1.14 1.08 0.53 1.28 1.05 0.80 0.50 1.80 1.30 1.35 1.00 1.13 1.8 1.7 1.3 1.18 1.06 1 1.6 1.97 1 1.67 3 1.1 3 1.63 1.32 1.5 3.2 1.9 1.3 1 2 1.5 1.21 1.9 1.19 1.6 1.4 1.4 1 2.9 1.16 1.44 1.45 3.40 3.40 2.80 2.00 1.57 1.70 2.50 3.50 1.18 2.80 4 1.70 4 2.08 2.14 2.33 2.59 4.16 2.60 2 4 2.34 2.00 3.80 1.46 4.20 3.40 1.80 1.20 4.10 1.45 48.0 43.8 43.9 46.3 43.6 46.3 45.1 50.7 42.1 42.0 43.0 39.6 27.0 52.4 34.0 46.1 46.4 46.1 45.5 42.4 49.6 45.0 47.0 44.4 49.0 42.1 47.1 46.6 47.2 41.0 50.0 33.4 49.3 PGI Case # 223 222 231 224 225 260 238 249 243 212 242 241 259 226 229 236 250 215 230 245 GENE EXPRESSION PROFILING AS A SCREENING TOOL Quality Controls RNAse Activity: Is the mRNA degraded? 18S:28S Ratio : A Critical Factor Ratio 1.0 Tissue pH Quality Control of mRNA Schizophrenic Control Bipolar 17.5 30 B3933 rRNA ratio = 0.50 15.0 12.5 10.0 Triplet #8 B3806 rRNA ratio = 1.35 25 20 B4069 rRNA ratio = 1.00 12.5 10.0 7.5 5.0 10 2.5 5 19 24 29 34 39 44 49 54 59 64 69 18S 0 28S 18S 0.0 19 Time (seconds) 24 29 34 39 0.0 28S 2.5 44 49 54 59 64 69 19 24 29 34 39 Time (seconds) 28S 5.0 18S Fluorescence Fluorescence Fluorescence 15 7.5 44 49 54 59 64 69 64 69 Time (seconds) 20.0 20.0 40 B4190 rRNA ratio = 1.20 17.5 15.0 12.5 B4737 rRNA ratio = 0.80 35 30 B4545 rRNA ratio = 0.50 17.5 15.0 12.5 25 10.0 10.0 Fluorescence Fluorescence Fluorescence 20 7.5 7.5 15 5.0 5.0 10 2.5 2.5 19 24 29 34 39 44 49 54 59 64 0.0 69 Time (seconds) 19 24 29 34 39 44 49 54 59 64 69 19 24 29 34 39 Time (seconds) 35 B4238 rRNA ratio = 1.60 30 25 44 49 25 B4605 rRNA ratio = 1.30 20 20 59 35 B3814 rRNA ratio = 1.30 30 25 15 Fluorescence 54 Time (seconds) 20 Fluorescence Fluorescence 15 10 10 15 5 10 34 39 44 5 49 54 59 64 0 69 0 Time (seconds) 19 24 29 34 39 44 49 54 59 64 28S 29 28S 24 18S 18S 19 28S 5 0 18S Triplet # 10 28S 18S 0 28S 18S 28S 5 0.0 18S Triplet #9 69 Time (seconds) 19 24 29 34 39 44 49 54 59 64 69 Time (seconds) 12.5 4.5 17.5 Fluorescence Fluorescence 7.5 5.0 1.5 5.0 1.0 24 29 34 39 44 49 54 59 64 69 2.5 19 24 29 34 39 0.0 28S 18S 0.0 28S 0.5 0.0 18S 2.5 Time (seconds) 44 49 54 59 64 19 69 B4314 rRNA ratio = 0.00 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 29 34 39 44 54 59 64 69 64 69 15.0 B5105 rRNA ratio = 1.30 40 35 30 B4237 rRNA ratio = 0.70 12.5 10.0 25 Fluorescence 3.0 2.5 7.5 Fluorescence Fluorescence 20 2.0 15 5.0 1.5 1.0 10 0.5 5 2.5 24 29 34 39 44 49 54 59 64 18S 0.0 28S 18S 0 19 28S 18S 0.0 69 19 Time (seconds) 24 29 34 39 44 49 54 59 64 69 19 24 29 34 39 44 Time (seconds) 7 49 54 59 Time (seconds) 17.5 4 B5083 rRNA ratio = 1.46 15.0 12.5 12.5 10.0 7.5 7.5 2 Fluorescence Fluorescence Fluorescence 3 5.0 5.0 1 2.5 24 29 34 39 44 49 54 59 64 69 19 24 29 34 39 Time (seconds) 0.0 28S 0.0 18S 18S 19 28S 2.5 0 B3927 rRNA ratio = 1.45 15.0 10.0 44 49 54 59 64 19 69 24 29 34 39 28S 5 18S B4375 rRNA ratio = 1.08 6 Triplet # 13 49 Time (seconds) 45 5.5 24 Time (seconds) 6.0 Triplet # 12 7.5 2.0 19 B4113 rRNA ratio = 1.30 10.0 2.5 28S 10.0 3.0 Fluorescence Triplet # 11 3.5 18S 12.5 B4981 rRNA ratio = 1.12 4.0 B4256 rRNA ratio = 1.90 15.0 44 49 54 59 64 69 64 69 Time (seconds) Time (seconds) 15.0 15.0 30 20 10.0 10.0 Fluorescence Fluorescence 7.5 5.0 5.0 10 2.5 2.5 5 B4462 rRNA ratio = 1.05 12.5 7.5 15 Fluorescence 28S 18S 28S 0.0 18S 0.0 0 18S Triplet # 14 B4751 rRNA ratio = 1.30 12.5 19 19 24 29 34 39 44 Time (seconds) 49 54 59 64 69 19 24 29 34 39 28S B4496 rRNA ratio = 1.80 25 44 Time (seconds) 49 54 59 64 69 24 29 34 39 44 Time (seconds) 49 54 59 Studies of Gene Expression Using Microarrays Are the microarray data reliable? Replicability of Gene Expression Profiling Comparison of Microarray Data: 1. Single Extract Run on Multiple Chips 2. Extracts From Different Lots Run at Different Times After Freezer Storage Data for 22,000 genes from human hippocampus! Laser Microdissection of Hippocampal Subfields and Layers CA4 SM = Stratum Molecular SR = Stratum Radiatum (GABA Neurons) SP = Stratum Pyramidale SO = Stratum Oriens (GABA Neurons) Benes, Lim, Matzilevich, Walsh and Subburaju. PNAS (2007) CA1 * * * = GABA Cells SO SP SR SM GC Schizophrenia Cell Cycle Regulation and DNA Repair Increased Expression Increased Expression Bipolar Disorder Mitosis Replication Facto Benes, Lim and Subburaju. PNAS (2009) Mitosis Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Activation Networks: Activation Networks Are Not Neural Circuits? Amygdalar Projections to Anterior Cingulate Cortex Van Hoesen (1993) Van Hoesen, 1993 CA2 CA3 CA1 SUBREGIONAL CHANGES IN SZ + BD HIPPOCAMPUS AD* CA4 CA3 CA2** CA1 Nonpyramidal N. (1998) GABAA RBA (1996) GluR5,6,7-IR (2001) TH-IR Varicosities (1999) GAD65 Terminals (1998) D1 mRNA (2004) GAD65 +GAD67 (2007) * ** AD = Area Dentata CA2 has the highest level of nuclear [3H]corticosterone binding + highest expression of kainate receptor protein Rodent Modeling for Postmortem Circuitry Abnormalities in Limbic Lobe of SZs and BDs Picrotoxin Experiments BLn of Amygdala Anterogradely Traced BLn Fibers Str. Oriens CA2/CA3 BLn = Basolateral Nucleus Berretta, Munno and Benes, J. Comp. Neurol., 1999 Benes and Berretta, Neuropsychopharmacology, 2001 Excitatory Influence of Amygdala and Medial Septal Afferents on Hippocampal Integration in SZ Area Dentata CA3/2 CA1 Perforant Path Entorhinal Cx Granule Layer SM Mossy Fibers SR Normal Control SP SO Schaffer Collaterals Alveus Area Dentata Schizophrenics + Bipolars Septal Nuclei Hypothalamus CA3/2 CA1 Subiculum Amygdala Entorhinal Cx GABAA Receptors Amygdala Activation of CA3/2 in Rats GABA Amygdalar Glutamate Kainate Receptors (GluR 5 or 6) Stratum Pyramidale Tretrameric Kainate Receptors GluR 6,7 GluR 6,7 Stratum Oriens GluR 5 Disinhibitory Interneuron Fast-Spiking Inhibitory Interneuron Basolateal Amygdalar Afferents TGFβ2 FGF2,6,9 VEGF Neuregulin GAD67 Network Kainate Receptor Subunits Cell Cycle Regulation GRIK3 GRIK1 GRIK2 TGFβR1 LEF1 GAD67 Β-Catenin Promoter SMAD3 RUNX2 GSK3β HDAC11 CDC25a DAXX DNA Replication/Repair POLI POLI POLH TLE1 Functional Differentiation Cyc E CDK2 POLG RPA3 Cyclin D2 CDK4/6 POLD BRCA1 G2 p53 De-Differentiation PAX4,5 G1 Arrest G1 Cyc B CDC2 E2F Benes , FM. Cell Cycle 2010; 9: 625-627 Benes, FM. Neuropharmacology 2011; 60: 1232-42. Abl RB DP-1 MBD4 CH3-CpG Domain CHK2 OFF No Mitosis Oxidative Stress Chromatin Strand DNA Damage DNA Polymerase Mutations Genomic Integrity Preserved? Duplications or Deletions Induced? Duplications and Deletions of Specific DNA Sequences for Important Genes Sheng, Demers and Benes. In preparation (2011) Informed Consent Genomics research presents special challenges Legal-next-of-kin (LNOK) must give consent Irreversible anonymization provides the greatest confidentiality BRAIN IMAGING OR POSTMORTEM STUDIES An NIH National Resource Which is more important for understanding psychiatric disorders? Imaging studies tell us about function Postmortem studies tell us about the molecular regulation of neural circuitry BOTH ARE EQUALLY IMPORTANT! Office of the Inspector General Department Health and Human Services “There must be “trust in the tissue banking community, i.e. organizations involved in procuring and using the donation will act as stewards of the gift.” HUB MODEL FOR NIH NATIONAL BRAIN BANKING Brain Bank 2 Brain Bank 1 HBTRC Mind Institute UC Davis Brain Bank Central Tissue Applications Brain Bank 3 Developmental Disorders Maryland Brain Bank 4 Substance Abuse Miami