Vocabulary
advertisement

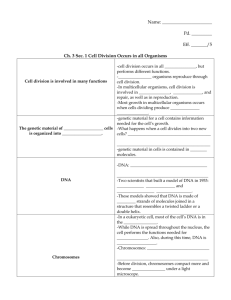
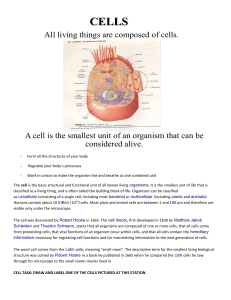
Unit 1 • Mean: the average of a set of numbers. To find, add all together and divide by the amount of #’s. • Peer review: Review process when an expert reviews the research paper written about an experiment. • Theory: a hypothesis which is supported by many experiments, repeated many times. • Basic Science: Science or research which investigates curiosity or interest, not to develop a product. • Applied Science: Science or research designed to solve modern problems to improve human condition. • SI Units: International system of units (meter, liter, second, gram) • Good lab practice: safe, common-sense habits to use while conducting experiments. • Control group: normal standard in an experiment which a scientist can use as a comparison. • Independent variable: single variable or factor which is changed or manipulated in an experiment. • Dependent variable: variable which is affected by the independent variable, is measured by the scientist. Unit 3 • pH scale: 0-14 scale used to compare concentrations of hydronium to hydroxide ions. Isotope: atoms of the same element which have different numbers of neutrons Ion: a charged atom Covalent bond: bond between two non-metals, where electrons are shared. Strongest bond type. Ionic bond: Bond which forms between a metal and a non-metal during which electrons are transferred and ions are made. Organic: Carbon containing Proton: subatomic particle with a positive charge found in the atom’s nucleus Electron: subatomic particle with a negative charge found in the space surrounding the nucleus of an atom Neutron: subatomic particle with no charge which is found in the atom’s nucleus. Enzymes: special proteins which lower the activation energy and catalyze reactions. Unit 3 • Eukaryote: complex cells which have a nucleus and membrane bound organelles • Prokaryotes: simple cells which do NOT have a nucleus or membrane bound organelles. • ATP: adenosine tri-phosphate, energy currency of cells • Nucleus: control center of cell, contains DNA • Mitochondria: converts energy from food into ATP, powerhouse of cell • Ribosome: protein synthesis • Golgi Apparatus: sort and package organic molecules • Lysosome: site of digestion of worn out parts and digestive enzyme storage • Cilia: short hair-like projections of eukaryotic cells, used for movement • Flagella: long tail-like projections of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, allow movement Unit 4 • Diffusion: movement of molecules from a high concentration to a low concentration • Osmosis: diffusion of water • Facilitated diffusion: diffusion through a protein channel • Active transport: movement of molecules from low to high concentration, uses energy (ex: endocytosis, exocytosis, protein pump) • Cellular respiration: breakdown of glucose into ATP • Mitosis: cell division of body cells (non-sex cell division) • Aerobic: with oxygen • Anaerobic: without oxygen • Glycolysis: step of cellular respiration, occurs in cytoplasm, breaks glucose into 2 pyruvates • Electron Transport Chain: step of aerobic respiration, occurs in inner mitochondrial membrane, creates ATP. Unit 5 • Central Dogma of Biology: DNA is replicated into DNA. DNA is transcribed into RNA, RNA is translated into proteins. • Nucleotide: a sugar, nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group; makes up nucleic acids • Replication: occurs in the nucleus before cell division, DNA is copied into DNA • Transcription: Occurs in nucleus, DNA is used as a template to make RNA • Translation: occurs at the ribosome, RNA is used as the instructions to make proteins • RNA: single stranded nucleic acid, bases: AUGC • DNA: double stranded nucleic acid, bases ATGC • Chargaff’s Rule: A binds to T, G binds to C, same % of A as T and G as C • Codon: sequence of three nucleotides which corresponds to an amino acid • Mutation: damage to DNA, possibly causing a different amino acid sequence to be made during protein synthesis Unit 6 • Genotype: genetic information carried in the DNA of the organism • Phenotype: the physical characteristics of an organism • Meiosis: Cell division resulting in gametes, results in 4 haploid cells • Diploid cell: cell having 2 complete sets of chromosomes (46 in humans) • Ex: Somatic Cells • Haploid cell: Cell having 1 complete set of chromosomes (23 in humans). • Ex: Gametic cells • Homologous chromosomes: set of chromosomes (one from each parent) which complete crossing over • Crossing over: Process during which homologous chromosomes exchange pieces of DNA, results in genetic variation (prophase I) • Homozygous: having two identical genes for a trait. – Ex: HH or hh • Heterozygous: having two different genes for a trait – Ex: Aa or Hh • Carrier: organism having heterozygous alleles for a recessive trait, is unaffected, but can pass on the recessive allelle Unit 7 • Evolution: genetic change over time • Natural selection: survival and reproduction of the fittest organisms to an environment • Autotrophs: organisms which make their own food • Heterotrophs: organisms that eat other organisms for food (energy) • Organic evolution: development of new species/evolution of life • Chemical evolution: inorganic molecules form organic molecules • Spontaneous generation: life is spontaneously created from non-living things • “most fit trait:” trait which allows an organism to reproduce more than an organism without the trait • Microevolution: changes in allele frequencies in a population, occurs over a smaller amount of time. • Macroevolution: development of new species from an ancestral form, occurs over long periods of time (thousands/millions of years) Unit 8 • Analogous structure: structures with a different structure/origin, same function • Homologous structure: structures with the same origin/structure, with different functions • Species: organisms which can have fertile offspring. • Gradualism: rate of speciation which is gradual and constant • Punctuated equilibrium: rate of speciation during which there are long periods of no change, then sudden bursts of change • Neuron: nerve cell • Tissue: group of cells which work together for a common function • Convergent evolution: species with different ancestors evolve to become more similar due to environment • Divergent evolution: populations with the same ancestor evolve to become different, into new species • Coevolution: population evolves due to the influence of another population, and vice versa. Unit 9 • Transpiration: process by which water evaporates from leaves of plants, pulling water upwards • Xylem: vascular tissue of plants which transports water and minerals • Phloem: vascular tissue of plants which transports food (glucose) • Cell wall: cell structure found outside the plasma membrane of plant cells which supports cells • Chloroplast: cell organelle found in plants, site of photosynthesis • Photosynthesis: process by which organisms create glucose from carbon dioxide, light, and water • Chlorophyll: primary plant pigment, absorbs sunlight • Stamen: male part of flower (anther+filament) where pollen is produced • Carpel/Pistil: female part of flower (ovary, style, stigma) • Angiosperm: vascular, seeding, flowering plant • Eubacteria: prokaryote with a cell wall made of peptidoglycan Unit 10 • Archaebacteria: prokaryote with cell wall not made of peptidoglycan, some live in extreme environments • Virus: non-living, protein capsule containing nucleic acid, must have host to reproduce • Animal: eukaryotic, no cell wall, mostly multicellular, all heterotrophic • Protist: eukaryotic, no cell wall, mostly single celled, can be autotrophic or heterotrophic • Fungi: eukaryotic, cell wall made of chitin, all heterotrophic • Plants: eukaryotic, cell wall made of cellulose, all autotrophic • Binomial nomenclature: classification system developed by Linnaeus which gives every type of organism a 2 part name: Genus species • Cyanobacteria: photosynthetic bacteria, provided oxygen for aerobic life to evolve • Hierarchy of taxonomy: domain, kingdom, phylum, class, order, family, genus, species Unit 11 Ecosystem: all biotic and abiotic factors of an area interacting with each other Community: multiple populations (species) interacting Population: All individuals of one species in a particular area Rule of 10%: 10% of the energy is passed on from one trophic level to the next, 90% is lost as heat and inefficiency Mutualism: symbiotic relationship when both organisms benefit/are helped Parasitism: symbiotic relationship when one organism benefits and one is harmed Commensalism: symbiotic relationship during which one organism benefits, the other is unaffected. Carrying capacity: the maximum amount of organisms an environment can sustain over time Predation: the killing and consumption of one organism by another Ecological Succession: Process of change of an ecosystem over time (primary or secondary)