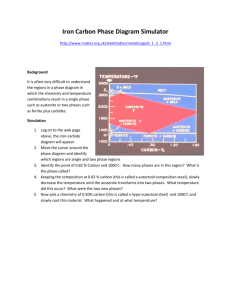
01 Memobust course Overall Design
advertisement

Overall design Eurostat Presented by • Eva Elvers • Statistics Sweden Outline • What is ‒ a survey? ‒ statistics? • The GSBPM • Quality – some perspectives • Design of a statistical survey – some aspects What is a survey? From EHQR 2009 1. Sample survey 2. Census 3. Statistical process using administrative source(s) 4. Statistical process involving multiple data sources 5. Price or other economic index process 6. Statistical compilation What is statistics? A statistical table • A statistical measure (e.g. sum, mean or median) is used to summarise • individual variable values (e.g. turnover) for • the statistical units (e.g. enterprise) in a group. • The totality of considered statistical units is called the population. • There are sub-populations; domains of estimation. • There are reference times for variables, units … Typical for statistics (1) • Statistical characteristics or parameters as above. • Parameters of interest, depending on use and user. • Target parameters based on target variables, target units, target population, … • Statistics are estimates aiming at the target parameters. Typical for statistics (2) • Variables of interest, target variables • Observation variables • Consider ‒ ‒ ‒ ‒ ‒ measurements; quality; costs; sources; response burden. Typical for statistics (3) • Population and subpopulations • Several unit types may be needed ‒ enterprise, kind of activity unit, local unit, … ‒ interest, target, observation • A frame leading to a frame population ‒ Compare with target population (unit type) ‒ Coverage deficiencies ‒ Time aspects Typical for statistics (4) • Consider sources for data collection ‒ direct data collection ‒ accessible from earlier collection ‒ administrative data • Express statistical inference ‒ finite population ‒ sample, register The GSBPM – Generic Statistical Business Process Model – the UNECE version in 2009, phases and sub-processes Phases of the statistics production process • Phases 1 – 3, preparatory ‒ Specify needs ‒ Design ‒ Build • Phases 4 – 8 ‒ Collect, Process, Analyse, Disseminate, Archive • Phase 9 ‒ Evaluate Quality Assurance and Quality Control • Q is fitness for use, fitness for purpose, ... • QA: ‒ Approaches and methods to achieve the intended/stated quality. ‒ Providing confidence that the quality requirements will be met. • QC: ‒ Verification that the quality achieved was as expected. ‒ Checks, ... Typical in a statistical office • Business register ‒ Basis, frame construction, auxiliary information • Primary statistics ‒ Short-term statistics (monthly, quarterly), STS ‒ Structural statistics (annual), SBS • Secondary statistics ‒ National accounts, Balance of payment etc. Output quality components European Statistics CoP 2011, EHQR 2009 • Relevance • Accuracy and reliability • Timeliness and punctuality • Coherence and comparability • Accessibility and clarity Accuracy and reliability (e.g. SIMS 2013) • Sources of error (in-accuracy) ‒ ‒ ‒ ‒ ‒ ‒ Sampling Coverage Measurement Non-response Processing Model assumption • Data revision (reliability) ‒ Data revision, average size Coherence and comparability • Meaning ‒ Adequacy of being combined, used together • Important ‒ Definitions: concepts, units, populations, … ‒ Methods • Examples ‒ Across domains, with National Accounts, … ‒ Comparability special case, e.g. EU geographical ‒ Over time Relevance • User needs ‒ Content: concepts, … ‒ Quality components • User satisfaction • Completeness ‒ Data (statistics) and metadata ‒ Regulations ‒ The system of surveys Design aspects • Survey situation ‒ Design a new survey ‒ Redesign a survey ‒ Continuous improvements • Scope ‒ Methodological, technical, … ‒ Set of surveys, survey, sub-process, tool, system, … Design aim: ”optimisation” • There may be a simple statement, like ‒ Minimum cost given quality. ‒ Maximum quality given cost (quality is multi-facetted). • Design, two core tasks are to make “optimal” ‒ choices, e.g. of methods; ‒ allocations, e.g. of resources. GSBPM and output quality Which principles do you use to design 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. the the the the the the frame? sample? data collection method? contact strategy? editing? estimation? What do you need to design • What is the input? (groups 1, 2, 6) • What is the output? (groups 3, 4, 5) Theory or principles for some parts/processes – four examples • Sampling and estimation ‒ Mean Squared Error, MSE. • Response process ‒ Comprehension, retrieval, ... • Data collection ‒ Modes, type of data, timeliness etc. • Editing ‒ Quality control. Design work in brief Design • a forthcoming survey round • for statistics (macro data) or micro data • through appropriate competences • in cooperation/agreement with customers/users/stakeholders so that • quality is sufficient for the intended use, • the production is within budget and cost-effective (in the long run), and • with regard taken to respondents (burden). To design you need to know • For appropriate choices and allocations: ‒ ‒ ‒ ‒ ‒ The population and how to reach its objects/units. Variations in the population and sub-groups. How questions are interpreted. Possibilities to reply, provide the information requested. ... How could you learn? • Pilot study ‒ Qualitative, make “discoveries” ‒ Quantitative, statistical inference • Embedded experiment ‒ On-going survey ‒ Utilise the sample Responsive/adaptive design • Plan with successive decisions ‒ Mostly described for household statistics and telephone interviewing ‒ Information from previous rounds ‒ Successive information this round (new survey) • Examples ‒ “Mile-stones” with re-considerations ‒ Reminder strategy, contact mode, … Paradata, metadata-driven • Process data, paradata ‒ Collect, suitably chosen set, with aim ‒ Analyse and improve • Metadata ‒ Information about the statistics ‒ For the statistics production: parameters, … What is included in an ”optimisation”? • Find e.g. the best quality for given cost and subject to a set of constraints, such as ‒ Regulations. ‒ Rules for data collection, response burden. ‒ Resources, financial and personnel. ‒ Quality depends on use(s) – user dialogue! ‒ Quality is multi-facetted! “Conclusions” – aspects on design • • • • • • Teamwork On-going work Constraints assist Metadata, paradata (process data) Architecture: methodology, IT, … Data integration