Analysis Midterm Review – Topics 2013/2014 6.1 Trigonometric
advertisement

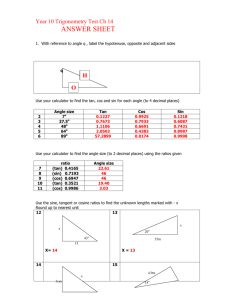
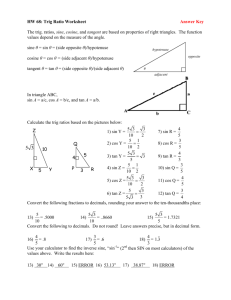
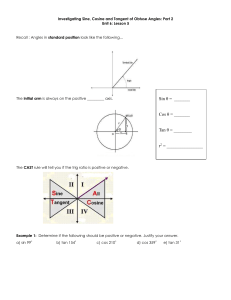
Analysis Midterm Review – Topics 2013/2014 6.1 Trigonometric Functions – Angles & Their Measures (Quiz: 6.1 Angles & Their Measures) 6.2 The Sine, Cosine, and Tangent Functions (Chart and Quiz: 6.2 SOH-CAH-TOA) Graphing Sine & Cosine (Quiz: Graphing) 7.1 Basic Trig Identities (Problem Set and Quiz: Basic Identities) 7.2-7.3 Addition & Subtraction Identities, Double Angle Identities, Half-Angle Identities (Quiz: Identities) Trigonometric Equations (Quiz: Trig Equations) 8.2 Right-Triangle Trig Applications (Quiz: Right Triangle Trig) 8.3 Law of Sines and 8.4 Law of Cosines (Quiz: Law of Sines/Cosines) 6.1 Trigonometric Functions – Angles & Their Measures Find the radian measure of three angles (at least one positive and one negative) in standard position that are coterminal with the given measure. 1. p 2. - 6 4p 5 Find the degree measure of three angles (at least one positive and one negative) in standard position that are coterminal with the given measure. 4. 505 3. 273 Convert the given degree measure to radians. (REDUCE) 4. 165 5. 48 Convert the given radian measure to degrees. 6. 3p 2 7. - 5p 8 6.2 The Sine, Cosine, and Tangent Functions SOH-CAH-TOA sin opposite hypotenuse cos adjacent hypotenuse tan opposite adjacent csc 1 hypotenuse sin opposite sec 1 hypotenuse cos adjacent cot 1 adj tan opp Coordinate Plane Identify the exact value for the given trig function. 1. sin780 =__________ 2. cos780 =__________ 3. tan780 =__________ 4. sin 5p =__________ 4 5. cos 5p =__________ 4 6. tan 5p =__________ 4 7. sin 11p =__________ 6 8. cos 11p =__________ 6 9. tan 11p = __________ 6 10. csc135 =_________ 11. sec135 =_________ 12. cot135 =_________ Assuming the terminal side of an angle in standard position lies in the given quadrant on the given straight line. Find sine, cosine, & tangent. 2 5 13. Quadrant IV: Line with equation y = - x . 14. Quadrant III: Line with equation 2y-3x=0 15. Quadrant II: Line perpendicular to 5y-10=x. Write the expression as a single real number. Do not use decimal approximations. 16. sin 5p p 5p p cos + cos sin 4 6 4 6 17. Find: sin q and tan q if cosq = - 6 p and £ q £ p . 10 2 18. What is the value of sine of an angle with 3 25 (quadrant 3) whose secant is ? 2 24 19. Find the cosecant of an angle whose terminal side in standard position passes through the point (-5,-6). Graphing Sine & Cosine Graph the following sine & cosine functions. Identify the amplitude, period, midline, phase shift, and critical points of each graph. 1. -2sin(3x) 2. cos( x ) 2 3. 6sin 4 x 3 2 4. Using the below graph of f (x) = -sin x , answer each of the below questions. 2 f(x) = 1∙sin(x) 1.5 1 0.5 π 4 0.5 π 2 3π 4 π 5π 4 3π 2 7π 4 2π 1 1.5 2 2.5 a) Identify the domain of f (x) = -sin x in interval notation. __________ b) Identify the range of f (x) = -sin x in interval notation. __________ æ 3p ö ÷. è 2 ø c) Find f ç æ 7p ö ÷ è 2 ø d) Find f ç ______________ ______________ e) Identify where f (x) = 0 for all values in the interval [ 0, 2p ] . _________ 7.1 Basic Trig Identities Basic Identities csc 1 sin sec cos 2 sin 2 1 1 cos tan sin cos 1 tan 2 sec 2 cot cos sin 1 cot 2 csc 2 Prove the following trigonometric identities. You must show ALL work to receive full credit! 1. sec x cot x csc2 x sin x 2. cos x cot x sin x csc x 3. sec 2 x cot 2 x tan 2 x csc 2 x sec 2 x csc 2 x Addition & Subtraction Identities, Double Angle Identities, Half-Angle Identities Addition and Subtraction Identities sin( x y ) sin x cos y cos x sin y sin( x y ) sin x cos y cos x sin y cos( x y ) cos x cos y sin x sin y cos( x y ) cos x cos y sin x sin y tan( x y ) tan x tan y 1 tan x tan y tan( x y ) tan x tan y 1 tan x tan y Double-Angle Identities sin 2 x 2 sin x cos x cos 2 x cos 2 x sin 2 x 2 tan x tan 2 x 1 tan 2 x cos 2 x 1 2 sin 2 x cos 2 x 2 cos 2 x 1 Half-Angle Identities sin x 1 cos x 2 2 cos x 1 cos x 2 2 tan x 1 cos x 2 1 cos x tan x 1 cos x 2 sin x tan x sin x 2 1 cos x 1. Using your addition/subtraction identities, find each of the following: 5 sin . 12 5 cos . 12 2. Given sin x = -3 3p and < x < 2p . Find each of the following: 5 2 sin2x cos2x tan2x 3. Using your half-angle identities, find each of the following: 5 sin 12 4. If csc 2 x 5 cos 12 5 tan 12 5 1 , find sin 2x. 2 Trig Equations Solve the following trigonometric equations using your knowledge of special trig values or the unit circle. All answers should be given in radian measure. 1. sin x 2 2 2. sec x 2 3. tan 2 x 1 2 4. 4 sin x 3 0 2 5. 4 cos x 4 cos x 1 0 csc 6. x 1 3 8.2 Right-Triangle Trig Applications 1. A 35 foot line is used to tether a helium-filled balloon. Because of a breeze, the line makes an angle of 68 with the ground. What is the height of the balloon? 2. A blimp flying at an altitude of 4280 feet spots a house on the ground. The angle of depression from the blimp to the house is 24 . Assuming the ground is flat, how far must the blimp fly to be directly over the house? 3. A ladder is resting against the side of a shed. If the ladder is 25 feet long & needs to reach 15 feet up the side of the shed, what angle will the ladder make with the ground? How far must the base of the ladder be? 4. A water tower is located 300 feet from a building. From a window in the building, the angle of elevation to the top of the tower is 35 . The angle of depression from the window to the bottom of the tower is 18 . a. How tall is the tower? b. How high is the window? 5. Maria needs to know the height of a tree. From a given point on the ground, she finds that the angle of elevation to the top of the tree is 25 . She then moves 35 feet closer to the tree. From the second point, the angle of elevation to the top of the tree is 38 . Find the height of the tree. 8.3 Law of Sines and 8.4 Law of Cosines (Quiz: Law of Sines/Cosines) a b c = = sin A sin B sinC a 2 = b 2 + c 2 - 2bc cos A b 2 = a 2 + c 2 - 2ac cos B c 2 = a 2 + b 2 - 2ab cosC Solve triangle ABC with the given information using the Law of Sines or the Law of Cosines. 1. a=10, b=16, A= 30 2. B= 20.67 , C= 34 , b=185. 4. a=6, b=12, c=16. 5. a=44, c=84, C= 42.2 3. a=7, c=16, A= 30