Vocabulary and Review Notes
advertisement

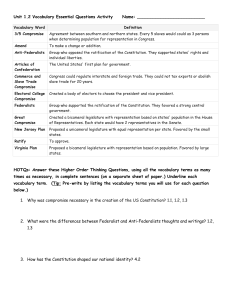
Vocabulary and Review Notes • This weeks vocabulary words: • article • Amendment • preamble • Constitution • Separation of power • Limited government • Checks and balances • Individual rights • One of several main parts of a document • Example: Newspapers have many articles in them. Article • A formal or official change made to a law, contract, constitution, or other legal document. • Example: There are many amendments that have been added to the Constitution to help us better define what it means. Amendment • An introduction to a formal document that explains its purpose. • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=30OyU4O80i4 Preamble • Montesquieu’s idea that power should be distributed amongst many parts of government, not just one person or branch. • Example: The United States government exhibits separation of power through the three branches of government: executive, legislative, and judicial. Separation of Power • Gives citizens more control on how they shape their local environment and policy; the government can only do what the people allow it to. • Example: The state of Florida cannot declare war on the country of Japan because the Constitution does not give the state that power. Limited government • A system in which each branch of government is able to check, or restrain, the power of the others. • Example: Congress is responsible for writing the budget every year, but the president has to approve it. This shows a check that the executive branch has on the legislative branch Checks and balances • A detailed written plan of government. • Example: Every state has a constitution, as well as the national government in the federalist structure. Constitution • The rights that allow people to pursue “life, liberty, and happiness” Individual rights • Colonies were established by King George of England • The King taxed the colonists so much that they decided to create a new country with the Declaration of Independence • The colonists fought the war for independence and wrote the first constitution: the Articles of Confederation History of the Constitution • When the A of C ended up being too weak to handle the United States’ problems, the Founding Fathers met to revise the Articles. • This meeting ended up being called the Constitutional Convention. History of the Constitution • Virginia Plan: 2-house legislature with a president where representation was based off population. • New Jersey Plan: one-house legislature with equal representation • Connecticut Compromise (Great Compromise): 2-house legislature, executive, and judicial branch. Upper house in the legislature has equal representation based on the New Jersey Plan, the lower house had proportional rep. based on the Virginia Plan. • 3/5 Compromise: When the Founding Father’s decided on the Great Compromise to create the legislature, they needed to figure out a way to determine population in the states with slaves for the House of Representatives. They decided that slaves would count as 3/5ths of a free person. Constitutional Convention • Creates a government with three branches: • Executive Branch: President, Vice President, and the Cabinet (advisors) • Legislative Branch: Congress • Senate (Equal) • House of Representatives (proportional) • Judicial Branch: Supreme Court U.S. Constitution