UNIT 3
advertisement

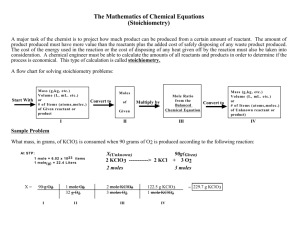
Instructional Unit Plan—UNIT 3 Teacher: Grade Level: 11th Content Area(s) Science: Chemical Reactions Implementation Dates: Unit Focus: New Mexico Content Standards, Benchmarks and Performances Addressed: Strand I: Scientific Thinking and Practice Standard I: Understand the processes of scientific investigations and use inquiry and scientific ways of observing, experimenting, predicting, and validating to think critically. 9-12 Benchmark I: Use accepted scientific methods to collect, analyze, and interpret data and observations and to design and conduct scientific investigations and communicate results. 1. Describe the essential components of an investigation, including appropriate methodologies, proper equipment, and safety precautions. 2. Design and conduct scientific investigations that include: testable hypotheses controls and variables methods to collect, analyze, and interpret data results that address hypotheses being investigated predictions based on results re-evaluation of hypotheses and additional experimentation as necessary error analysis. 3. Use appropriate technologies to collect, analyze, and communicate scientific data (e.g., computers, calculators, balances, microscopes). Strand I: Scientific Thinking and Practice Standard I: Understand the processes of scientific investigations and use inquiry and scientific ways of observing, experimenting, predicting, and validating to think critically. 9-12 Benchmark II: Understand that scientific processes produce scientific knowledge that is continually evaluated, validated, revised, or rejected. 1. Understand how scientific processes produce valid, reliable results, including: consistency of explanations with data and observations openness to peer review full disclosure and examination of assumptions testability of hypotheses repeatability of experiments and reproducibility of results. 2. Use scientific reasoning and valid logic to recognize: faulty logic cause and effect the difference between observation and unsubstantiated inferences and conclusions potential bias. Strand I: Scientific Thinking and Practice Standard I: Understand the processes of scientific investigations and use inquiry and scientific ways of observing, experimenting, predicting, and validating to think critically. 9-12 Benchmark III: Use mathematical concepts, principles, and expressions to analyze data, develop models, understand patterns and relationships, evaluate findings, and draw conclusions. 1. Create multiple displays of data to analyze and explain the relationships in scientific investigations. 2. Use mathematical models to describe, explain, and predict natural phenomena. Strand II: The Content of Science Standard I (Physical Science): Understand the structure and properties of matter, the characteristics of energy, and the interactions between matter and energy. 9-12 Benchmark I: Understand the properties, underlying structure, and reactions of matter. 9-12 Properties of Matter Chemical Reactions 12. Know that chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms, and that they occur on many timescales (e.g., picoseconds to millennia). 13. Understand types of chemical reactions (e.g., synthesis, decomposition, combustion, redox, neutralization) and identify them as exothermic or endothermic. 14. Know how to express chemical reactions with balanced equations that show: • conservation of mass • products of common reactions. Strand III: Science and Society Standard I: Understand how scientific discoveries, inventions, practices, and knowledge influence, and are influenced by, individuals and societies. 9-12 Benchmark I: Examine and analyze how scientific discoveries and their applications affect the world, and explain how societies influence scientific investigations and applications. Science and Society 9. Describe how scientific knowledge helps decision makers with local, national, and global challenges (e.g., Waste Isolation Pilot Project [WIPP], mining, drought, population growth, alternative energy, climate change). 10. Describe major historical changes in scientific perspectives (e.g., atomic theory, germs, cosmology, relativity, plate tectonics, and evolution) and the experimental observations that triggered them. 11. Know that societal factors can promote or constrain scientific discovery (e.g., government funding, laws and regulations about human cloning and genetically modified organisms, gender and ethnic bias, AIDS research, alternative-energy research). Science and Individuals 15. Know that science plays a role in many different kinds of careers and activities (e.g., public service, volunteers, public office holders, researchers, teachers, doctors, nurses, technicians, farmers, ranchers). Description of knowledge and skills required by the Standards Vocabulary: chemical reaction, reactant, product, synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, double replacement, combustion, coefficient, subscript, aqueous solution, complete ionic equation, spectator ion, net ionic equation, precipitate, soluble, product, reactant, shift left, shift right, concentration, endothermic, exothermic, catalyst, mole, avagadro’s number, one step conversion, two step conversion, hydrate, empirical formula, molecular formula, stoichiometry, mole ratio, percent yield, and theoretical yield. Concepts: Skills: Description of the Assessments that will be used to provide evidence of student learning that targets the standards: PERFORMANCE STANDARD 1. Describe the essential components of an investigation, including appropriate methodologies, proper equipment, and safety precautions. 2. Design and conduct scientific investigations that include: testable hypotheses controls and variables methods to collect, analyze, and interpret data results that address hypotheses being investigated predictions based on results re-evaluation of hypotheses and additional experimentation as necessary error analysis. 3. Use appropriate technologies to collect, analyze, and communicate scientific data (e.g., computers, calculators, balances, microscopes). 4. Understand how scientific processes produce valid, reliable results, including: consistency of explanations with data and observations openness to peer review full disclosure and examination of assumptions testability of hypotheses repeatability of experiments and reproducibility of results. ASSESSMENT Students will use appropriate equipment when performing laboratories Design and conduct a scientific investigation related to Properties of Matter (ex. Separation of Aspirin*) that include: testable hypotheses controls and variables methods to collect, analyze, and interpret data results that address hypotheses being investigated predictions based on results re-evaluation of hypotheses and additional experimentation as necessary error analysis. Major investigation (lab) Teacher choice Major investigation (lab) Teacher choice 5. Use scientific reasoning and valid logic to recognize: faulty logic cause and effect the difference between observation and unsubstantiated inferences and conclusions potential bias. Major investigation (lab) Teacher choice 6. Create multiple displays of data to analyze and explain the relationships in scientific investigations. Major investigation (lab) Teacher choice 7. Use mathematical models to describe, explain, and predict natural phenomena. Standardized Test Practice Chapter 11 #1-10 pg 351 8. Know that chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms, and that they occur on many timescales (e.g., picoseconds to millennia). 9. Understand types of chemical reactions (e.g., synthesis, decomposition, combustion, redox, neutralization) and identify them as exothermic or endothermic. 10. Know how to express chemical reactions with balanced equations that show: • conservation of mass • products of common reactions. “Chapter 10 Study Guide For Content Mastery Section 10.3”* Chapter 10 Assessment problems 90-94 page 305 “Chapter 10 Study Guide For Content Mastery Section 10.3”* Chapter 10 Assessment problems 90-94 page 305 Students will complete “Chapter 18 Review Chemical Equilibrium”* “Stoichiometry Assessment”* Description of the rubrics or criteria that will be used to assess student performance: GISD Rubrics Learning Activities – Description of the learning activities that will develop the knowledge and skills required by the performance standard: Types Chemical Reactions Know that chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms, and that they occur on many timescales (e.g., picoseconds to millennia). Understand types of chemical reactions (e.g., synthesis, decomposition, combustion, redox, neutralization) and identify them as exothermic or endothermic. Engage Activities Students will simulate a “volcano reaction” Teacher demonstrates a series of definite chemical reactions “Chemical Rxns Demo” Acid-Base neutralization Baking soda-vinegar Burn piece of Mg Explore Activities Think Pair Share: Students will demonstrate everyday examples of chemical reactions. Explain Activities Teacher and student develop Cornell notes on evidence of chemical reaction and five basic inorganic chemical types. Pgs 284-291 Vocabulary Building to include 4-square type Vocabulary Cards and Word Wall*: chemical reaction, reactant, product, synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, double replacement, combustion. Elaborate Foldable/Booklet on five reaction types. Activities Evaluate Standardized Test Practice Chapter 6 #1-12 pg383 or Teacher Generated Assessment Product Prediction – Balancing Chemical Reactions Know how to express chemical reactions with balanced equations that show: conservation of mass, products of common reactions. Engage Simply Science: Reaction Equations http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAssetId=695C 3823-CF15-4958-A2A11979B72FEEE4&blnFromSearch=1&productcode=US Demonstration of conservation of Mass using effervescences tablets, Erlenmeyer Flask and balloon. Reconnect to IS2 Explore Teacher will provide set of unbalance chemical reactions for students to balance. Explain Teacher and student develop Cornell notes, reconnect to naming Activitie and balancing chemical reactions. Pgs 280-282 s Vocabulary Building to include 4-square type Vocabulary Cards and Word Wall*: coefficient and subscript. Elaborat Students will complete “Reaction Worksheet”* e Teachers will choose from: “Reaction Problems”* Activitie s Explain Teacher and student develop Cornell notes on complete ionic Activitie equations and net ionic equations, solubility/precipitation. s Vocabulary Building to include 4-square type Vocabulary Cards and Word Wall*: aqueous solution, complete ionic equation, spectator ion, net ionic equation, precipitate, and soluble. Elaborat Student will perform Lab 7 Chemistry Small-Scale “Solutions and e Precipitates”* Activitie s Evaluate “Chapter 10 Study Guide For Content Mastery Section 10.3”* Chapter 10 Assessment problems 90-94 page 305 Students will complete Standardized Test Practice p307 #1-8 Moles Use mathematical models to describe, explain, and predict natural phenomena. Engage Activities Discussion question: What is a counting unit? When we talk about a dozen, what number do you think of? Explore Activities Think Pair Share: Have students come up with other examples and discuss. Internet search recommended. Internet Activity “How Big is a Mole?”* Explain Activities Teacher and student develop Cornell notes on the mole, avagadro’s number, molar mass and conversion. Pgs 309-327 Vocabulary Building to include 4-square type Vocabulary Cards and Word Wall*: mole, avagadro’s number, one step conversion, two step conversion. Elaborate Discovery lab “How much is a Mole” page 309 Activities Students will complete “Measuring Atoms Activity* “Molar Mass Worksheet”* Extra Credit: “Molennium Mole Pattern”* Explain Activities Teacher and student develop Cornell notes on hydrates and empirical/molecular formulas. Pgs 328-346 Vocabulary Building to include 4-square type Vocabulary Cards and Word Wall*: hydrate, empirical formula, molecular formula Elaborate MiniLab “Percent Composition and Gum” page 329 Activities Or ChemLab 11 “Hydrated Crystals” page 342 Evaluate Standardized Test Practice Chapter 11 #1-10 pg 351 Stoichiometric Calculations Know how to express chemical reactions with balanced equations that show: • conservation of mass • products of common reactions. Engage Activities Sandwich/S’more Activity* Explore Activities Classroom discussion on Section Focus Transparency 45 “Limiting Reactants” Explain Activities Teacher and student develop Cornell notes on molar ratio, Stoichiometric process, calculating percent yield. Pgs 352-373 Elaborate Activities Explain Activities Elaborate Activities Evaluate Unit Resources: “Stoichiometry Overview”* Vocabulary Building to include 4-square type Vocabulary Cards and Word Wall*: Stoichiometry, mole ratio, percent yield, theoretical yield Students will perform miniLab “Baking Soda Stoichiometry” page 362 Or Lab 12-2 “Stoichiometry of a chemical reaction” And “How It Works” page 376 Teacher and student develop Cornell notes on limiting reactant stoichiometry. Pgs 364-369 ChemLab 12 “A Mole Ratio” page 374 “Stoichiometry Assessment”* generated from test bank “volcano reaction” Erlenmeyer flask (10) Baking Soda Baking Powder Vinegar Food Dye Conservation of Mass Demonstration Effervescent tablets Erlenmeyer flask balloon “Solutions and Precipitates”* 1.0M BaCl2 1.0M CuSO4 1.0M FeCl3 1.0M KI 1.0M NaCl 1.0M Na2CO3 1.0M NaOH 1.0M Na2SO4 1.0M Pb(NO3)2 24 – well microplate Pipettes (9) “How Big is a Mole?” Computer access Textbook Other Book resources “How much is a Mole” Centimeter ruler Paper clip “Measuring Atoms Activity” 1” Iron Nail Balance “Percent Composition and Gum” Balance Weighing paper 250 – mL beakers (2) Pieces of chewing gum (2) Stirring rod Paper towels Window screen (10cm x 10 cm) Scissors Clock or timer “Hydrated Crystals” Bunsen burner Ring stand and ring Crucible and lib Clay triangle Crucible tongs Balance Epsom salts (hydrated MgSO4) Spatula Spark lighter or matches Sandwich Activity Bread Meat Cheese S’more Activity Graham Crackers Marshmallows Bar Chocolate “Baking Soda Stoichiometry” Ring stand Ring Clay triangle Crucible Crucible tongs Bunsen burner Balance Baking soda (NaHCO3) “Stoichiometry of chemical reaction” 24-well microplate thin-stem pipet balance distilled water paper towels NaHCO3 CaCO3 KHCO3 HCl “A Mole Ratio” Iron metal filings, 20 mesh Copper (II) sulfate pentahydrate (CuSO4 . 5H2O) Distilled water Stirring rod 150–mL beaker 400-mL beaker 100-mL graduated cylinder Weighing paper Hot plate Beaker tongs Technology links: Simply Science: Reaction Equations http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAssetId=695C3823-CF154958-A2A1-1979B72FEEE4&blnFromSearch=1&productcode=US