Introduction to Physiology: The Cell and General Physiology
advertisement

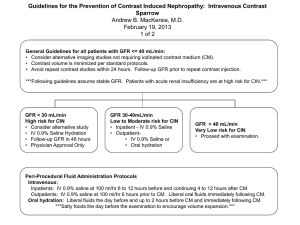
Nephron: functional unit of the kidney Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Figure 26-3; Guyton and Hall Nephron Tubular Segments Figure 26-4; Guyton and Hall Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Structure of the juxtaglomerular apparatus: macula densa Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Figure 26-17; Guyton and Hall Cortical and Juxtamedullary Nephron Segments Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Figure 26-5; Guyton and Hall • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=glu0dz K4dbU Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Summary of Kidney Functions • Excretion of metabolic waste products: urea, creatinine, bilirubin, hydrogen • Excretion of foreign chemicals: drugs, toxins, pesticides, food additives • Secretion, metabolism, and excretion of hormones - renal erythropoetic factor - 1,25 dihydroxycholecalciferol (Vitamin D) - Renin • Regulation of acid-base balance • Gluconeogenesis: glucose synthesis from amino acids • Control of arterial pressure • Regulation of water & electrolyte excretion Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Basic Mechanisms of Urine Formation Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Figure 26-8; Guyton and Hall Renal Handling of Different Substances Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Figure 26-9; Guyton and Hall Renal Handling of Water and Solutes Filtration Reabsorption Water (liters/day) Excretion 180 179 1 Sodium (mmol/day) 25,560 Glucose (gm/day) 180 Creatinine (gm/day) 1.8 25,410 0 0 150 180 1.8 Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Glomerular Capillary Filtration Barrier Figure 26-10; Guyton and Hall Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. The Ability of a Solute to Penetrate the Glomerular Membrane Depends on: • Molecular size ( small molecules > filterability) • Ionic charge (cations > filterability) Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Effects of Size and Electrical Charge of Dextran on Filterability by Glomerular Capillaries Figure 26-11; Guyton and Hall Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Clinical Significance of Proteinuria • Early detection of renal disease in at-risk patients - hypertension: hypertensive renal disease - diabetes: diabetic nephropathy - pregnancy: gestational proteinuric hypertension (preeclampsia) - annual “check-up”: renal disease can be silent • Assessment and monitoring of known renal disease • “Is the dipstick OK?”: dipstick protein tests are not very sensitive and not accurate: “trace” results can be normal & positives must be confirmed by quantitative laboratory test. Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Figure 26-12; Guyton and Hall Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Glomerular Hydrostatic Pressure (PG) • Is the determinant of GFR most subject to physiological control • Factors that influence PG - arterial pressure (effect is buffered by autoregulation) - afferent arteriolar resistance - efferent arteriolar resistance Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Effect of Afferent and Efferent Arteriolar Constriction on Glomerular Pressure Ra Re PG Blood Flow Blood Flow GFR GFR Ra GFR + Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. PG Renal Blood Flow Re GFR + Renal Blood Flow Effect of changes in afferent arteriolar or efferent arteriolar resistance Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Figure 26-14; Guyton and Hall determined by : FF = GFR / RPF G RBF GFR RE + PG Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. _ Summary of Determinants of GFR Kf PB G GFR GFR GFR A FF PG GFR PG PG GFR GFR GFR RA RE (as long as Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. G G RE < 3-4 x normal) Assessing Kidney Function • Albumin excretion (microalbuminuria) • Plasma concentration of waste products (e.g. BUN, creatinine) • Urine specific gravity, urine concentrating ability • Imaging methods (e.g. MRI, PET, arteriograms, iv pyelography, ultrasound etc) • Isotope renal scans • Biopsy • Clearance methods (e.g. 24-hr creatinine clearance) • etc Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Clearance • Clearance is a general concept that describes the rate at which substances are removed (cleared) from the plasma. Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Clearance Technique Renal clearance of a substance is the volume of plasma completely cleared of a substance per min. Where: Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Cs x Ps = Us x V Cs = Us x V Ps Cs = clearance of substance S Ps = plasma conc. of substance S Us = urine conc. of substance S V = urine flow rate Use of Clearance to Measure GFR For a substance that is freely filtered, but not reabsorbed or secreted (inulin, 125 I-iothalamate, ~creatinine), renal clearance is equal to GFR amount filtered = amount excreted GFR x Pin = GFR = Uin x V Uin x V Pin Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Calculate the GFR from the following data: Pinulin = 1.0 mg / 100ml Uinulin = 125 mg/100 ml Urine flow rate = 1.0 ml/min U x V in GFR = Cinulin = Pin GFR = 125 x 1.0 1.0 Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. = 125 ml/min Steady-state relationship between GFR and serum creatinine concentration Figure 27-19; Guyton and Hall Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Clearances of Different Substances Substance inulin glucose sodium urea Clearance (ml/min) 125 0 0.9 70 Clearance of inulin (Cin) = GFR if Cx < Cin: indicates reabsorption of x if Cx > Cin: indicates secretion of x Clearance creatinine (Ccreat) ~ 140 (used to estimate GFR) Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Control of Glomerular Filtration 1. Sympathetic Nervous System RA + R E GFR + RBF 2. Catecholamines ( norepinephrine) RA + R E GFR + RBF 3. Angiotensin II RE GFR + RBF (prevents a decrease in GFR) Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Control of Glomerular Filtration 4. Prostaglandins RA + R E GFR + RBF 5. Endothelial-Derived Nitric Oxide (EDRF) RA + R E GFR + RBF 6. Endothelin RA + R E Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. GFR + RBF Control of Glomerular Filtration 7. Autoregulation of GFR and Renal Blood Flow • Myogenic Mechanism • Macula Densa Feedback (tubuloglomerular feedback) • Angiotensin II ( contributes to GFR but not RBF autoregulation) Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Renal Autoregulation 120 Renal Artery Pressure (mmHg) 100 80 Glomerular Filtration Rate Renal Blood Flow 0 Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. 1 2 3 Time (min) 4 5 Renal Blood Flow and GFR Autoregulation Figure 26-16; Guyton and Hall Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Macula Densa Feedback GFR Distal NaCl Delivery Macula Densa NaCl Reabsorption (macula densa feedback) Afferent Arteriolar Resistance GFR (return toward normal) Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Myogenic Mechanism Arterial Pressure Stretch of Blood Vessel Cell Ca++ Permeability Blood Flow Vascular Resistance Intracell. Ca++ Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Regulation of GFR by Ang II GFR Macula Densa NaCl Renin Blood Pressure AngII Efferent Arteriolar Resistance Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Macula densa feedback mechanism for GFR autoregulation Copyright © 2006 by Elsevier, Inc. Figure 26-18; Guyton and Hall