Cellular Architecture
advertisement

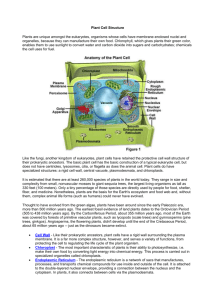
Cellular Architecture Or the typical/nontypical cell Figur I. Limits to cell size A. Surface to volume ratio 1. function of membrane 2. relationship of surface area to volume 3. consequences of growing too large 1 mm 2 mm 2 mm 1 mm Figur I. Limits to cell size B. Control issues 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Informational flow Transcription Diffusion Translation Cell gets too large, lag time in the control of activities 6. Analogy II. Few Generalizations • A. Procaryotic vs. eukaryotic • B. Typical cell – 1. animal – 2. plant – 3. discuss the similarities first III. Organelles of synthesis • A. Introduction – 1. – 2. – 3. – 4. – 5. Going to act as an assembly line Nucleus Endoplasmic reticulm ribosome Golgi apparatus III. Organelles of synthesis B. Nucleus-headquarters 1. chromatin 2. chromosomes 3. nucleolus 4. double membrane with pores Nuclear Pores From Surface of Nuclear Membrane Artist conception of nuclear pores III. Organelles of synthesis • • • • C. 1. 2. 3. Endoplasmic Reticulum definition nickname types of – Rough – Smooth Rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum Endoplasmic reticulum continuous with pores III. Organelles of synthesis • • • • D. 1. 2. 3. Ribosomes-protein synthesis found free in cytoplasm-endogenous use attached to E.R.-proteins for export responsible for translation of mRNA into protein Ribosomes translate mRNA III. Organelles of synthesis • D. Golgi Body or Golgi Apparatus • 1. nick name of bottling center • 2. modifies product • 3. concentrates product • 4. packages product into vesicles • 5. exports via exocytosis III. Organelles of synthesis • E. Cell membrane with exocytosis IV. Organelles of homeostasis • • • • • • A. Mitochondria Nickname Structure Endosymbiosis More active tissue Both animal and plant B. Chloroplasts • Nickname • Structure • Endosymbiosis Mitochondria and chloroplasts are tied tightly together Cell wall Vacuole Granum Plasma membrane Stroma Nuclear envelope Nucleolus Smooth ER Rough ER Nuclear pores Chromatin Nucleus Ribosomes Chloroplast Rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER) Figur C. Lysosome • Nickname • Structure • Functions D. Peroxisomes • • • • Similar in appearance to lysosomes Contain enzymes important in lipid breakdown Detoxification centers Possess enzyme catalase important in the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide E. Cytoskeleton Composed of microtubules and microfilaments 1. Microtubules • “Skeleton” of the cell • Produce the structural framework for cilia and flagella 2. microtubules • Act as a railway along which organelles travel • Microtubules may walk past one another • Motor molecules may transport organelles from one area of the cytoplasm to another 3. microfilaments a. b. “muscles” of the cell Same proteins that are found in our muscles c. d. Cytokinesis pseudopods Microfilaments (cont) e. produce swaying of microvilli f. Movements of cytoplasmic streaming Relationship of the cytoskeleton to the cell membrane and extracellular fibers F. Cell wall of plant cells • • • • Primary cell wall Secondary cell wall Middle lamellae pectin Importance of plasmodesmata Plant cell walls Plasmodesmata Plasmodesmata G. Centrioles H. Central vacuole I. Cilia and flagella • Microtubules • 9 +2 • Triplets in basal body • Form from centrioles?