File
advertisement

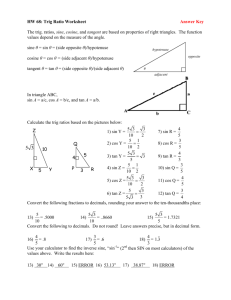
Advanced Pre-Calculus Unit 5 - Analytic Trigonometry January 5th – 22nd, 2016 Date Tuesday 1/5/2016 Wednesday 1/6 Thursday 1/7 Friday 1/8 Monday 1/11 Tuesday 1/12 Wednesday 1/13 Thursday 1/14 Friday 1/15 Tuesday 1/19 Wednesday 1/20 Thursday 1/21 Friday 1/22 Topic Simplifying Trig Identities Verifying Trig Identities Did it Assignment p. 2 notes page 1 notes pages 3/4 Finish pp. 3/4 Simplifying/ Verifying Trig Identities pp. 4/5 Quiz: Simplifying/ Verifying Trig Identities Study Unit Circle Finish problems pp. 1 to 5 pp. 6/7 Quiz: Unit Circle Solving Trig Equations notes page 6/7 Solving Trig Equations Sum & Difference Formulas p. 8 Finish pp. 8/9 notes pages 8/9 Sum & Difference Formulas notes # 27, 29 Quiz: Solving Trig Equations Double & Half Angle Formulas Finish p. 10 Evens pp. 11/12 notes page 11/12 odds Right Triangle Trig Application Problems notes page 13 Right Triangle Trig p. 14 1 – 5 p. 15 6 – 10 Quiz: Sum & Difference, Double & Half Angle Formulas Review Study Test #5: Analytic Trig Print next unit. Notes: Trigonometric Identities 1. tan x cos x 2. sec x cot x 5. sin x 1 6. 9. sec x(sec x cos x) 10. 2 Go over Properties. 3. (1 cos x)(1 cos x) sin cot cos csc2 x 1 cos x Simplify the following. 7. cot x csc x 2 11. cos x sin x 1 sin 2 x 2 4. (sec x 1)(sec x 1) 8. (csc A 1)(csc A 1) 12. sin x cos x csc x sec x 1 Assignment: January 5th 1. sec2 θ (1 – sin2 θ) 6. sec x cot x sin x 11. Simplify the following. 7. 1 cot A 1 1 2 cos A cot 2 A 2 12. (sec2 x 1)(csc2 x 1) 23. (1 – sin2θ)(1 + tan2θ) 8. csc2 x(1 cos 2 x) sin 2 a 1 cos a 15. (sec B tan B )(sec B tan B ) 19. 3. (sin 1)(sin 1) sin x cot x 2. 24. 9. tan 2 x 17. 1 sec x 1 tan2 θ – sec2θ secθ – (tanθ sinθ) 21. 25. 2 5. tan x sec x 2 1 1 2 sin A tan 2 A 13. cos x(sec x cos x) sin x cos x 16. 1 cos 2 x 20. 4. 1 tan tan csc cos(sec – cos) 14. 10. 2 1 sin 2 A tan 2 A cos2 A(sec2 A 1) sin 2 x 18. + cos x cos x 22. 1 cot x 1 cos x 2 26. 2 csc2x (1 – cos2x) 2 Notes/Assignment: January 6th 1. 1 1 1 2 sec csc 2 4. sin x cos x cot x csc x 2 Verify each identity. sec x sin x tan x cot x 2. 3. 2 8. sin x cos x cot x csc x Work only on one side. 1 tan 1 sin 1 2 2 6. cos x csc x cot x 5. sin x(sec x csc x) tan x 1 7. 2 cos x sin x 1 3 cos x 2 Verifying Trig Identities 9. 1 tan sec csc tan 10. sin 2 x cos x 1 1 cos x 11. 1 tan 2 csc 2 2 tan 12. 1 sin 2 cot 2 2 1 cos 13. sin x cot x cos x 2 cot x sin x 14. 1 tan 2 x sec 2 x 2 2 sin x cos x 15. 1 sin csc tan cos 1 3 16. sec sin tan cot 19. sin x cos x 1 tan x cos x 22. 1 2 sin 2 17. sin 2 cos 2 1 2 cos 2 20. x 2 cos 2 x 1 sin 2 x sec 2 x 1 2 cos x 2 Simplify the following. 1. sin (–x) 3. tan (–x) 8. 1 tan 2 x 1 cot 2 x 9. 4. csc (–x) tanx (sinx + cosx cotx) 2 2 5. sec (–x) 10. sin x cos x tan x 21. 1 cot 23. 2 cos x sin x cos x 1 Assignment January 7th 2. cos (–x) 18. csc 2 x 1 cot 2 x 24. 2 csc 2 sec 2 x(1 sin 2 x) 1 6. cot (–x) 7. 11. (cos2θ)(sec2θ–1) sec 2 x tan 2 x csc x 4 12. 1 1 + 2 sec x csc 2 x 13. cos 2 x + sin x 15. sin x 18. tan 2 x 1 tan x csc 2 x 22. sin x tan x cos x 2cos2 θ – sin2 θ + 1 sec 2 x 16. sec 2 x 1 19. cotx secx 17. 20. 23. sec x sin cos 2 sin 2 1 cos sec 14. sec tan – cos cot x tan x 24. sec x tan x sec x tan x 21. sec x cos x sin 2 x sec x sinθ (cscθ – sinθ) 5 Notes/Assignment: January 11th 1. 2 cos x 3 0 5. 4 cos x 2 cos x 1 8. cos 3x 1 12. sin 2 x sin x 2 0 2. Trig Equations Solve each equation. 3 sec x 2 0 6. 3. sin 2 x 1 2 sec x 2 9. 2 tan 5x 2 7. 10. sec 2x 2 13. 2 cos 2 x 5 cos x 3 0 4. tan 2x 1 3 tan x sin x sin x 11. 2 sin x cos x 2 sin x 0 14. tan 2 x 2 tan x 1 0 6 15. sec 2 x 3 sec x 2 16. 4 sin 2 x 4 x 1 0 17. 2 cos 2 x 3 cos x 1 0 18. 2 cos 2 x cos x 19. tan x sec x tan x 20. 2 sin 2 5 x 3 sin 5 x 1 0 21. sin 2x cos x 22. sin 2x 2 cos x 0 23. cos 2x sin x 0 24. cos 2x sin x 1 25. cos2x 3cosx 1 26. cos 2x cos x 7 Assignment: 27. January 12th Trig Equations 1 cos x 1 sin x 28. 30. 2 sin 2 x 2 cos x Notes/Assignment: January 13th Solve each equation. sin 2 x 0 1 cos 2 x 29. sin 2 x cos 2 x 1 32. 2 sec 2 x tan 2 x 3 31. 2 sin x csc x 0 Sum and Difference Formulas Simplify each Expression. sin _________ 1. cos25°cos15° – sin25°sin15° _________ 2. cos _________ 3. sin140°cos50° – cos140°sin50° _________ 4. sin3cos1.2 – cos3sin1.2 7 cos 5 7 sin _________ 5. tan 325 tan 86 1 tan 325 tan 86 _________ 6. tan 2 x tan x 1 tan 2 x tan x _________ 7. tan 140 tan 60 1 tan 140 tan 60 _________ 8. tan 240 tan 140 1 tan 240 tan 140 5 8 Evaluate: ______________ 9. sin75°cos15° + sin15°cos75° _______________ 10. sin15°cos30° + sin30°cos15° ______________ 11. cos105°cos60° + sin 105°sin60° ______________ 12. cos105°cos15° + sin 105°sin15° ______________ 13. tan 75 tan 30 1 tan 75 tan 30 ______________ 14. tan 60 tan 30 1 tan 60 tan 30 ______________ 15. tan 100 tan 50 1 tan 100 tan 50 ______________ 16. tan 200 tan 70 1 tan 200 tan 70 ______________ 17. cos 5 5 cos sin sin 12 12 12 12 ______________ 18. cos 7 5 7 5 cos sin sin 6 6 6 6 ______________ 19. sin 4 4 cos sin cos 3 3 3 3 ______________ 20. sin 2 2 cos sin cos 3 3 3 3 Find the exact value of each expression. (no calculators) 21. cos 75° 22. cos 165° 23. sin 105° 24. sin 75° 25. cos 15° 26. sin 15° 9 Evaluate. 27. If sin x 3 24 (x is in Quadrant I) and sin y (y is in Quadrant II), find sin (x + y). 5 25 28. If sin x 4 1 (x is in Quadrant III) and sin y (y is in Quadrant II), find sin (x – y). 5 2 Given sin u 5 3 and cos v , both in quadrant II. find: 13 5 29. sin (u + v) 30. cos (u + v) 31. tan (u + v) 32. sin (u – v) 33. cos (u – v) 34. tan (u – v) 10 Double Angle Formulas cos 2 A cos 2 A sin 2 A sin 2 A 2 sin A cos A tan 2 A 2 tan A 1 tan 2 A cos 2 A 2 cos 2 A 1 cos 2 A 1 2 sin 2 A Simplify: _________ 1) 2 cos 2 10 1 _________ 3) 2 sin _________ 5) __________ 2) 2 cos 2 42 1 x x cos 2 2 x x cos 4 4 __________ 4) 2 sin 2 tan 3x 1 tan 2 3x __________ 6) 2 tan 16 1 tan 2 16 _________ 7) cos 2 4 A sin 2 4 A __________ 8) cos 2 13 sin 2 13 _________ 9) 1 2 sin 2 21 __________ 10) 1 2 sin 2 49 _________ 11) 2 tan 25 1 tan 2 25 __________ 12) 1 2 sin 2 _________ 13) 4 tan x 1 tan 2 x __________ 14) 4 sin x 2 7 7 cos 12 12 Simplify, then Evaluate: ______________ 15) 2 sin 15 cos15 _______________ 16) ______________ 17) 2 tan / 8 1 tan 2 / 8 _______________ 18) ______________ 19) cos 2 ______________ 21) 1 2 sin 2 45 ______________ 23) cos 2 ______________ 25) 2 sin 90 cos 90 12 3 sin 2 sin 2 12 3 2 cos 2 / 8 1 1 2 sin 2 _______________ 20) 4 sin 8 12 cos 8 _______________ 22) 2 sin 30 cos 30 _______________ 24) 6 tan 75 1 tan 2 75 _______________ 26) 2 cos 2 / 12 1 11 Half Angle Formulas sin A 1 cos A 2 2 cos A 1 cos A 2 2 tan A 1 cos A 2 1 cos A tan A 1 cos A 2 sin A tan A sin A 2 1 cos A Simplify: 1 cos 80 2 __________ 1) __________ 3) 1 cos / 7 2 1 cos / 6 2 __________ 5) __________ 7) 1 cos 32 2 __________ 2) __________ 4) __________ 6) __________ 8) 1 cos14 2 1 cos / 5 2 1 cos / 4 2 1 cos 212 2 __________ 9) 1 cos 26 sin 26 __________ 10) 1 cos 64 sin 64 __________ 11) 1 cos / 7 sin / 7 __________ 12) 1 cos / 9 sin / 9 __________ 13) __________ 15) 1 cos 44 1 cos 44 sin 66 1 cos 66 __________ 14) 1 cos 74 1 cos 74 __________ 16) sin 106 1 cos 106 Simplify, then Evaluate: _______________ 17) _______________ 19) 1 cos / 2 sin / 2 1 cos 240 2 _______________ 18) _______________ 20) sin 120 1 cos 120 1 cos / 3 2 12 Note: January 19th For each problem: 1. Draw a triangle. 2. Solve. 3. Answer the question in a complete sentence. 4. Show all work Angle of elevation: represents the angle from the horizontal upward to an object. Angle of depression: represents the angle from the horizontal downward to an object. 1. While on a family vacation in Egypt, you are standing outside one of its great pyramids. Bored of the tour, you decide to take on some “practical” applications of your Pre-Calculus class. With a meter stick (that you always carry with you just in case), you measure the base of the pyramid to be 230 m. With your protractor, you find that the faces of the pyramid make an angle of 51.2 with the ground. How tall is the pyramid? 2. You are asked to find the height of a nearby building. From where you initially stand, you measure the angle of elevation to be 36 . Moving closer to the building by 50 feet, the angle of elevation becomes 58 . To the nearest foot, what is the height of the building? 3. The ramp leading to a bridge must gain 8 feet in elevation. If the angle of elevation of the ramp is to be 4 , find the length of the ramp. 4. A surveyor is standing 115 feet from the base of the Washington Monument. The surveyor measures the angle of elevation to the top of the monument as 78.3˚. How tall is the Washington Monument? 5. A signal flare is seen by two observers, R2-D2 and C3-P0 (who are 5.4 miles apart). R2-D2 observes the angle of elevation to the flare to be 20 , while C3-P0 observes the angle of elevation to be 32 . How high up is the flare? 13 Assignment: January 19th – 20th For each problem: 1. Draw a triangle. 3. Answer the question in a complete sentence. 2. Solve. 4. Show all work 1. Bilbo and Frodo are standing 2.32 miles apart when they see a hot air balloon floating over their heads. Bilbo’s angle of elevation to the balloon is 28 while Frodo’s angle of elevation to the balloon is 37 . How high up is the balloon? 2. Hamlet is storming a castle and needs to find the height of the parapet in order to build scaffolding high enough to go over the walls. From where he is standing, he measures the angle of elevation to be 35 . He moves 50 m closer to the castle and measures the angle of elevation to be 50 . Find the height of the castle walls. 3. The ramp leading to a bridge must gain 10 feet in elevation. If the angle of elevation of the ramp is to be 3 , find the length of the ramp. 4. From the top of a building 25 m high, the angle of elevation of a weather balloon is 54 . From the bottom of the building, the angle of elevation is 61 . How high is the weather balloon? 5. Bilbo decides to wage war on the elves, and sends a missile their way. He stands 2 km from the launching pad and observes the missile ascend vertically. After 3 seconds, the angle of elevation between the Bilbo and the missile is 21 . Five seconds later, the angle of elevation is 35 . How far did the missile travel during those 5 seconds? 14 6. A safety regulation states that the maximum angle of elevation for a rescue ladder is 72˚. A fire department's longest ladder is 110 feet. What is the maximum safe rescue height? 7. At a point 200 feet from the base of a building, the angle of elevation to the bottom of a smokestack is 35˚, whereas the angle of elevation to the top is 53˚. Find the height of the smokestack alone. 8. For the right triangle given, find all unknown sides and angles. B c a 34˚ A b =19.4 C 9. A signal flare is seen by two observers, R2-D2 and C3-P0 (who are 5.4 miles apart). R2-D2 observes the angle of elevation to the flare to be 20 , while C3-P0 observes the angle of elevation to be 32 . How high up is the flare? 10. Find the length of a skateboard ramp when the height of the ramp is 4 feet and the angle formed where the ramp touches the ground is 18.4˚. 15