Midterm Review 6.1 – Graphing angles and radian measure: 1.
advertisement

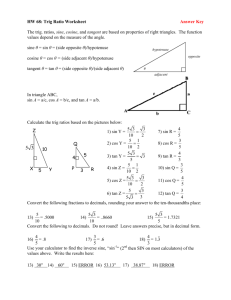
Precal/Trigonometry Midterm Review 6.1 – Graphing angles and radian measure: 1. Find an angle in the interval [−4𝜋, −2𝜋) that is conterminal with the given angle. 5𝜋 103𝜋 a. b. − 4 2. 14 Find an angle in the interval [4𝜋, 6𝜋) that is conterminal with the given angle. a. 5𝜋 7 b. − 91𝜋 3 3. Scientists created a new unit of time called the farganfugan. There are 22 farganfugans in one hour. On a clock labeled in farganfugans, find how far the tip of a 7 inch long farganfugan hand moves in 13 farganfugans. 4. A manufacturing accident caused a batch of clocks to be produced that had 14 hour markers and no minute markers. As a consequence, the hour minute hand of the clock now makes 1 full revolution every 70 minutes. If the hour minute hand is 3 inches long, find the distance that the tip of the hour minute hand moves in 1 minute. What about in 36 minutes? 8.1 – Right triangle trig: 5. Find the values of the six trig functions of the angle 𝜃. 6. Label each special triangle with acceptable side lengths. 𝜋/6 𝜋/4 7. A small plane is flying at an altitude of 10,000 ft. The radar tower of an airport spots the plane flying at an angle of elevation of 57°. Find the distance from the plane to the base of the radar tower. 8. A police helicopter is flying at an altitude of 800 ft. A stolen car is sighted at an angle of depression of 72°. Find the distance from the helicopter to the car. 6.2 and 6.3 – Trig functions of any angle, the unit circle, and Fundamental identities: 9. Find the exact value of each expression or write undefined if necessary. a. cos 210° b. sin 3𝜋 4 c. tan 11𝜋 6 d. sec 210° e. cot 7𝜋 3 f. 4 tan 17𝜋 𝜋 cos 3 4 + sin 7𝜋 𝜋 csc 6 6 g. cos 90° 10. 7𝜋 2 21𝜋 − 4 b. cos ( 1000𝜋) 𝜋 4 𝜋 1+𝑔( ) 4 1−𝑓( ) 17𝜋 )− 2 b. 𝑓 ( c. tan (− 13𝜋 )+ 3 𝑔( 1−𝑔(𝜋/4) 1+𝑓(5𝜋/6) 17𝜋 )− 2 b. 𝑓 ( 𝜋 k. sin ( 2 + 80𝜋) l. tan ( 2 + 31𝜋) 13𝜋 3 + 801𝜋) 𝜋 3 35𝜋 2𝜋 ℎ( ) 5𝜋 c. 𝑓 (√3 ⋅ 𝑔 ( 12 ⋅ ℎ ( 4 ))) 13𝜋 )+ 3 𝑔( 𝜋 ℎ (3 ) In each case, find the exact value of each of the remaining trig functions of 𝜃. 7 a. csc 𝜃 = − 4 and cos 𝜃 < 0 2 3 b. tan 𝜃 = − 3 and csc 𝜃 > 0 5 c. cos 𝜃 = 5 and0 < 5𝜃 + 4𝜋 < 4𝜋 2 d. sec 𝜃 = − 4 and sin 𝜃 ⋅ cos 𝜃 > 0 14. 3𝜋 j. sec(−630°) Let 𝑓(𝜃) = 3 sin 𝜃, 𝑔(𝜃) = cos(3𝜃), and ℎ(𝜃) = tan3 𝜃. Find the exact value of each expression. a. 13. 25𝜋 2 Let 𝑓(𝜃) = 2 sin 𝜃, 𝑔(𝜃) = cos(2𝜃), and ℎ(𝜃) = tan2 𝜃. Find the exact value of each expression. a. 12. i. cot Find the exact value of each expression. a. sin 11. 3𝜋 2 h. sin e. tan 𝜃 = − 3 and5𝜋 < 5𝜃 + 2𝜋 < 8𝜋 Use identities to find the exact value of each expression. Do not use a calculator. b. cos2(33°) − sin2 (57°) a. sec 8 cot 8 sin 8 d. sin 8 csc 8 e. sin2(33°) + sin2 (57°) h. csc 𝜃 sin 𝜃 − tan 𝜃 cot 𝜃 𝜋 i. csc 8 sec 3𝜋 8 c. 1 − tan2 1 + sec 2 1 f. tan2 1 − sec 2 1 − tan g. 1 − cot 2 20° + sec 2 70° 3𝜋 𝜋 cot 8 8 j. sin2 𝑥 − 2 tan2 𝑥 + 2cot 2 𝑥 + 2sec 2 𝑥 − 2csc 2 𝑥 + cos 2 𝑥 15. Let sin 𝜃 = 𝑎, cos 𝜃 = 𝑏, and tan 𝜃 = 𝑐. a. 3 sin(−𝜃) − sin 𝜃 Write each expression using only 𝑎, 𝑏, and𝑐. b. 3cos(−𝜃 − 6𝜋) + 2 sin(𝜃 + 2000𝜋) − 4cot(−𝜃 + 17𝜋) c. 3 sin(−𝜃) − sec(−𝜃) d. 4cos(𝜃 − 6𝜋) + 2 csc(𝜃 + 2000𝜋) − 4tan(−𝜃 + 17𝜋) 6.4, 6.5, 6.6 – Graphing trig functions: 16. Use the amplitude, period, and phase shift to graph one period of each functions. a. 𝑦 = 3 sin 4𝑥 b. 𝑦 = −2 cos 2𝑥 e. 𝑦 = −3 cos(𝑥 + 𝜋) h. 𝑦 = sin(2𝑥) + 1 c. 𝑦 = 3 cos 3 𝜋 2 4 f. 𝑦 = cos (2𝑥 + ) 𝑥 3 d. 𝑦 = − sin 𝜋𝑥 𝜋 g. 𝑦 = −3 sin ( 𝑥 − 3𝜋) 3 e. sin(𝜃 + 𝜋) 17. Graph two periods of each function. 𝜋 a. 𝑦 = 4 tan 𝑥 𝜋 b. 𝑦 = −2 tan 𝑥 c. 𝑦 = − tan (𝑥 − ) 4 1 𝜋 2 2 𝜋 e. 𝑦 = − cot 𝑥 d. 𝑦 = 2 cot 3𝑥 4 f. 𝑦 = 2 cot (𝑥 + ) g. 𝑦 = 3 sec 2𝜋𝑥 2 h. 𝑦 = −2 csc 𝜋𝑥 5 i. 𝑦 = 3 sec(𝑥 + 𝜋) j. 𝑦 = csc(𝑥 − 𝜋) 2 7.1, 7.2 – Inverse trig functions: 18. Find the exact value of each expression. a. sin−1 1 19. b. cos−1 1 d. sin−1 (− √3 ) 2 1 e. cos −1 (− 2) f. tan−1 (− √3 ) 3 Find the exact value of each expression. a. cos (sin−1 √2 ) 2 3 b. sin(cos−1 0) 4 3 c. cos (tan−1 4) d. tan [sin−1 (− 4)] 1 e. tan [cos−1 (− 5)] 20. c. tan−1 1 f. sin [tan−1 (− 3)] Find the exact value of each expression or write undefined if necessary. a. sin (sin−1 √7 ) 8 e. cos(cos −1 𝜋) i. sin−1 (sin 2𝜋 ) 3 b. sin (sin−1 8 ) √7 1 f. tan (tan−1 2) j. sin−1 (sin 3 c. cos (cos −1 4) 𝜋 g. tan(tan−1 2) 7𝜋 ) 9 d. cos(cos−1 3.14) h. sin−1 (sin 7 ) 𝜋 k. cos−1 [cos (− 4 )] l. cos −1 [cos (− 27𝜋 )] 14 7.3 – Trig equations: 21. For each equation, find all solutions. 1 a. cos 𝑥 = − 2 22. b. sin 𝑥 = √2 2 c. 2 sin 𝑥 + 1 = 0 d. √3 tan 𝑥 − 1 = 0 e. cos 2𝑥 = −1 Solve the equation on [0,2𝜋). a. cos 2𝑥 = −1 b. 4 sin 3𝑥 − 4 = 0 e. cos2 𝑥 − 2cos 𝑥 = 3 i. sin 𝑥 = tan 𝑥 𝑥 c. tan 2 = −1 f. 2 cos 2 𝑥 − sin 𝑥 = 1 j. sin 𝑥 = −0.6031 d. tan 𝑥 = 2 cos 𝑥 tan 𝑥 g. 4 sin2 𝑥 = 1 k. 5 cos2 𝑥 − 3 = 0 h. cos 2 𝑥 − sin2 𝑥 − sin 𝑥 = 1 l. sec 2 𝑥 = 4 tan 𝑥 − 2