Arts
advertisement

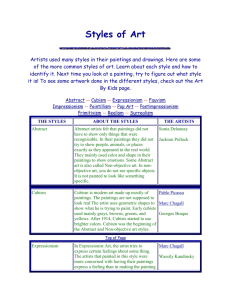
Music, Visual Arts, Physical Education, and Health http://subjectareatestprep.pdshrd.wikispaces.net/file/view/Fine+Arts+SAE+revised+10-07.ppt SEE QUIA for additional support & tutorials Fine Arts PowerPoint Excerpts taken from: http://books.google.com/books?id=iNgK130I1FgC&pg=PA233&lpg=PA233&d q=Knowledge+of+skills+and+techniques+in+music+and+visual+arts&sourc e=bl&ots=5mf6jWXTXZ&sig=q2RzNlkWDTnEHF1RUiqhQPRU6I&hl=en&ei=uHv9S9mqOcSclgeV1JnLBw&sa=X&oi=book_resul t&ct=result&resnum=7&ved=0CDMQ6AEwBg#v=onepage&q=Knowledge%2 0of%20skills%20and%20techniques%20in%20music%20and%20visual%20 arts&f=false 27 Knowledge of skills and techniques in music and visual arts 1. Identify appropriate vocal literature (e.g., age-appropriate range and vocal ability; diverse cultures, genres, and styles). Elements of Music Power Point 2. Identify developmentally appropriate singing techniques (e.g., posture, breath support, tone quality, and vocal range). 3. Identify correct performance techniques for rhythmic and melodic classroom instruments (e.g., nonpitched percussion, recorder, autoharp, and/or keyboard). 4. Read and interpret simple, traditional and nontraditional music notation (e.g., melodic, rhythmic, and harmonic). http://library.thinkquest.org/15413/theory/theory.htm 5. Select safe and developmentally appropriate media, techniques, and tools to create both two-dimensional and three-dimensional works of art. 6. Identify appropriate uses of art materials and tools for developing basic processes and motor skills. 28 Knowledge of creation and communication in music and visual arts 1. Identify the elements of music (e.g., rhythm, melody, form, texture, timbre, and dynamics) and ways they are used in expressing text; ideas; emotions; and settings, time, and place. Elements of Music Power Point 2. Demonstrate knowledge of strategies to develop creative responses through music to ideas drawn from text, speech, movement, and visual images. SEE sec 31 3. Demonstrate knowledge of strategies to develop creative responses through art to ideas drawn from text, music, speech, movement, and visual images. SEE sec 31 4. Identify the elements of art and principles of design (e.g., line, color, shape, form, texture, balance, and movement) and ways they are used in expressing text, ideas, meanings, and emotions. 29 Knowledge of cultural and historical connections in music and visual arts 1. Identify characteristics of style in musical selections, or music genre is a categorical and typological construct that identifies musical sounds as belonging to a particular category and type of music that can be distinguished from other types of music. 2. Demonstrate knowledge of how music reflects particular cultures, historical periods, and places. 3. Identify characteristics of style in works of art. http://library.thinkquest.org/J001159/artstyle.htm Abstract Abstract artists felt that paintings did not have to show only things that were recognizable. In their paintings they did not try to show people, animals, or places exactly as they appeared in the real world. They mainly used color and shape in their paintings to show emotions. Some Abstract art is also called Non-objective art. In non-objective art, you do not see specific objects. It is not painted to look like something specific. Cubism Cubism is modern art made up mostly of paintings. The paintings are not supposed to look real The artist uses geometric shapes to show what he is trying to paint. Early cubists used mainly grays, browns, greens, and yellows. After 1914, Cubists started to use brighter colors. Cubism was the beginning of the Abstract and Non-objective art styles. Expressionism In Expressionist Art, the artist tries to express certain feelings about some thing. The artists that painted in this style were more concerned with having their paintings express a feeling than in making the painting look exactly like what they were painting. Fauvism Fauvism was an art style that lasted only four years, beginning in 1905. The leader of this movement was Henri Matisse. The word Fauvism is french for "wild beasts". It got this name because the paintings had bright and unusual colors. The subjects in the paintings were shown in a simple way, and the colors and patterns were bright and wild. Impressionism Impressionism was developed in France during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. These pieces of art were painted as if someone just took a quick look at the subject of the painting. The paintings were usually in bold colors and did not have a lot of detail. The paintings in this style were usually outdoor scenes like landscapes. The pictures were painted to look like they were shimmering. Pointillism In Pointillism, the artist uses small dots or strokes of paint to make up the pictures. From far away, these dots blend together to form the picture and give the impression of different colors as they blend together. Pop Art Pop art can be any every day item that is drawn in a brash and colorful way. Pop Art is short for Popular Art. It is inspired by comic strips, advertising, and popular entertainment. Postimpressionism Postimpressionism began in the 19th century. It was mainly still lifes and landscapes. The postimpressionists liked to use lots of colors and shadows. Primitivism Primitive Art looks like art that is done by a child. Usually the picture is painted very simply, and the subjects are "flat", or two-dimensiona Realism Realism is a type of art that shows things exactly as they appear in life. It began in the 18th century, but the greatest Realist era was in the mid-19th century. Most Realists were from France, but there were some famous American painters who were Realists also. Surrealism (Dali) Surrealists paintings were generally based on dreams. Their paintings were filled with familiar objects which were painted to look strange or mysterious. They hoped their odd paintings would make people look at things in a different way and change the way they felt about things. They thought that their paintings might stir up feelings in the back of peoples minds. 4. Demonstrate knowledge of how visual arts reflect particular cultures, historical periods, and places. 30 Knowledge of aesthetic and critical analysis of music and visual arts 1. Identify strategies for developing students’ analytical skills to evaluate musical performance. 2. Identify strategies for developing students’ analytical skills to evaluate works of art. 31 Knowledge of appropriate assessment strategies in music and visual arts 1. Identify a variety of developmentally appropriate strategies and materials to assess skills, techniques, creativity, and communication in music. 2. Identify a variety of developmentally appropriate strategies and materials to assess skills, techniques, creativity, and communication in art. 33 Knowledge of physical, social, and emotional growth and development 1. Identify the structure, function, and interrelatedness of the systems of the human body. Science: Circulatory, Respiratory, Skeletal, Nervous, Digestive, Reproductive 2. Identify the principles of sequential progression of motor skill development. 3. Demonstrate knowledge of human growth and development and its physical social and emotional well being. 4. Identify major factors associated with social and emotional health (e.g., communication skills, self-concept/self efficacy, internal and external motivators, fair play, conflict resolution, character development/self respect, and stress management). 5. Identify problems associated with physical, social, and emotional health. 6. Identify factors related to responsible sexual behavior. 32 Knowledge of personal health and wellness 1. Demonstrate knowledge of the interrelatedness of LACK of physical activity, PHYSICAL fitness, and health & Hydration 2. Demonstrate basic knowledge of nutrition and its role in promoting health. Vitamins & Minerals 3. Identify the process of decision making and goal setting in promoting individual health and wellness. Avoiding risks, Weight Control Strategies, 4. Demonstrate knowledge of common health problems and risk behaviors associated with them. 34 Knowledge of community health and safety issues SAFETY first!!! 1. Identify factors contributing to substance use and abuse and identify signs, symptoms, effects, and prevention strategies. 96- ABUSE 2. Demonstrate knowledge of resources from home, school, and community that provide valid health information, products, and services. 3. Identify appropriate violence prevention strategies in the home, school, and community. 4. Identify appropriate safety and injury prevention strategies in the home, school, and community. 35 Knowledge of subject content and appropriate curriculum design 1. Distinguish between developmentally appropriate and inappropriate instructional practices that consider the interaction of cognitive, affective, and psychomotor domains. 2. Identify various factors (e.g., environment, equipment, facilities, space, safety, and group diversity) to consider when planning physical activities. 3. Analyze the influence of culture, media, technology, and other factors when planning health and wellness instruction. 1/4/2011 12:56:00 PM 1/4/2011 12:56:00 PM