PHYSICS UNIT 1 OUTLINE
advertisement

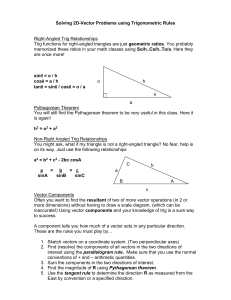
PHYSICS C/HL UNIT 1 STUDY GUIDE List four basic concepts which Physics studies and the four general force laws of Physics State two characteristics of the scientific method List four fundamental SI units Define what derived SI units are and differentiate between derived and fundamental units Convert various non-SI units into SI units given the non-SI units’ conversion factor Convert the following prefixes into scientific notation: Femto-, Pico-, Nano-, Micro-, Milli-, Centi-, Deci-, Kilo-, Mega-, Giga-, TeraConvert conventional numbers into scientific notation and vice versa Add, subtract, multiply and divide using scientific notation State units in the accepted SI format Define order of magnitude State and compare order of magnitude of selected systems in the universe (range of size, mass and time in the universe) List factors influencing the accuracy of making measurements (uncertainties) and analyze situations where parallax applies Define accuracy and precision Distinguish between random and systematic errors and recognize experimental methods for reducing their impact State the measurement from a display giving proper number of significant digits and listing the uncertainty Graphical show uncertainty (error bars) List four rules determining significant digits Round after adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing using significant digits State uncertainties as absolute, fractional and percentage uncertainties Determine propagated uncertainties (add, subtract, multiplication, division, powers, and trig) Determine uncertainties in the slope and intercepts (minimum, maximum fit and error bars) of a line graph State ratios of quantities as differences of orders of magnitude Solve for one particular variable in terms of the other variables in an equation. Recognize the dependent and independent variable and choose the proper convention for plotting them Define interpolate and extrapolate Recognize the graph of a line, parabola and inverse proportional graph Given a set of data, plot the data and describe in equation from the resulting graph Describe the significance of the slope and y intercept point of a line, and the value of k in a parabolic and inverse proportional graph Give an application of the line, parabola, inverse, and inverse2 graph Given the degrees of an angle, determine its sin, cos, and tan, and given a sin, cos or tan of an angle, determine the angle’s degrees Convert from degrees to radians and vice versa Given a right triangle with one length and two angles, solve for the other angle and lengths of the triangle Without a calculator give the sin and cos values for 0, 30, 45, 60, and 90 degrees Transform equations involving powers and exponentials into lines of the form y = mx +b by using substitution and log-log and semi-log graph paper Analyze log-log and semi-log graphs to determine the parameters of the equations Use and interpret the symbology of calculus in setting up and interpreting equations Use deferential and integral calculus to determine the derivative and integral of basic physics equations (polynomial, trig , and exponential functions) State the difference between scalar and vector quantities and give examples of both. Graphically display vectors and add/subtract them Add and subtract vector quantities by Establishing a coordinate system Resolving the vectors into components using Trig Adding as scalars Reforming the resultant vector using Trig. Multiply/Divide vectors by scalars Interchange between compass degrees, standard math notation and N/S of E/W units for describing vectors Use and interpret the unit vector notation i, j, k for x, y, z axes Compute the cross and dot product using unit vectors Solve problems using determinants and matrices when multiplying vectors