25-8-11 Garden plants
advertisement

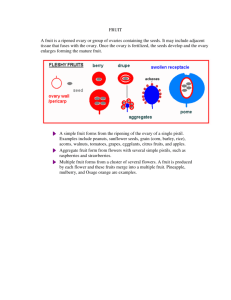
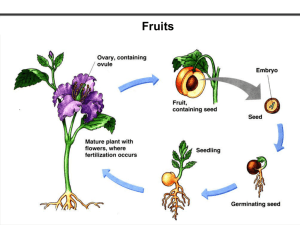
GARDEN PLANTS RSBS 18 August 2011 Jonathan Loh You Qing OVERVIEW Herbs & Spices Fruits Toxic Plants Medicinal Plants SPICES “I often quote myself. It adds spice to my conversations.” - George Bernard Shaw SPICES: Outline • History & uses • Aroma & essential oils (volatile organic oils) History & Uses • Peppercorn & currency • Funeral pyres & anointing • The Spice Trade (3BC – 19th Century) • Mainly…enhancing flavours • Intro: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bttLYrg9CzI Coriander • Coriandrum sativum; Family Umbelliferae • Leaves, fruits used • Uses (fruits): – 45% of curry powder – Diuretic, carminative, stomachic, emmenagogue, aphrodisiac properties – Essential oils for pharmaceuticals Coriander • Fruits: – Essential oils (0.4-1.0% Vol./Weight), mainly linalool (floral with touch of spiciness) – Minor; a-pinene, gterpinene, geranyl acetate, camphor, geraniol • Roots, stems, leaves: Aldehydes Chinese Matrimony Vine Chinese Matrimony Vine • • • • • Lycium chinensis; Family Solanaceae Native to China, Japan (bonsai plant) Fruits used TCM tonic: leaves into tea, fruits into wine Seeds: aphrodisiac properties, roots: antifebrile, antirheumatic tonic Chinese Matrimony Vine • Fruits rich in carotene (more orange, more β-carotene) – Carotenes & photosynthesis – Protect plant against UV – Prevent decline in cognition – Anti-oxidant – Pro-Vitamin A (vision) Torch Ginger Torch Ginger • Etlingera elatior; Family Zingiberaceae • Flowering shoot: laksa, rojak What’s common? The spices lah! • Braised pork belly/pig’s trotters: – – – – Star anise Cloves Cinnamon Garlic • Briyani: – – – – – – – – – – – Star anise Nutmeg Cumin Pepper Cloves Cardamom Cinnamon Coriander Ginger Onions Garlic Cinnamon Cloves • Syzgium aromaticus; Family Myrtaceae • Native to the Moluccas (Indonesia), used since the time of Christ • Major spice in spice trade Cloves • Dried unopened flower buds used • Essential oils: eugenol, eugenyl acetate, bcaryophyllene • Distillation into clove oil for perfumes, cleaning agent, poultices, stomach rub Cardamom • Elettaria cardamom; Family Zingiberaceae • Dried whole fruits, seeds used • One of the most expensive (labour in harvesting, processing; ripening irreg.) • Essential oil from seeds: 1,8-cinerole, a-terpinyl acetate, oleoresin • Heart tonic, carminative, diuretic, laxative, stomachic Star Anise Star Anise • Illicium verum; Family Illiaceae • More in Chinese than Western cooking • Treatment of lumbago, vomiting, promote menstruation Star Anise • Catechin, pro-anthocyanidin • Essential oils: – Anethole (liquorice taste) – Chavicol (peppery tatse) – Anisaldehyde (vanilla-like taste) • Manufacture of Tamiflu: Shikimic acid FRUITS “Everyone who enjoys thinks that the principal thing to the tree is the fruit, but in point of fact the principal thing to it is the seed. -- Herein lies the difference between them that create and them that enjoy.” - Friedrich Nietzsche FRUITS: Outline • Basic fruit structure • Classification: By Placentation • Classification: By Fruits • Intro: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=a6rFCMTfFog Basic Fruit Anatomy Placentation • Marginal – Blue pea • Parietal – Papaya • Laminar / Superficial – Water lily • Axile – Tomato • Free-central – Kiwi • Basal – Sunflower FRUITS A. Simple B. Aggregate i. Succulent Berry Pome C. Multiple ii. Dry Drupe Dehiscent Indehiscent Hesperidia Achene Pepo Caryopsis Follicle Capsule Legume Nut Samara Schizocarp S. A. M. • Simple: – Formed from 1 flower; ovary has 1 carpel / many fused carpels. • Aggregate: – Develop from 1 flower with many free carpels; 1 fruit from 1 carpel. – E.g. Strawberry • Multiple: – Develop from inflorescence as a bunch. – Juicy part: stalk holding bracts up. – E.g. Pineapple Androecium Corolla Pistil Calyx S > Succulent > Berry • Pericarp fleshy throughout • No hard stony endocarp • Many seeds embedded in pulp S > Succulent > Berry • Hesperidia: – Epicarp, mesocarp fused to form thick layer – Endocarp membranous, divides central pulp into little sections S > Succulent > Berry • Pepo: – Outer wall of pericarp develops from receptacle, becomes firm and hard – Inside remains soft with seeds embedded S > Succulent > Pome • Fleshy part: fusion of receptacle & fruit wall Epicarp S > Succulent > Drupe • Pericarp divided into epicarp (outer skin), mesocarp (thick, fleshy), endocarp (stony) *Coconut: mesocarp- fibrous husk, endosperm- white flesh S > Dry > Dehiscent • Dehiscents: Split open when ripe, scattering seeds S > Dry > Dehiscent • Follicle: – Forms from 1 ovary with 1 carpel, splits open on only 1 side – Peony S > Dry > Dehiscent • Legume: – Fruit forms from 1 ovary with 1 carpel; split open on 2 sides – Blue Pea • Capsule: – Fruit is many-seeded – Split in various ways – Carpels fused into an ovary – Durian S > Dry > Indehiscent • Indehiscents: Dry fruit wall, does not split open to release seeds; wall must decay before seeds released S > Dry > Indehiscent • Achene: – Fruit with single loose seed – Seed coat does not fuse with fruit wall – *Cypsela: calyx forms hair-like structures, in Tridax S > Dry > Indehiscent • Caryopsis/Grain: – One-seeded fruit, seed coat fused with fruit wall – Cereals, e.g. maize S > Dry > Indehiscent • Nut: – Pericarp becomes hard and woody/leathery – Fruit formed from ovary where carpels have fused – Usually 1 seed – Cashewnut, chestnut S > Dry > Indehiscent S > Dry > Indehiscent • Samara: – Outer wall of pericarp flattened (angsana, Casuarina) – Sepals enlarged to form wing-like structures (Dipterocarpus) – Fruit has 1 or 2 seeds S > Dry > Indehiscent • Schizocarp: – Fruits formed from ovary where carpels fused – Ripening, carpels split open; each part indehiscent, does not release seed – Desmodium, carrot, castor Join the Organic Rebellion at: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hVrIyEu6h_E MEDICINAL PLANTS “The art of medicine consists of amusing the patient while Nature cures the disease.” - Voltaire Jackfruit • Artocarpus heterophyllus; Family Moraceae • Chemicals: acetylcholine, hydrocyanic acid • Burma, China, Philippines: sap used to treat ulcers, abscesses (area swollen with pus) • Fruit pulp: cooling agent, tonic • Roots: treat diarrhoea, wood for convulsions Durian • Durio zibethinus; Family Bombacaceae • Malays: deconcoction of roots to treat lingering fever; deconcoction of leaves as bath for jaundice treatment Singapore Rhododendron • Melastoma malabathricum; Family Sendudok • Malaysia, Indonesia: Leaves as remedy for diarrhoea, dysentery; wash for ulcers and smallpox pastules so scars do not develop Pomegranate • Punica granatum; Family Punicaceae • Chemicals: Pelletierine, resin • Dried fruit skin: treat diarrhoea, rectocele – High astringent tannin content, antidiarrhoeal activity • Bark: treat bad breath, nose bleeding, piles, sore throat • Leaves: treat itch; (+ roots): treat irregular menstruation • Flowers: treat burns Cacao Tree • Theobroma cacao; Family Sterculiaceae • Chemicals: Caffeine, theobromine • Deconcoction of roots used in Philippines to increase menstrual flow, induce abortion Lalang • Imperata cylindrica; Family Gramineae • Chemicals: Anemonin, oxalic acid, saponin • Underground stem: treat cough, coughing of blood, influenza, blood in urine, internal bleeding, jaundice, kidney diseases • Roots: diuretic, contain fever, stop bleeding • Flowers: blood in sputum (saliva & mucus), nose bleeding, quench thirst Hydrangea • • • • Hydrangea macrophylla; Family Saxifragaceae Chemical: Hydrocyanic acid Flowers to treat malaria and heart diseases Leaves and shoots as antimalarial drug Cupid’s Shaving Brush • Emilia sonchifolia; Family Compositae • Chemicals: Alkaloids • Leaves made into a tea, drunk to reduce fever and treat dysentery Pepper • Piper nigrum; Family Piperaceae • Chemicals: chavicine, crytone, peperonal, piperanine, piperetline, piperine, transpinocarveol • Treat colic, rheumatism, headache, diarrhoea, dysentery, cholera, menstrual pains • Remove excessive gas in system, increase urine flow Lotus • Nelumbo nucifera; Family Nymphaeaceae • Chemicals: Anonaine, armepavine, isoquercitrin, liriodenine, nelumboside, nuciferine, oxoushinsunine, quercitin, roemerine • Antidote for mushroom poisoning • Leaf, leaf stalk, underground stems, stamens: astringent, haemostatic • Leaf + other herbs: treat sunstroke, diarrhoea, dysentery, fever, dizziness, vomiting of blood • Stalks + other herbs: treat excessive bleeding from uterus • Seeds: tonic TOXIC PLANTS “Lady Nancy Astor: Winston, if you were my husband, I'd poison your tea. Churchill: Nancy, if I were your husband, I'd drink it.” - Winston Churchill http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=trWzDlRvv1M Hydrangea • • • • All plant parts poisonous Chemicals: febrifugine, hydrangenol, loganin Abdominal pain, vomiting Febrifugine a hundred times more active than quinine as an antimalaria drug, practical application limited by toxicity • Hydrangenol as an allergenic agent • Loganin bitter, laxative activity Castor Oil Plant • • • • Ricinus communis; Family Euphorbiaceae Toxic plant parts: seeds, leaves Chemicals: ricin, ricinine One of the most toxic plants known; burning sensation in mouth, nausea, vomiting, severe pain in stomach, diarrhoea • Single seed of 0.25g has lethal dose Yellow Sage • • • • Lantana camara; Family Verbenaceae Toxic plant parts: leaf, stem, berries Chemicals: Lantadene A, B 1 of 10 most toxic weeds in the world; vomiting, diarrhoea, fall into coma, liver damage • Common in sheep in NE Australia, India THAT’S ALL, FOLKS!