Elementary - Madison County Schools
advertisement

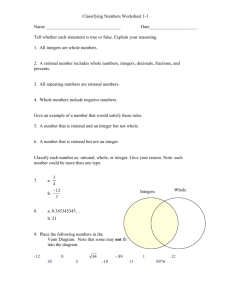
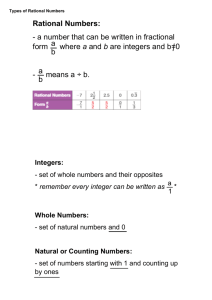
MADISON COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS District Curriculum Map for Mathematics: Grade 7 Unit Description Unit 2 Rational Numbers Suggested Length: 3 weeks Big Idea(s) What enduring understandings are essential for application to new situations within or beyond this content? Essential Question(s) What questions will provoke and sustain student engagement while focusing learning? Enduring Standards: Which standards provide endurance beyond the course, leverage across multiple disciplines, and readiness for the next level? Operation Meanings and Relationships – The same number sentence (e.g. 12-4 = 8) can be associated with different concrete or real-world situations, AND different number sentences can be associated with the same concrete or real-world situations. Properties – For a given set of numbers there are relationships that are always true, and these are the rules that govern arithmetic and algebra. Basic Facts and Algorithms – Basic facts and algorithms for operations with rational numbers use notions of equivalence to transform calculations into simpler ones. How can you add and subtract rational numbers to solve real-world problems? How can you multiply and divide rational numbers to solve real-world problems? How can you use rational numbers to solve multi-step, real-world problems? Enduring Understandings Understand operations of rational numbers Standards for Mathematical Practice 1 - Make sense of problems and persevere in solving them 2 - Reason abstractly and quantitatively. 4 - Model with mathematics. 5 - Use appropriate tools strategically. 6 - Attend to precision. 7 - Look for and make use of structure. Standards for Mathematical Content 7.NS.1b Interpret sums of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts. 7.NS.1c Understand subtraction of rational numbers as adding the additive inverse, p – q = p + (–q). Show that the distance between two rational numbers on the number line is the absolute value of their difference, and apply this principle in real-world contexts. 7.NS.1d Apply properties of operations as strategies to add and subtract rational numbers. 7.NS.2a Understand that multiplication is extended from fractions to rational numbers by requiring that operations continue to satisfy the properties of operations, particularly the distributive property, leading to products such as (– 1)(–1) = 1 and the rules for multiplying signed numbers. Interpret products of Curriculum and Instruction 2015-2016 Page 1 of 6 MADISON COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS District Curriculum Map for Mathematics: Grade 7 rational numbers by describing real-world contexts. 7.NS.2b Understand that integers can be divided, provided that the divisor is not zero, and every quotient of integers (with non-zero divisor) is a rational number. If p and q are integers, then –(p/q) = (–p)/q = p/(–q). Interpret quotients of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts. 7.NS.2c Apply properties of operations as strategies to multiply and divide rational numbers. 7.NS.2d Convert a rational number to a decimal using long division; know that the decimal form of a rational number terminates in 0s or eventually repeats. 7.NS.3 Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving the four operations with rational numbers. (NOTE: Computations with rational numbers extend the rules for manipulating fractions to complex fractions.) Supporting Standard(s): Which related standards will be incorporated to support and enhance the enduring standards? 7.NS.1a Describe situations in which opposite quantities combine to make 0. For example, a hydrogen atom has 0 charge because its two constituents are oppositely charged. 7.NS.1b Understand p + q as the number located a distance |q| from p, in the positive or negative direction depending on whether q is positive or negative. Show that a number and its opposite have a sum of 0 (are additive inverses). Interpret sums of rational numbers by describing real-world contexts. 6th Grade Enduring Understanding – Number 6.NS.1 Interpret and compute quotients of fractions, and solve word problems involving division of fractions by fractions, e.g., by using visual fraction models and equations to represent the problem. For example, create a story context for (2/3) ÷ (3/4) and use a visual fraction model to show the quotient; use the relationship between multiplication and division to explain that (2/3) ÷ (3/4) = 8/9 because 3/4 of 8/9 is 2/3. (In general, (a/b) ÷ (c/d) = ad/bc.) How much chocolate will each person get if 3 people share 1/2 lb of chocolate equally? How many 3/4-cup servings are in 2/3 of a cup of yogurt? How wide is a rectangular strip of land with length 3/4 mi and area 1/2 square mi? 6.NS.2 Fluently divide multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm. 6.NS.3 Fluently add, subtract, multiply, and divide multi-digit decimals using the standard algorithm for each operation. 6.NS.4 Find the greatest common factor of two whole numbers less than or equal to 100 and the least common multiple of two whole numbers less than or equal to 12. Use the distributive property to express a sum of two whole numbers 1–100 with a common factor as a multiple of a sum of two whole numbers with no common factor. For example, express 36 + 8 as 4 (9 + 2). Curriculum and Instruction 2015-2016 Page 2 of 6 MADISON COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS District Curriculum Map for Mathematics: Grade 7 Instructional Outcomes What must students learn and be able to do by the end of the unit to demonstrate mastery? I am learning to…. convert a rational number to a decimal using long division (7.NS.2d) explain that the decimal form of a rational number terminates (stops) in zeroes or repeats (7.NS.2d) add rational numbers and interpret sums of rational numbers by describing real world contexts (7.NS.1b) subtract rational numbers and apply the principle of subtracting rational numbers in real world contexts (7.NS.1c) recognize that the process for multiplying fractions can be used to multiply rational numbers including integers. (7.NS. 2a) know and describe the rules when multiplying signed numbers. (7.NS.2a) multiply rational numbers and interpret the products of rational numbers by describing real world contexts (7.NS.2a) apply properties of operations to multiply rational numbers (7.NS.2c) explain why integers can be divided except when the divisor is 0. (7.NS.2b) describe why the quotient or integers is always a rational number (7.NS.2b) know and describe the rules when dividing signed numbers (7.NS.2b) recognize that –(p/q) = -p/q = p/-q (7.NS.2b) divide rational numbers and interpret the quotient of rational numbers by describing real world contexts (7. NS. 2b) identify and apply properties of operations to add, subtract, multiply and divide rational numbers (such as distributive, multiplicative inverse, multiplicative identity, commutative for multiplication, associative for multiplication, etc. (7.NS.1d and 2c) solve real world and mathematical problems by adding, subtracting, multiplying and dividing rational numbers, including complex fractions (7.NS.3) Vocabulary What vocabulary must students know to understand and communicate effectively about this content? Essential Vocabulary Irrational number, rational number, complex fraction, long division, repeating decimal, terminating decimal Supporting Vocabulary Additive Identity, Associative Property, Commutative Property, Distributive Property, Order of Operations, dividend, divisor, factor, integer, multiplicative inverse, product, quotient, Multiplicative Property of Zero, Multiplicative Identity, dividend, divisor, estimate, evaluate, expression Resources/Activities Resources/Activitie s What resources could we use to best teach this unit? Curriculum and Instruction From www.georgiastandards.org Use the following unit to access tasks and instructional strategies specific to rational numbers concepts. https://www.georgiastandards.org/CommonCore/Common%20Core%20Frameworks/CCGPS_Math_7_7thGrade_Unit 1.pdf Ann Shannon Formative Assessment Lessons (search by standard) http://map.mathshell.org/lessons.php?gradeid=22 Shodor Activities by Content Strand 2015-2016 Page 3 of 6 MADISON COUNTY PUBLIC SCHOOLS District Curriculum Map for Mathematics: Grade 7 http://www.shodor.org/interactivate/standards/organization/354/ EngageNY Lessons by Strand https://www.engageny.org/resource/grade-7-mathematics NCTM Illuminations – search for games, lessons and interactives by grade level and content http://illuminations.nctm.org Remember there are other sources in your school that may not be listed on this common resources list due to variation in each individual school. Examples of other great resources your school may have access to include: GoMath, Connected Math, IXL, Compass, MobyMax, Laying the Foundation, Carnegie, etc. The Kentucky Numeracy Project is also a great resource that can be searched by CCSS and grade level K-4 for RTI and gap closure purposes. Find this resource at http://knp.kentuckymathematics.org/#!/page_knphome. Kentucky teachers can use it for free. Just put in your school email address and the username “mathfun”, and password is “859”. Common Misconceptions Curriculum and Instruction Students can often confuse the properties when applying them to problems. Students can often forget to distribute to all terms in the parenthesis. Students can sometimes forget to apply the integer sign rules when applying the properties of numbers. Students often confuse the values of negative numbers and misinterpret the value when comparing. Students can misinterpret the sign rules due to a lack of understanding why the products/quotients should be negative (incorrect mathematical reasoning). Students can sometimes forget to apply the integer sign rules when applying the properties of numbers. Students often think that the last number on a calculator is the ending of a number. For multi-step problems, students can sometimes confuse the order of operations. Students often have a difficult time interpreting word problems to determine the task and the information needed. 2015-2016 Page 4 of 6 Curriculum and Instruction 2015-2016 Page 5 of 6 Curriculum and Instruction 2015-2016 Page 6 of 6