Technical College / Mosul
advertisement
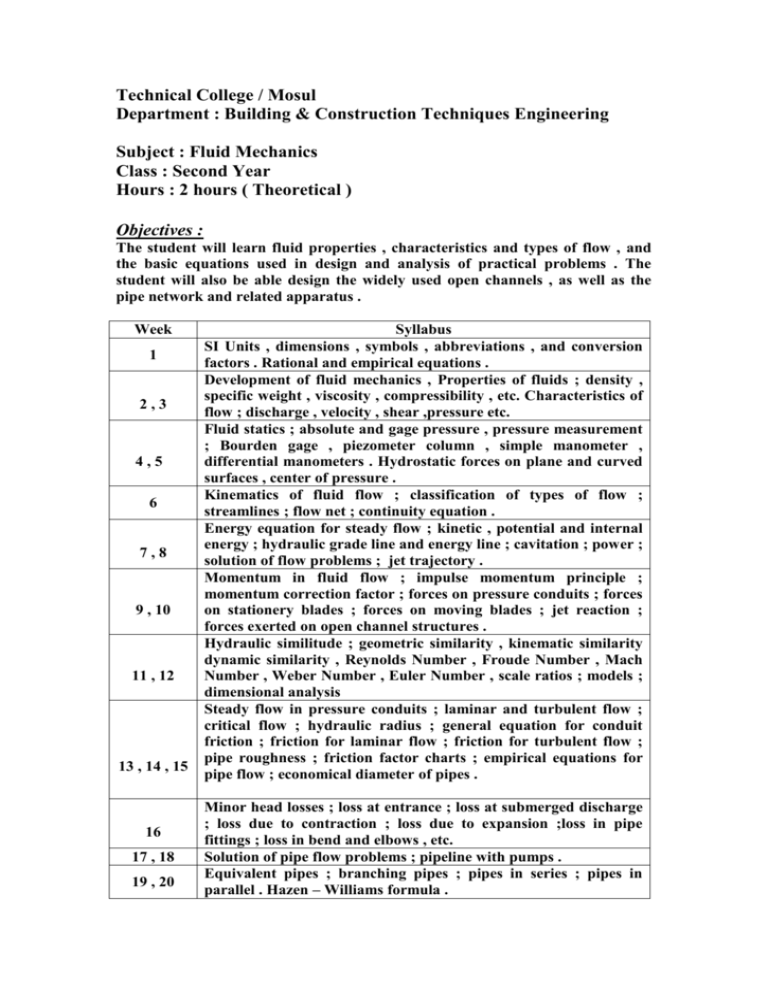
Technical College / Mosul Department : Building & Construction Techniques Engineering Subject : Fluid Mechanics Class : Second Year Hours : 2 hours ( Theoretical ) Objectives : The student will learn fluid properties , characteristics and types of flow , and the basic equations used in design and analysis of practical problems . The student will also be able design the widely used open channels , as well as the pipe network and related apparatus . Week 1 2,3 4,5 6 7,8 9 , 10 11 , 12 13 , 14 , 15 16 17 , 18 19 , 20 Syllabus SI Units , dimensions , symbols , abbreviations , and conversion factors . Rational and empirical equations . Development of fluid mechanics , Properties of fluids ; density , specific weight , viscosity , compressibility , etc. Characteristics of flow ; discharge , velocity , shear ,pressure etc. Fluid statics ; absolute and gage pressure , pressure measurement ; Bourden gage , piezometer column , simple manometer , differential manometers . Hydrostatic forces on plane and curved surfaces , center of pressure . Kinematics of fluid flow ; classification of types of flow ; streamlines ; flow net ; continuity equation . Energy equation for steady flow ; kinetic , potential and internal energy ; hydraulic grade line and energy line ; cavitation ; power ; solution of flow problems ; jet trajectory . Momentum in fluid flow ; impulse momentum principle ; momentum correction factor ; forces on pressure conduits ; forces on stationery blades ; forces on moving blades ; jet reaction ; forces exerted on open channel structures . Hydraulic similitude ; geometric similarity , kinematic similarity dynamic similarity , Reynolds Number , Froude Number , Mach Number , Weber Number , Euler Number , scale ratios ; models ; dimensional analysis Steady flow in pressure conduits ; laminar and turbulent flow ; critical flow ; hydraulic radius ; general equation for conduit friction ; friction for laminar flow ; friction for turbulent flow ; pipe roughness ; friction factor charts ; empirical equations for pipe flow ; economical diameter of pipes . Minor head losses ; loss at entrance ; loss at submerged discharge ; loss due to contraction ; loss due to expansion ;loss in pipe fittings ; loss in bend and elbows , etc. Solution of pipe flow problems ; pipeline with pumps . Equivalent pipes ; branching pipes ; pipes in series ; pipes in parallel . Hazen – Williams formula . 21 , 22 23 , 24 25 26 , 27 , 28 29 , 30 Pipe networks ; Hardy cross method ; computer aided pipe – network analysis Open channel flow ; Chezy and Manning formulae ; solution of uniform flow problems ; most efficient cross section ; partial flow in circular cross sections ; subcritical and supercritical flow ; critical depth in non rectangular channels ; hydraulic jump ; hydraulic of culverts . Fluid measurements ; measurement of fluid properties ; measurement of static pressure ; velocity measurement by different methods ; measurement of discharge ; orifices ; nozzles ; coefficients of contraction ; coefficient of velocity ; coefficient of discharge ; Venturi tube ; nozzle meter ; orifice meter ; rectangular weirs ; triangular weirs ; board crested weir ; overflow spillway ; sluice gate . Measurement of liquid surface elevation . Other methods of measuring discharges ; elbow meter ; rotameter . Unsteady flow problems ; discharge with varying head . Unsteady flow in pipes . Water hammer . Surge tanks . References 1. Daugherty, R. L. et al ( Fluid Mechanics with Engineering Application ) , McGraw-Hill Book Co. 2. Albertson, M. L. et al. ( Fluid Mechanics for Engineers ) 3. Morris, H. , M. and Wiggert, J. M. ( Applied Hydraulics in Engineering ) . 4. Venard & Street ( Elementary Fluid Mechanics ) 5. Giles, R. V. ( Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics ) McGraw-Hill Book Co. Schaum outline series . 6. Khurmi ( A Text Book of Fluid Mechanics ) , S. Chand & Company Ltd. . جميل ( مباديء ميكانيك الموائع ) مطبعة جامعة بغداد، المالئكة.7