Unit 2 - Free Response Essay Questions
advertisement

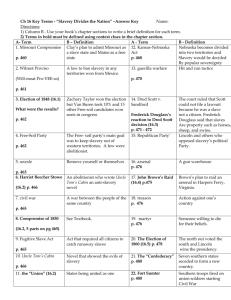
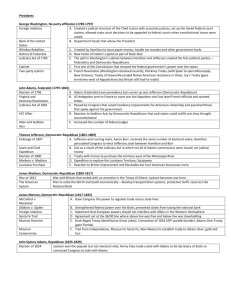
Unit 2 - Free Response Essay Questions A.P. US History Andrew Jackson’s election as President marked the beginning of a new age in American political history. Assess the validity of this generalization. • 1st Term 1828-1832 – “Kitchen Cabinet” • The “Age of the Common Man” #2- – Expansion of voting rights to non property holders • Election of 1824 – Jackson wins popular vote, losses electoral – Corrupt Bargain • Election of 1828 – “Mudslinging” – Character Debate (Jackson v. J.Q. Adams) – Establishment of the Democratic Party – The Spoils System – Indian Removal Act – Favored “Small Government” but Not Afraid to use the Power of the Presidency – Nullification Crisis • Tariff of 1828 • Force Act 1832 • 2nd Term 1832-1836 – The Bank Crisis • Panic of 1837 – Emergence of the Whig Party • Election of 1836 – Martin Van Buren hand picked successor #3- Early U.S. foreign policy was primarily a defensive reaction to perceived or actual threats from Europe. Assess the validity of this generalization with reference to U.S. foreign policy on TWO major issues during the period from 1789-1825 • French Revolution 1789 & Napoleonic Wars 1789-1799 / 1800-1815 – American Neutrality challenged (Washington, Adams, Jefferson, Madison) – XYZ Affair / Alien & Sedition Acts – Creation of the American Navy (Adams) – Quasi War (1794) – Louisiana Purchase (1803) – Embargo Act 1807 & NonIntercourse Acts 1808 • The War of 1812 – Impressment of American Ships & Sailors – Federalists Opposed War / Republicans Demanded War “War Hawks’ • The War of 1812 Continued… – Tecumseh & Native American “Threat” in the West – 1814 Washington Burns – Treaty of Ghent (Ended War, didn’t address impressment or trading rights) – Battle of New Orleans 1814 • The Monroe Doctrine (1823) – Caused by successful revolutions in Latin America between 18041825 – Written by J.Q. Adams but attributed to James Monroe – Stated that the Western Hemisphere (North / South America) was off limits to European colonization #4- • • Manifest Destiny = Americans had a God given right to the Western Territory to the Pacific Ocean Constitutionality of the purchase Lewis & Clark Expedition Missouri Compromise Line = Land for expansion of slavery Indian Removal Act (1830) – – – • • All Native American tribes east of the Mississippi will be relocated Worchester v. Georgia Trail of Tears (1838) The Texas Revolt (1836) – – – – Land Grants (Emprasarios) for Catholicism / Citizenship in Mexico Slavery brought into territory Battle of the Alamo (1836) Republic of Texas until 1845 when annexed by the United States Oregon Country – – The Louisiana Purchase (1803) – – – • Although Americans perceived Manifest Destiny as a benevolent movement, it was in fact an aggressive imperialism pursued at the expense of others. Assess the validity of this statement with specific reference to American expansionism in the 1840’s. • “54 40 or Fight”= American northwestern border should be extended to the latitude deep in Canadian territory Oregon Treaty 1846 = Signed with Great Britain / established a more reasonable border (Obtains OR, WA, ID, WY, MT) The Mexican-American War (1846-1848) – – – – – Disputed border lines between Mexico (Nueces) and U.S. (Rio Grande) U.S. / Mexican Army sent to guard the Rio Grande Matamoros Skirmish – “American Blood… spilt on American Soil” Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo The Case of California #5- • Analyze the ways in which supporters of slavery in the nineteenth century used legal, religious, and economic arguments to defend the institution of slavery. Southern Paternalism – Belief that slavery benefited everyone – Slaves could not care for themselves, therefore white owners had to be responsible for them • • The Southern Economy – Centered on agriculture (Cotton & Tobacco) – 75% of worlds cotton from American South (1850) = Global Impact – Transition from slave to free labor would • not be worth the initial impact it would cast on the economy. • The “Religious” Argument – Biblical interpretation – Bible lacked a clear and concise admonition against slavery, the institution was surely deemed appropriate. – Precedence Argument = forced servitude was acceptable. – “Saving Souls” Through Christianity Protection of “Property” under the Constitution – Slaves were considered property – Supreme Court Supports this idea with the “Dred Scott Decision” – Focusing their argument on the rights of slave-holders to transfer their "property" (in other words, their slaves), to the new territories, Avoiding Civil War – Constitutional Convention 1787 – Missouri Compromise 1821 – Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo and the Compromise of 1850