SIUnits
advertisement

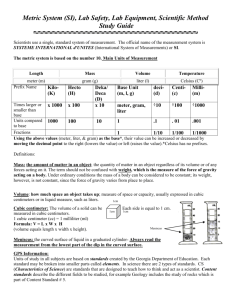
The International System of Units Yewande Dayo Student Pharmacist Objectives Demonstrate an understanding of SI units Convert units within SI units State equivalent measure between SI units and other systems of measure used in pharmacy practice Convert between SI units and other systems of measure used in pharmacy practice Apply SI units correctly in calculations The International System of Units Was formerly called the metric system and it is the internationally recognized decimal system of weights and measures The base units of the SI are the meter and kilogram For length, the primary unit is the meter For volume, the primary unit is the liter For weight, the primary unit is the gram Subdivisions and multiples of the primary units, their relative values and corresponding prefixes are shown in the table below Guidelines for Using SI Units Unit names and symbols are not capitalized except in headings and beginning of a sentence. Exception for liter. May be capitalized or in lower case. e.g. 2 L or 2 l, 3 mm and 4 g; not 3 Mm and 4 G Periods are not used following SI symbols except at the end of a sentence e.g. 4 mL and 4 g, not 4 mL. and 4 g. A compound unit that is a ratio or quotient of two units is indicated by a solidus (/) or a negative exponent. e.g. 5 mL/h or 5 mLh-1 , not 5 mL per hour Symbols should not be combined with spelled-out terms in the same expression e.g. 3 mg/mL not 3 mg/milliliter Plurals of units when spelled out, have an added “s”. 5 mLs is wrong! Two acceptable symbols of microgram – mcg & µg Symbol for square meter is m2 Cubic centimeter cm3 = mL; CC not accepted in SI Decimal fractions are used not common fractions 3.25 not 3 1/2 To prevent medication errors, a zero should be placed in front of a leading decimal point e.g. 0.5 g not .5 g Trailing zeros should not be placed following a whole number on prescriptions e.g. 5 mg, not 5.0 mg when selecting units, the unit that will result in a numeric value of between 1 and 1000 is selected e.g. 500g not 0.5kg; 1.96 kg not 1960 g; 750 mL not 0.75 L Some Applications of SI units in Pharmacy Manufacture/labeling of pharmaceutical products Write, fill and compound Rx and medication orders Milligram or microgram amounts e.g. 325mg or 30 mg/5 mL Express laboratory results Usually in gram, milligram and microgram quantities Dose patients In kilogram and kiloliter quantities mg/dL Nanotechnology 1 – 1000 nm Measurements of Length The primary unit of length is the meter 1 kilometer (km) = 1000.000 meters 1 hectometer (hm) = 100.000 meters 1 dekameter (dam) = 10.000 meters 1 meter (m) = 1.000 meter 1 decimeter (dm) = 0.100 meter 1 centimeter (cm) = 0.010 meter 1 millimeter (mm) = 0.001 meter 1 micrometer (μm) = 0.000,001 meter 1 nanometer (nm) = 0.000,000,001 meter Conversion of the most common length denominations 1000 millimeters (mm) = 100 centimeters (cm) 100 centimeters (cm) = 1 meter (m) Measurements of Volume The 1 primary unit of volume is the liter kiloliter (kL) = 1000.000 liters 1 hectoliter (hL)= 100.000 liters 1 decaliter (daL)= 10.000 liters 1 liter (L) = 1.000 liter 1 deciliter (dL)= 0.100 liter 1 centiliter (cL) = 0.010 liter 1 milliliter (mL) = 0.001 liter 1 microliter (µL)= 0.000,001 liter Measurements of Weight The primary unit of weight is the gram 1 kilogram (kg) = 1000.000 grams 1 hectogram (hg)= 100.000 grams 1 decagram (dag)= 10.000 grams 1 gram (L) = 1.000 gram 1 decigram (dL)= 0.100 gram 1 centigram (cL) = 0.010 gram 1 milligram (mL) = 0.001 gram 1 microgram (µL)= 0.000,001gram Prescriptions Written Using SI Units These use Arabic numerals before the abbreviations for the denominations Weights are written as grams and decimals of a gram 3 g or 3.4 g Volumes are written as milliliters and decimals of a milliliter 10 g; 300 mL 5 mL or 20.5 mL E.g. RX Dextromethorphan HBr 320 mg Guiafenesin 3.2 g Cherry Syrup, to make 240 mL Conversion of SI Units To change a unit to the next smaller denomination, move the decimal point one place to the right To change a unit to the next larger denomination, move the decimal point one place to the left Other Systems of Measurement Two other systems of measurement exist The avoirdupois system (widely used in the US for measuring weight and selling goods; predominant in commerce) The apothecary system (used to be predominant in pharmacy for volume and weight measure) Example 1 A patient receives 500 mcg of estradiol benzoate by injection every day for 3 weeks. How many grams of estradiol benzoate does the patient receive during the course of therapy? Example 2 Two kilograms of a drug are used to make 40,000 tablets. (a) How many milligrams are in each tablet (b) How many grams would be required to make 60 tablets? Example 3 One pint of a cough syrup is dispensed to a patient who takes 1 tablespoonful of the syrup four times a day for a week. How many doses of the syrup will remain in the original bottle after the full course of therapy? Example 4 If a vial contains 40 mg of tobramycin sulfate per milliliter, how many micrograms of tobramycin sulfate would be in 0.1 mL? Example 5 A prescription calls for 0.060 g of one ingredient, 2.5 mg of another and enough of a third to make 0.5 g. How many milligrams of the third ingredient should be used? Example 6 Are the terms mcg/mL and mg/L equivalent or not equivalent? Example 7 How many grams of digoxin (LANOXIN) would be required to make 25,000 tablets each containing 250 mcg of digoxin? Example 8 A patient is instructed to take three 50-mcg tablets of pergolide mesylate (PERMAX) daily. How many milligrams of the drug would the patient receive weekly? Example 9 A liquid oral concentrate of morphine sulfate contains 2.4 g of morphine sulfate in a 120-mL bottle. Calculate the concentration of morphine sulfate on a mg/mL basis. Example 10 An intravenous solution contains 500 µg of a drug substance in each milliliter. How many milligrams of the drug would a patient receive from the intravenous infusion of a liter of the solution? Example 11 A vial contains 80 mg of drug in 2 mL of injection. How many milliliters of the injection should be administered to obtain 0.02 g of drug? Example 12 A 125-mL container of amoxicillin contains 600 mg/5 mL. How many milliliters would be used to administer 400 mg of amoxicillin? Case 1 A nurse telephones a pharmacy regarding the proper quantity of an injection to administer to a pediatric patient from a 1-mL vial containing 0.1 mg of digoxin. The attending physician had prescribed a dose of 25 mcg. How many milliliters should be the pharmacist’s response? Case 2 A hospital pharmacist is asked to prepare an intravenous infusion of dopamine. Based on the patient’s weight, the pharmacist calculates a dose of 500 mcg/min for continuous infusion. The concentration of a premixed dopamine infusion is 400 mg/250 mL. What is the concentration of the infusion on a mcg/mL basis? How many milligrams of dopamine is the patient to receive in the first hour of treatment? How long will the infusion last?