Astronomy A100 Midterm 1 (alternate)
advertisement

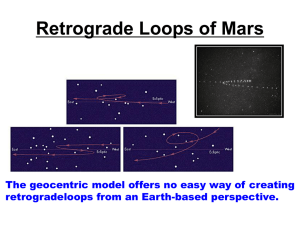
Astronomy A100 Midterm 1 solutions Fall 2006 ______________________________________ Name Multiple Choice (3 points each): 1) Is Polaris (aka the North Star) the brightest star in the night sky? a) yes b) no c) it is tied with other stars for the brightest d) Polaris is not up at night 2) Which of the following best describes the Ecliptic plane? a) the path the moon covers in the sky b) the path the sun covers in the sky c) another term for the celestial equator d) all of the above 3) In Ptolemy’s model, where was the position of the earth? a) in the center b) in orbit around the sun c) just off of the center d) Ptolemy’s model did not include the earth 4) The ancient Greeks knew the earth was a sphere. a) true b) false 5) Which of the following is the most accurate statement about the views of ancient Greece? a) All believed that the earth was the center of the universe. b) Most that the earth was the center of the universe, but a few argued that the sun could be at the center. c) Most that the sun was the center of the universe, but a few argued that the earth could be at the center. d) All believed that the sun was the center of the universe. 6) During the time of Ancient Greece and in the early Dark Ages, what was at the North Celestial Pole? a) nothing b) Vega c) The moon d) Polaris (aka the North Star) 7) Which of the following most accurately describes Ptolemy’s model for the Solar System? a) Earth was near the center, circular orbits, no epicycles b) Earth was near the center, circular orbits, with epicycles to explain retrograde motions c) sun near the center, circular orbits, no epicycles d) sun was near the center, circular orbits, with epicycles to explain retrograde motions 8) Which of the following most accurately describes Copernicus’s model for the Solar System? a) Earth was near the center, circular orbits, no epicycles b) Earth was near the center, circular orbits, with epicycles to explain retrograde motions c) sun near the center, circular orbits, no epicycles d) sun was near the center, circular orbits, with epicycles to explain retrograde motions 9) The telescope was invented by: a) the Arabs about 900 AD b) the Vikings about 1200 AD c) Galileo about 1600 AD d) Isaac Newton about 1700 AD 10) Which of the following was not an accomplishment of Tycho Brahe? a) Proving that comets were not in the atmosphere. b) Created a sun centered model of the solar system which was accepted by later astronomers (although the public disregarded it during his lifetime). c) Made measurements of Mars to an accuracy of 1 arc minute d) Tycho did all of the above. 11) What is Kepler’s 1st law? a) orbits are circular b) orbits are elliptical c) orbits are triangular d) orbits have no shape 12) If the sun is at 1 focus of the earth’s orbit, what is at the other focus? a) the sun b) the moon c) nothing d) the earth 13) What is Kepler’s 2nd law? a) equal area with equal time b) the area per time depends on what part of the orbit you are in c) orbits are not constant, so there is no way to calculate the area per time covered d) orbits don’t exist 14) What is Kepler’s 3rd law? a) orbits are circular b) the earth is the center of the universe c) the sun is the center of the universe d) The square of the period relates to the 3rd power of the semi-major axis 15) Which of the following does Galileo NOT get credit for? a) Inventing the telescope. b) Being the first to observe Neptune. c) Observing Sunspots. d) Galileo get credit for all of these 16) Which of the following does Galileo NOT get credit for? a) finding the mountains on the moon b) discovering that gravity accelerates all objects at the same rate regardless of their masses c) discovering the rotation of the sun d) Galileo gets credit for all of these things 17) Newton Discovered that as 2 objects get further apart: a) the force of gravity drops b) the force of gravity remains constant c) the force of gravity increases d) the force of gravity no longer exists once the 2 objects are separated 18) Newton also discovered: a) That apples fall faster than pears. b) That gravity only exists on the surface of an object. c) That gravity extends outward far beyond the earth. d) That gravity at large distances creates a repulsive force which keeps everything from crashing into the sun. 19) The corona of the sun is several million degrees. If a spacecraft could shield itself from the rest of the sun, how would the corona affect the ship? a) move it forward in time b) fry it c) crush it d) nothing 20) On what part of the sun would you find sun spots? a) corona b) core c) photosphere d) radiative zone 21) You have a solid object at some temperature. What type of spectrum of light will it emit? a) none b) emission c) continuous d) absorption 22) Where on the sun could you land? a) bottom of the photosphere b) core c) coronal hole d) no where 23) How dense is the sun? a) about as dense as air b) about as dense as water c) about as dense as lead d) more dense than any material on the earth! 24) In the radiative zone, how long does it take a single light photon to go from the bottom of the radiative zone to the top of the radiative zone? a) 10 seconds b) 10 minutes c) 10 years d) 1 million years 25) From which part of the sun is most of the light we can see emitted from? a) corona b) core c) photosphere d) radiative zone 26) Which is the correct order of the layers of the sun from the center to the furthest out? a) core, radiative zone, convection zone, photosphere, corona b) core, radiative zone, convection zone, corona, photosphere c) core, convection zone, radiative zone, photosphere, corona d) core, convection zone, radiative zone, corona, photosphere 27) The spectrum of the sun has absorption lines. What does that tell us about the sun? a) What the sun is made of. b) The top layer of the photosphere is “thin”. c) The top of the photosphere is cooler than the bottom. d) All of these. 28) Which of the following is NOT a light wave? a) an X-ray b) a radio wave c) a gamma ray d) these are all light waves 29) You have a solid object surrounded by a cooler gas. What kind of spectrum will this produce? a) none b) emission c) continuous d) absorption 30) You have a “thin” cool gas with nothing behind it. What kind of spectrum will this produce? a) none b) emission c) continuous d) absorption SHORT ANSWER: (15 points each) 1) Name 4 types of objects you can see in the night sky which are astronomical (and outside our atmosphere). Planets Moon Stars Constellations Satellites Galaxies 2) Why did Ptolemy’s model last for 1400 years? Give at least 2 reasons. 4 sentences maximum. It worked! It was accurate! 400 yrs later the dark ages slowed progress of science to a standstill The church tended to control beliefs Nobody did measurements accurate enough to be able to show the flaws in the system. 3) Early in his career, Kepler made a somewhat accurate model of the solar system using circular orbits. His model agreed well with most of the observations made by his mentor Tycho Brahe. However, at two places in the orbit of Mars, his model differed from the observations by 8 arc minutes (which is only ¼ the diameter of the moon). What did Kepler decide was the cause of this error? How did Kepler rectify this error (if at all)? How did this decision impact astronomy (if at all)? 1-2 sentences per question maximum. • • • He decided the model was in error. He fixed the error by trying different orbits than circular and finally came upon elliptical orbits. This created models based on observations, and gave us the solar system as we understand it to be today. 4) What is a sunspot? If you were directly above a sunspot (so that you could not see the rest of the sun), would the sunspot appear to be dark or bright, and why? 3 sentences max. • • • A sunspot is a dark part of the sun which is cooler than the rest of the surrounding areas. A sunspot would be bright. Sunspots just appear dark because they emit a less light than the surrounding areas.