chapter 5 part two
advertisement

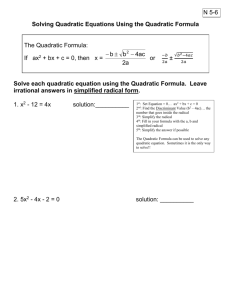
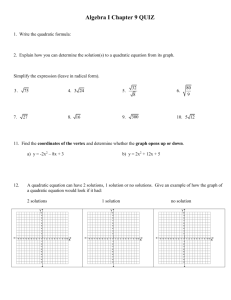
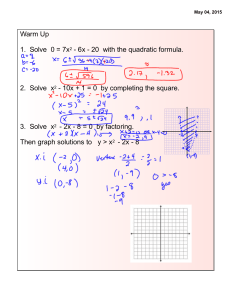
Algebra II Chapter 5 Notes PART II 5.5 Complex Numbers and Roots Make a list of the first 15 perfect squares: Simplify the radicals. a. 36 b. 4 c. 49 d. 169 e. 64 Steps for simplifying radicals: (1) Find the largest factor of the number that is a perfect square. (2) Rewrite the expression as the __________________________ of _________ radical expressions (3) Take the square root (of the __________________ ___________________) and leave the non-perfect square in the radical symbol. Together: Simplify the radical. 28 162 Simplify the radical expression. 1. 200 2. 44 3. 20 4. 80 5. 440 6. 16 7. 32 180 8. i = _______ (which represents an imaginary unit) Together: Simplify the radical. A. 45 B. 50 C. Example 1: a. b. c. d. e. f. 1 162 9 Steps for solving quadratic equations when there is no linear term (in the form ax² + c =0) Step 1: Isolate ___________ Step 2: Take the _______________ of the square (which is the ______________ _______________ to both sides of the equation) Remember that you will have TWO solutions (one ___________, one ___________) Example 2: a. b. c. d. e. f. Example 3: Solve. 1. ( x 3) 2 4 44 2. 3( x 3) 2 2 52 3. ( x 2) 2 5 45 4. 2( x 3) 2 2 58 Complex Conjugate: Together (find the conjugate): a. 3 – 5i b. –5 + 3i c. 25i – 17 Example 4: a. b. c. d. e. f. d. –16i 5.6 The Quadratic Formula The quadratic formula is used to solve quadratic functions in the form f(x) = ax² + bx + c The formula is: x You must __________ the formula!!!!!!! b b 4ac 2a 2 Example 1: Find the zeros of the quadratic function by using the quadratic formula. A. f ( x) 2 x 2 16 x 27 B. C. f ( x) 2 x 2 5 x 3 D. f ( x) 4 x 2 4 x 9 f ( x) 4 x 2 3 x 2 Find the zeros of the quadratic function by using the quadratic formula. E. f ( x) 9 x 2 6 x 11 F. f ( x) 2 x 2 x 2 G. f ( x) 2 x 2 x 15 H. f ( x) 5 x 2 7 x 3 I. f ( x) x 2 3 x J. f ( x) 2 x 2 5 The discriminate is used to find the __________________ and __________________of solutions for a quadratic function. The formula for the discriminate is ______________________. Discriminant Quadratic Formula: b 2 4ac 0 b 2 4ac 0 (_________ Number) b 2 4ac 0 (_________) (__________ Number) y y y _____ _________ solutions x x x ____ _________ solution ____ __________ solutions Example 3: Find the type and number of solutions for each equation. a. x2 6x 7 0 d. x 2 4 x 4 0 b. x 2 6 x 9 e. x 2 4 x 8 c. x 2 11 6 x f. x 2 2 4 x 5.7 Solving Quadratic Inequalities Steps for graphing quadratic inequalities 1. Graph the parabola that defines the boundary a. Use a _________________ line for ≥ and ≤ b. Use a _________________ line for > and < 2. Shade the appropriate region a. Shade _________________________ the parabola for y > or ≥ b. Shade _________________________ the parabola for y ≤ or < c. OR use a test point (typically 0,0) if true shade the region including the origin, if false shade the region excluding the origin. Example 1: a. b. y y x x c. d. y y x x Example 2: a. b. c. d. Example 3: a. b. c. d. Example 4: 5.8 Pattern for quadratic function:____________________________________________ Example 1: A. B. C. D. 5.8 Calculator steps for finding a quadratic model for a given data set [stat] [enter] enter data into L1 and L2 [stat] [calc] [#5 QuadReg] [enter] [enter] Record equation for the line of best fit (a is slope and b is y-intercept) Record R² Quadratic model: _________________________________________________________ Quadratic regression: _____________________________________________________ Example 2: Example 3: 5.9 Complex numbers: _______________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________ Example 1: A. B. C. D. E. F. G. H. i = _______ i² = ______ Example 2: a. b. c. d. e. f. g. h. i. j. Example 3: a. b. d. e. c. Rationalize the denominator: _________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Example 4: a. b. c. d. e. f.