Quiz 2
advertisement

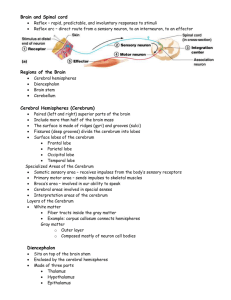
Name Anatomy and Physiology II – Quiz 2 – Spring 2004 1. Which of the following is not true about the spinal cord? a. It is part of the central nervous system; b. It is responsible for coordinating simple reflexes; c. It contains both white matter and gray matter; d. It gives rise to cranial nerves. 2. The left hemisphere of the cerebrum has commissural fibers that pass to the right hemisphere through the structure in the brain called the: a. corpus callosum; b. midbrain; c. limbic system; d. thalamus; e. reticular activating system. 3. In general, ‘gray matter; in the nervous system contains: a. axons leading to the brain; b. cell bodies and interneurons; c. dendrites and sensory neurons; d. axons of motor neurons. 4. If a neurosurgeon said that a patient received damage to spinal nerve S-3, the consequences may be noticed in: a. the leg; b. the neck; c. the arms; d. the abdomen; e. the organs of the chest. 5. A man was in a car accident and some damage was done to the man’s head. As a consequence, he had difficulty with his vision and with coordinating his body movements. The areas of the brain which were damaged probably were: a. the post central gyrus and the cerebellum; b. the temporal lobe of the cerebrum and the cerebellum; c. the occipital lobe of the cerebrum and the cerebellum; d. the precentral gyrus and the temporal lobe. 6. When an action potential from a sensory neuron enters the spinal cord it enters by way of: a. a neuroglial (glial) cell; b. the dorsal root; c. the ventral root; d. an interneuron. 7. In the spinal cord, ascending and descending tracts are generally found in the: a. central canal; b. white matter; c. gray matter; d. posterior horn. 8. Feeding, fighting, fear and sexual reproduction are associated with the system of the brain call the . 9. The reticular activating system in the brain stem is important for: a. maintaining alertness and consciousness; b. regulating hunger and weight; c. a sense of touch; d. controlling heart rate and respiratory rate. 10. MATCHING: Sensation of touch Initiation of motor movements Visual sensations Auditory sensation 11. a. temporal lobe b. parietal lobe c. frontal lobe d. occipital lobe What is nerve “cross-over” or decussation, and where does it usually occur? 12. The diagram given below represents a section of the spinal cord and the attached spinal nerves. I. If the spinal nerve root was cut at “A” indicated on the diagram, what would the immediate consequence be to the person? II. What is the name of the structure at B, and what is found there? 13. The figure below represents a midsagittal section of the human brain. I. Label the thalamus and state one of its important functions. II. Label the pons and state one of its important functions. 14. The radial nerve, the median nerve, and the ulnar nerve all emerge from the brachial . 15. What are some symptoms of Parkinson’s disease and what neurotransmitter is secreted in lower quantities in this disease? (2 points) 16. Your ability to feel a touch on the skin overlying the quadriceps muscle would depend on an ascending sensory pathway that follows one of the routes indicated below. Circle the letter in front of the correct answer. a. sciatic nerve lumbar plexus dorsal root of spinal nerve ascending pathway thalamus pre-central gyrus of cerebrum. b. femoral nerve sacral plexus ventral root of spinal cord ascending pathway thalamus post-central gyrus of cerebrum. c. femoral nerve lumbar plexus dorsal root of spinal cord ascending pathway thalamus post-central gyrus. d. sciatic nerve sacral plexus ventral root of spinal cord ascending pathway thalamus pre-central gyrus of cerebrum.