kinematics1_1151
advertisement

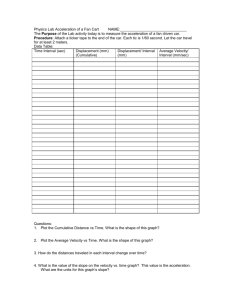
Kinematics-1 The study of HOW objects move: Graphs Equations Motion maps Verbal descriptions Overview Kinematics: Motion Description of Position and displacement velocity »average »instantaneous acceleration »average »instantaneous 10 Position vs Time Plots Gives location at any time. Displacement is change in position. Slope gives velocity. x (m) Write a description of this motion. The object accelerates for the first 1 second, moving 3 m in that time. Then it slows down until its velocity is 0 at the 4 m mark. At the 4 m mark, it begins to speed up in the negative direction until it is at the 2 m mark at 2 s. 3 4 t -3 12 Position vs Time Plots Gives location at any time. Displacement is change in position. Slope gives velocity. x (m) Position at t=3, x(3) = 1 3 Displacement between t=1 and t=3. 4 Dx = 1.0 m - 2.0 m = -1.0 m Average velocity between t=1 and t=3 v= t -3 -1 m / 2 s = -0.5 m/s 12 Instantaneous and Average Instantaneous Speed - speed at any given instant in time; speedometer reading, for example Average Speed – total distance divided by total time of travel; rate you would have to travel constantly to cover the same distance in the same time Velocity vs Time Plots Gives velocity at any time. Area gives displacement Slope gives acceleration. v (m/s) 3 1.5 Velocity at t=2, v(2) = 3 m/s Displacement between t=0 and t=3: t=0 to t=1: ½ (3m/s) (1 s) = 1.5 m t=1 to t=3: (3m/s) (2 s) = 6 m 7.5 m 6 4 t -3 Average velocity between t=0 and t=3? 7.5 m / 3s = 2.5 m/s Change in v between t=3 and t=5. Dv = -2 m/s – 3 m/s = -5 m/s Average acceleration between t=5 and t=3: a = -5 m/s / (2 s) = -2.5 m/s2 18 Velocity vs Time Plots Gives velocity at any time. Area gives displacement Slope gives acceleration. v (m/s) 3 Write a description of this motion. The object accelerates from 0 m/s to 3 m/s during the first second. Then for 2 seconds, it travels at a constant velocity of 3 m/s. From 3 seconds to 5 seconds, it accelerates in the negative direction from 3 m/s to –2 m/s. 1.5 6 4 t -3 18 Acceleration vs Time Plots Gives acceleration at any time. Area gives change in velocity a (m/s2) Acceleration at t=4, a(4) = 3 -2 m/s2 Change in v between t=4 and t=1. Dv = 6 +4 m/s 24 t=1-3: Dv = (3m/s2)(2s) = 6 m/s t=3-4: Dv = (-2m/s2)(1s) = -2 m/s t -3 21 Example x (meters) 100 0 -100 position vs. time -200 -300 0 v (m/s) 5 10 t (seconds) 15 20 • • • • Where is velocity zero? Where is velocity positive? Where is velocity negative? Where is speed largest? • Where is acceleration zero? • Where is acceleration positive? 20 0 -20 -40 velocity vs. time -60 -80 -100 0 5 10 t (seconds) 15 20 48 Summary of Concepts kinematics: A description of motion position: your coordinates displacement: Dx = change of position velocity: rate of change of position average : Dx/Dt instantaneous: slope of x vs. t acceleration: rate of change of velocity average: Dv/Dt instantaneous: slope of v vs. t 50 Velocity Slope of x vs t gives v vs t x(t) 4s Area under v vs t gives Dx! Which plot best represents v(t) v(t) v(t) t Dx Dt 5s t v(t) t t Acceleration (m/s2) The average acceleration is the change in velocity divided by the change in time. Dv a Dt v(t) Dv Dt Instantaneous acceleration is limit of average velocity as Dt gets small. It is the slope of the v(t) plot t v(t) t 31 Speeding Up & Slowing Down •Negative acceleration can mean speeding up or slowing down. The same is true with positive acceleration. Instantaneous Velocity Instantaneous velocity is the limit of the average velocity as the time interval approaches 0. Dx dx v lim Dt 0 Dt dt It is the instantaneous rate of change of position with time. Instantaneous rate of change is the derivative – which means slope of a graph at a point Acceleration Acceleration is a vector quantity defined as the rate at which an object changes its velocity. An object is accelerating if it is changing its velocity. Acceleration Slope of V vs T – 1 Time (s) Velocity(m/s) 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 10 5 10 Acceleration Slope of V vs T -- 2 Time (s) Velocity(m/s) 0 0 1 10 2 20 3 30 4 40 5 50 Constant Positive Velocity Constant Negative Velocity Position – Time Constant Acceleration • Positive Velocity Positive Acceleration Positive Velocity Negative Acceleration Negative Velocity Negative Acceleration Negative Velocity Positive Acceleration Passing Lane When does the red car pass the blue car? Where How does the red car pass the blue car? fast is each traveling at that time? Passing Lane Velocity-Time Passing Lane – Position-Time