TOK: Knowledge & Belief Study Sheet Name: Date of test: PERSON
advertisement
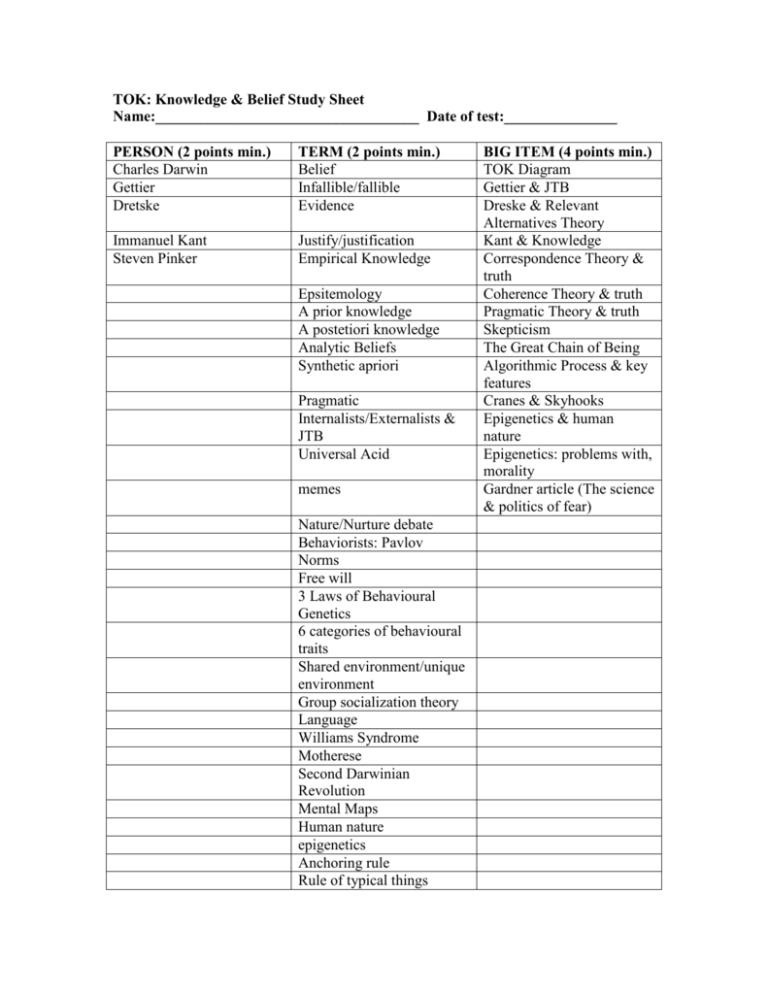
TOK: Knowledge & Belief Study Sheet Name:___________________________________ Date of test:_______________ PERSON (2 points min.) Charles Darwin Gettier Dretske TERM (2 points min.) Belief Infallible/fallible Evidence Immanuel Kant Steven Pinker Justify/justification Empirical Knowledge Epsitemology A prior knowledge A postetiori knowledge Analytic Beliefs Synthetic apriori Pragmatic Internalists/Externalists & JTB Universal Acid memes Nature/Nurture debate Behaviorists: Pavlov Norms Free will 3 Laws of Behavioural Genetics 6 categories of behavioural traits Shared environment/unique environment Group socialization theory Language Williams Syndrome Motherese Second Darwinian Revolution Mental Maps Human nature epigenetics Anchoring rule Rule of typical things BIG ITEM (4 points min.) TOK Diagram Gettier & JTB Dreske & Relevant Alternatives Theory Kant & Knowledge Correspondence Theory & truth Coherence Theory & truth Pragmatic Theory & truth Skepticism The Great Chain of Being Algorithmic Process & key features Cranes & Skyhooks Epigenetics & human nature Epigenetics: problems with, morality Gardner article (The science & politics of fear) Example rule Good bad rule Exposure effect Confirmation bias Group polarization TOK: PERCEPTION & EMOTION STUDY SHEET Name: ______________________________ Date of test:_____________ PERSON (2 point min.) Paul Maclean Dr. Jill Bolte Taylor Dr. V.S. Ramachandran Dr. Richard Nibett Edward de Bono Dr. Paul Ekman (genetics & emotions) TERM (2 point min.) Triune brain (& diagram) Brain stem Limbic system Neuron (& diagram) 3 types of neurons Synapse (& diagram) Neurotransmitters “Lock & Key”method Central Nervous system Peripheral Nervous system Serotonin “I smell burnt toast” Motor Projection Area of the brain Somatosensory Projection area Mirror box illusion Blind sight Capras delusion Rubber hand Illusion Similarity Proximity Continuity Closure “Maintaining Perceptual constancy” Perceiving distance: monocular cues, binocular cues Anthropormorphism Moran’s Canon BIG ISSUE (4 point min.) Optical Illusions Teenage Brain (article) Second Brain Sensory Profiles article Right/Left brain Ramachandran’s observations & conclusions Mirror Neurons Proprioception Synethesia Gestalt How culture molds habits of thought (article) Lateral thinking Parallel thinking Emotional Intelligence “Our of your mind, not out of your body” (article) Turing Test for consciousness Binding True Colors test fMRI Amygdala Higher Emotions TOK Math Study Sheet Name: ___________________________ Day of test: _________________ Person (2 points min.) Term (2 points min.) Euclid Axioms Bernhard Riemann N. I. Lobachevsky Rules of Inference Theorems Fibonacci Peano Postulates Einstein Deductive Reasoning Godel Lorenz Inductive Reasoning Elliptical geometry Feigenbaum Fibonacci Series Golden Ration/Golden Number Speed of Light Frame dragging Black Holes Electron Orbitals Uncertainty principle Copenhagen Interpretation Double slit experiment Super positioning Big Issue (4 points min.) Axioms: apriori knowledge Euclid’s Geometry Non-Euclidian geometry Special//General theories of Relativity Gravity Probe Experiment Quantum Logic Quantum computer solves problem, without running Godel’s Incompletness Theorem Chaos Theory Schrodinger’s cat thought experiment Butterfly Effect Lorentz attractor Bifurcation Koch curve fractal Mandlebrot set TOK Ethics Unit Study Sheet Name:____________________________________ Date of test: ____________________ PERSON (2 points TERMS (2 points min.) BIG ISSUE (4 points min.) minimum) Sinbad et al Universal Laws – some Self Interest Theory: Ethical possible eg. Egoism Harry Browne & Ethical Categorical imperative Criticisms of Ethical egoism egoism Ayn Rand & “The virtue of Kant: physical laws, moral Virtue ethics, issues of selfishness” laws cultural relativism & ethical objectivism Aristotle & virtue ethics Kant: Universal Law Kant & Universal Law theory John Stuart Mill Kant: The law of respecting Criticisms of Kantian ethics others Jeremy Bentham “The greatest happiness of Utilitarian theory the greatest number” David Hume Law of Diminishing Bentham & Mill on Marginal Returns (and Utiliarianism diagram) E.O. Wilson Trolley-ology Problems/criticisms of Utiliarianism Social contract theory Hume & Ethics (Hobbes) Scientific Ethics X Phi = Experimental Philosophy TOK: Natural Sciences Study Sheet Name: _____________________________Test date: ___________________ Person (2 points min.) Term (2 points min.) Karl Popper Basic Sci. Method (#1) Thomas Kuhn Paradigm Imre Lakatos Hardcore Paul Feyerabend Protective belt Positive heuristic Pseudoscience Big Issue (4 points min.) Principle of Falsification (sci. method #2) Falsification: advantages/problems Scientific Revolutions (sci. method #3) Research Programs (sci. method #4) Anything goes – Against Method, 1975 Limits of Science – article’s main points TOK: Language Unit Name: Test Date: ____________________________ Person (2 points min.) Ludwig Wittgenstein Martin Heidegger George Orwell Nietzsche Bertrand Russell Vienna Circle Term/Word (2 points min.) Communication Loop Language as transactional communication Language as transactionalj comm. Language as expressive comm. Tractacus Wittgenstein’s “language games” Emotive Words Lang. as Social Comm Lang. as Comm with self Phenomenology Big Issue (4 points min.) 3 features of language Functions of Language (in general) Swear words Bewitchment of Language (in general) Hermeneutics & examples Structuralism (or semiotics) Categories & Classification Nietzsche and your opinions of him Logical Positivism & example Being & Time: Husserl Will and Representation (Schop) Language uses symbols Meaning of Words “Game” multiple meanings Language creates reality Newspeak Language infers & judges Language Classifies Language changes Ubermensch Will to Power Eternal Return Linguistic Philosophy Picture Theory of Meaning: Logical Form “Later Wittgenstein”: language as tool Method as used by Heidegger Heidegger & existence For Duncan’s classes, only study what we have learned: TOK: LOGIC AND REASON STUDY SHEET Name: _________________________________________ Date of Test: __________________ Person (2 points min.) Aristotle – logic, his incorrect assumption Stoics – logic Term (2 points min.) Analytic philosophy Gottlob Frege Russell’s paradox Bertrand Russell Formalism Vienna Circle Principia Mathematica Continental school “Is” “disgrace to the human race” “and” Big Issue (4 points min.) 3 informal fallacies: defined/examples Deductive logic: explained, example, problems with model Symbolic logic: explained, example, problems with model Inductive Logic: explained, example, problems with model Matrix Logic: explained, example, problems with model Fuzzy Logic: defined, advantages, four step process, uses of, strengths/weaknesses Fuzzy Logic vs. Boolean Paradox Cretan paradox Barber paradox “arithmetic trembles” Russell’s set Cantor’s theorem Hempel’s paradox Syllogism Venn Diagram Logic Fuzzy logic: applications: camcorders, belief systems, temperature, etc. Venn Diagram, various examples