Introduction to Natural Products
advertisement

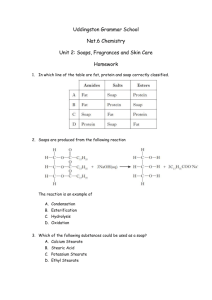
• • • • Terpenes Alkaloids Pheromones Antibiotics • When we discuss the terpenes we are most interested in the carbon skeleton. Isoprene Head Tail Isoprene Head Tail Head Tail Isoprene Head Tail Terpene Classification • • Class Name Carbon Number Isoprene Units Terpene Classification • • • • • Class Name Carbon Number Monoterpene 10 Isoprene Units 2 Terpene Classification • • • • • • Class Name Carbon Number Monoterpene 10 Sesquiterpene 15 Isoprene Units 2 3 Terpene Classification • • • • • • • Class Name Carbon Number Monoterpene 10 Sesquiterpene 15 Diterpene 20 Isoprene Units 2 3 4 Terpene Classification • • • • • • • Class Name Carbon Number Monoterpene 10 Sesquiterpene 15 Diterpene 20 Triterpene 30 Isoprene Units 2 3 4 6 Monoterpene Examples CH 2OH Myrcene Geraniol O a-Terpinene O O Menthone Cineole O OH Menthol Carvone Thujone Sesquiterpene Examples OH CH 2 OH Farnesol Bulgarene Eudesmol O Atractylone Caryop hyllene Aromadendrene O O OH Germacrone Linderene Representative Diterpenes CH 2 OH Phytol COOH Kaurene Pimeric acid HO O O O M arrubin COOH Abietic acid Representative Triterpenes CH 2 OH HO HO HO Isoprene Units in Terpenes O Limonene a -Pinene Camphor OH b -Selinene Guaiol Isoprene Units in Terpenes O Limonene Camphor a -Pinene OH b -Selinene Guaiol Isoprene Units in Terpenes O Limonene Camphor a -Pinene OH b -Selinene Guaiol Isoprene Units in Terpenes O Limonene Camphor a -Pinene OH b -Selinene Guaiol Isoprene Units in Terpenes O Limonene Camphor a -Pinene OH b -Selinene Guaiol Non-Isoprenoid Terpenes O Valerane Eremophilone b-Vetivone Alkaloids Nitrogen containing, basic natural products often have powerful biological activity alkaloids are not as conveniently organized by some common structural component. Piperidine Me N N N H Pyrrolidine N H Pyrrolizidine Tropane N H Indole Quinoline NH Isoquinoline N H Examples of alkaloids HO N H O Coniine N Me AcO NH2 HO N Morphine HO N Slaframine N MeO N Quinine N O Strychnine O N Me N N H MeOOC COOMe COOMe MeO N H HO Antiobiotics There are many classes of antibiotics; four are listed as major groups: b-lactams ( includes the penicillins); tetracyclines (tetracycline); macrolides (erythromycin) and peptides (gramacidin). For the purposes of this course, we will be primarily concerned with macrolide antibiotics and highly-oxygenated compounds. Practice Problem #1 • For each of the example terpenes given to you, find the isoprene units that are contained in the carbon skeleta.