Propaganda Techniques Packet
advertisement

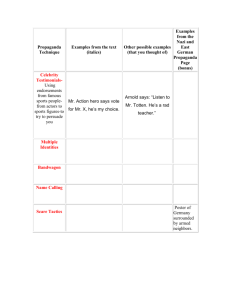
Name ____________________________ Propaganda Techniques What are propaganda techniques? They are the methods and approaches used to spread ideas that further a cause – a political, commercial, religious, or civil cause. 1. Name Calling – This technique consists of attaching a negative label to a person or thing. People engage in this type of behavior when they are trying to avoid supporting and/or defending their own opinions with facts. Rather then explain what they believe in, they prefer to try to tear their opponent down. Example: In a campaign speech to a logging company, the Congressman referred to his environmentally conscious opponent as a “tree hugger.” Or A battery company like Energizer claims that their brand can outlast the Rayovac brand. 2. Glittering Generalities – This technique uses important sounding “glad words” that have little or no meaning. These words are used in general statements that cannot be proved or disproved. Words like “good,” “honest,” “fair,” “best,” “family values,” “rights,” and “perfect” are examples of “glad” words. This type of technique appears often in politics and political propaganda. Example: In a magazine you see an ad for a vacation to Disney World. The ad claims that it is the best family vacation destination and the kids will have the most fun ever, 3. Plain Folks – this technique uses a folksy approach to convince us to support someone or something. These ads depict people with ordinary looks doing ordinary things. These ads have a down home folksy appeal to them. Example: After a morning speech to wealthy Republican donors, George W. Bush stops by McDonald’s for a burger, fries, and photo-op. 4. Testimonials – are quotations or endorsements which attempts to connect a famous or respectful person with a product or item. Testimonials are closely related to the transfer technique. Testimonials are often used in advertising and political campaigns. Oprah appears in a television ad supporting Barack Obama for our next President. Or Jessica Simpson for Proactive Acne Medicine…she states that Proactive works for her and keeps her skin looking clear. Or A commercial shows a doctor (possibly wearing a white lab coat). He states that if you have asthma you should use this brand of medicine because it is the best one on the market. 5. Transfer – an attempt to make the subject (you) view a certain item in the same way as they view another item. (to link the two things together in the subject’s mind) By linking an item to something the subject respects or enjoys, positive feelings can be generated for it. However, in politics, this technique is mostly used to transfer bad feelings towards a politician. Transfer employs the use of symbols, quotes, or the images of famous people to convey a message not necessarily associated with them. When using transfer, the speaker attempts to persuade us through the indirect use of something we respect, such as a patriotic or religious image, to promote his/hers idea. Example: A candidate for a political office is running an ad that has him standing in front of an American Flag. Or You see an ad with a picture of Tiger Woods holding a bottle of Gatorade. 6. Bandwagon – the basic idea behind the bandwagon approach is just that, “getting on the bandwagon.” The propagandist puts forth the idea that everyone is doing this, or everyone supports this person/cause, so…so should you. (nobody wants to be left out of what is perceived as a popular trend) Example: Everyone in Lemmington is behind Jim Duff for Mayor. Shouldn’t you be part of this winning team? Or Millions have tried this product. Don’t be the last one. 7. Repetition – The product name or keyword or phrase is repeated several times. 8. Emotional Words – This technique involves the propagandist using words that stimulate positive feelings in the viewer. Words such as: luxury, beautiful, paradise, and economical. Many times the advertisers are trying to tug at your heart strings. Example: A high class car dealer runs an ad for an expensive car. They describe the car as luxurious and spacious. It is different than any other car that you have driven or seen. Or You see a family making holiday memories together by baking cookies. 9. Exaggeration/Hyperbole – This technique involves exaggerating or overstating an idea or product’s value. Propagandists use exaggeration or "hype" to create impressive sounding words that are nonetheless meaningless and vague. Examples: You will never need another cleaning product! Your kids will ask for it everyday! 10. Euphemism - A euphemism is a substitution of an agreeable or less offensive expression in place of one that may offend or suggest something unpleasant to the listener. THINK POSITIVE CONNOTATIONS! Examples: Pre-owned for used or second-hand, restroom for toilet, downsizing for laying off 11. Stereotyping (or Simplification) - A conventional, formulaic, and oversimplified conception, opinion, or image. One that is regarded as embodying or conforming to a set image or type. Example: Women shopping at a clothing store or grocery store. Men shopping at hardware or a home improvement store. Or Women cleaning the house. (ads for cleaning products) Men driving large trucks or working with tools. 12. Fear – This technique is very popular among political parties and Political Action Committees in the U.S. The idea is to present a dreaded circumstance and usually follow it up with a kind of behavior needed to avoid that horrible event. This technique is used a lot during wartime and political issues.