Links for Cell City Webquest
advertisement

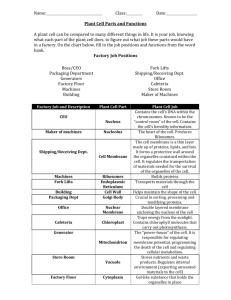
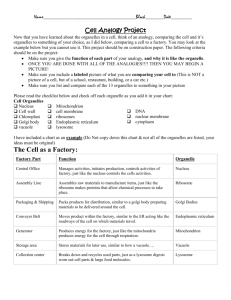
Name _________________ Date ____________ Period ______ # _____ Links for Cell City Webquest Advanced Biology 2013-2014 Screening Assessment Part I http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_theory http://www.bio.miami.edu/~cmallery/150/unity/cell.text.htm http://www.hobart.k12.in.us/jkousen/Biology/cell.htm http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/history/hooke.html http://inventors.about.com/library/inventors/blroberthooke.htm Screening Assessment Part II http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/3dcell.htm http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cell_(biology) http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.htm http://www.wiley.com/legacy/college/boyer/0470003790/animations/cel l_structure/cell_structure.htm http://library.thinkquest.org/12413/karyotes.html (Click on prokaryotes- the champion and eukaryotes- the challenger to understand the fundamental differences between these cell types.) http://www.ucmp.berkeley.edu/alllife/virus.html Screening Assessment Part III http://waynesword.palomar.edu/lmexer1a.htm http://www.cellsalive.com/cells/cell_model.htm http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rABKB5aS2Zg (Cell Song) http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=wRZthGlzEUc (Cells Song- Mr. Parr) Pictures of Edible Cells http://www.instructables.com/id/Plant-Cell-Cake/ http://www.flickr.com/photos/aedra/70045368/in/photostream/ Name _________________ Date ____________ Period ______ # _____ Point Values for Cell City Screening Assessments, Assignments, and Projects 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Animal or Plant Cell Cardstock Drawing, Labeling, and Functions of Organelles within the Cell (30 points) Due in class Screening Assessment 1 (21 points) Due in class Screening Assessment 2 (21 points) Due in class Screening Assessment 3 Part A (36 points) Due in class Screening Assessment 3 Part B (12 points) Due in class In Class Cell Quiz (40 points) Cell City Analogy (18 points) Due in class Create Your Own Cell Analogy (30 points) Due Edible Cell Project (50 points) We will construct these in class on ___________. Total= 248 points We will also be doing a lab on osmosis and plasmolysis as we perform these computerized assignments. These will also count for points in the cell unit. The points for these labs are undetermined at this time. Name _________________ Date ____________ Period ______ # _____ History of the Cell Theory (pages 69-71) (Screening Assessment Part 1- 21 points) 1. The first person to discover the cell was ___________ ___________. 2. He was born on ___________________ and was from _____________, __________________________. 3. His most famous microscopic observation was made by using thin slices of _____________ (dead plant cells). 4. He called them cells because the box-like cells he observed reminded him of the cells of a ______________. 5. The cell theory was made in _________. The three men who contributed to it were _________________, _______________, and _______________. 6. The cell theory (right along with biogeneis) was one to replace the theory that says that life can originate from nonliving objects, which we know as _______________ _____________ (wrong). 7. The nine modern tenets to the cell theory are: *a. All known living things are made of ___________. *b. The cell is the basic _____________ and ______________ unit of a living thing. *c. All cells come from ___________________ cells by cell division. d. Cells contain _____________________ information which is passed from cell to cell during cell division. e. All cells are basically the _______________ in chemical composition. f. All ____________ ______________ of life occurs within cells. g. Some organisms are made up of only one cell and are known as ___________. h. Other organisms are composed of a number of cells and are ______________. i. The activity of an organism depends on the ____________ activity of individual cells. 8. Name the three exceptions to the cell theory. 1. Are viruses alive? 2. Mitochnodria and chlorplasts have their own genetic information and can reproduce independently from the rest of the cell. 3. If all cells come from pre-existing cells, where did the first cells come from? Name _________________ Date ____________ Period ______ # _____ Comparing Prokaryotic Cells, Eukaryotic Cells, and Viruses (pages 74- 75 and 483 – 488) (Screening Assessment Part 2- 21 points) 1. Draw all structures found in a prokaryotic cell, an eukaryotic cell, and a virus in the circles below. On the prokaryotic cell, label the cell membrane and the DNA that is located in the nucleoid. On the eukaryotic cell, label the cell membrane and the nucleus. On the virus, label the capsid and the tail. Prokaryotic 2. Complete the following table. Characteristics Prokaryotes Cell Organization (unicellular, multicellular, or not cellular) 2 examples of organisms Where is the genetic information stored? Organelles Found/Internal Structure (simple vs. complex Virus Eukaryotic Eukaryotes Viruses Name _________________ Date ____________ Period ______ # _____ Comparing Plant and Animal Cells (page 90) (Screening Assessment Part 3 a - 36 points) Directions: Complete the chart below and answer the questions that follow. Cell Part or Organelle Cell Membrane Is It Found In A Plant Cell? Is It Found In A Animal Cell? Cell Wall Chloroplast Chromatin Cytoplasm/Cytosol Endoplasmic Reticulum Golgi Bodies Lysosomes/Peroxisomes Mitochondrion Nucleus Nuclear Membrane Nucleolus Ribosome Vacuole (small or large) Centrioles (2) Questions: 1. What cell parts do animal cells have that plant cells do not have? 2. What cell parts do plant cells have that animal cells do not have? 3. Why do plant cells have cell walls and animal cells do not? 4. Why do think plant cells have bigger vacuoles than animal cells? 5. How does a cell’s structure relate to its function? See pg. 72 in your textbook. You may use a red blood cell, a nerve cell, or a skin cell as an example to illustrate this. Name _________________ Date ____________ Period ______ # _____ Comparing Plant and Animal Cells VENN Diagram (Screening Assessment Part 3 b - 12 points) Directions: Fill in the VENN Diagram to compare PLANT CELLS to ANIMAL CELLS. Use the words in the word box. cell membrane cell wall chloroplast mitochondria nucleus ribosome centrioles rough ER smooth ER PLANT CELL ANIMAL CELL Both cytoplasm large central vacuole or small vacuoles Golgi apparatus Name _________________ Date ____________ Period ______ # _____ Cell City Analogy (18 points) In a far away city called Grant City, the main export and production product is the steel widget. Everyone in the town has something to do with steel widget making and the entire town is designed to build and export widgets. The town hall has the instructions for widget making, widgets come in all shapes and sizes and any citizen of Grant can get the instructions and begin making their own widgets. Widgets are generally produced in small shops around the city, these small shops can be built by the carpenter's union (whose headquarters are in town hall). After the widget is constructed, they are placed on special carts which can deliver the widget anywhere in the city. In order for a widget to be exported, the carts take the widget to the postal office, where the widgets are packaged and labeled for export. Sometimes widgets don't turn out right, and the "rejects" are sent to the scrap yard where they are broken down for parts or destroyed altogether. The town powers the widget shops and carts from a hydraulic dam that is in the city. The entire city is enclosed by a large wooden fence, only the postal trucks (and citizens with proper passports) are allowed outside the city. Match the parts of the city (underlined) with the parts of the cell. 1. _____________________________________________ Mitochondria 2. Ribosomes _____________________________________________ 3. Nucleus _____________________________________________ 4. Endoplasmic Reticulum _____________________________________________ 5. Golgi Apparatus _____________________________________________ 6. Protein _____________________________________________ 7. Cell Membrane _____________________________________________ 8. Lysosomes ____________________________________________________________ 9. Nucleolus _____________________________________________ Name _________________ Date ____________ Period ______ # _____ Create Your Own Analogy (30 points) Create your own analogy of the cell using a different model. Some ideas might be a school, a house, a car, a manufacturing facility (factory), a city, a sport’s team or anything you can imagine. You may do one of the following options to complete this assignment: 1. You can draw the analogy and label the corresponding parts in your analogy and where they correspond to the cell. 2. You can write a story describing your analogy. You must underline all of the parts in your analogy that represent a cell structure/organelle. You must also make a list of the structures and organelles with their corresponding analogy structure. See the Cell As a City analogy on the previous page for an example of this technique. No matter which method you choose you must include the following organelles in your analogy: cell membrane, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, ribosomes, protein (product made), Golgi apparatus, mitochondria, nucleus, nucleolus, and lysosomes. This is worth 30 points of the total project and will tell me if you have really learned what you need to know about cells. Please do not forget to do this critical step! An example of a Cell As a Factory (Option 1) would be the following: Jobs in the Factory Cell Organelle as it relates to the factory Shipping/Receiving Department & Doors of Factory The doors of the factory let certain people through while others are not allowed to pass in or out of the factory. This allows the factory to have structural support and protects it from others. This is just like the cell membrane which lets certain materials pass into or out of the cell because it is semi-permeable. The shipping and receiving department of the factory which is also part of the doors of the factory must supply the factory with raw materials coming into the factory and ship the finish product out to its suppliers. The cell membrane must also do this for necessary nutrients to pass into the cell and allow waste products and proteins to be exported out of the cell. Name _________________ Date ____________ Period ______ # _____ Factory Floor The factory floor is where all of the materials are moved around and where the other parts of the factory are located on the inside just like the cytoplasm in a cell is where organic compounds react and are moved around and the place where the organelles are found. Central Executive Office/Chief Executive Officer (CEO) The central executive office runs the factory and controls all of its activity. The cell’s nucleus has the instructions for all cell activity and determines what proteins are to be made and stores all the plans for any proteins that the cell currently makes or has made in the past. The central executive officer has the blueprints for making the product and tells the workers which products to build and when to make them. This is like the nucleolus which makes ribosomes with the instructions from the nucleus. These ribosomes are later sent to the cytoplasm (factory floor) and the ER (assembly line) where they will be further processed. Assembly line (where workers do their work) The assembly line is the place where the unfinished product is assembled. The ER is like the assembly line because it uses the instructions from the nucleus to assemble proteins (RER) or lipids (SER) which will later be transported to the Golgi apparatus. Workers in the assembly line Finished product Finishing/Packaging Department The assembly line workers read plans to assemble the parts of what will be the finished product. This is analogous to the ribosome which is made in the nucleolus and functions to make protein, the cell’s final product. The finished product (let’s say copy paper) is the product being made by the factory. This is analogous to specific types of protein that are made from the instructions located in the nucleus of the cell. The finishing/packaging department is responsible for inspecting the product for flaws, cleaning the product, wrapping it so that it is not broken during shipping, and transporting the finished product out of the factory. The Golgi apparatus is like the finishing/packaging department in that it takes the assembled protein from the ER, further processes it, and forms a vesicle for transportation of the protein out of the cell (exocytosis). Maintenance Crew The maintenance crew helps to keep everything orderly, to get rid of the trash, and to repair or dispose of old machinery. The maintenance crew also functions as a second line of defense if someone were to pass through the front door by chasing them out of the factory. This is like the lysosomes in that they break down (digest) old, worn out organelles and serve as a line of defense for the cell by destroying viruses or bacteria that may enter the cell. Power Plant The power plant provides electricity (energy) that is made from generators which burn fuel and produce heat, which is used to make steam and then converted into electricity. This supply of electricity allows the factory’s machines to run just like the mitochondria provides energy in the form of ATP to the cell so it’s organelles can do work. Name _________________ Date ____________ Period ______ # _____ The Edible Cell/Cell Model Project Guidelines (50 points) Purpose: To construct a 3-d model of a typical plant or animal cell using materials that are edible. Rules for Constructing the Cell: 1. The models must include the following organelles: a. cell membrane b. nuclear membrane c. nucleus d. nucleolus e. mitochondria f. ribosomes g. rough endoplasmic reticulum h. smooth endoplasmic reticulum i. cytoplasm (cytosol) j. lysosomes/peroxisomes k. Golgi apparatus (Golgi bodies) 2. If your group is constructing a plant cell, the model must also include a cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large central vacuole. 3. If your group is constructing an animal cell, the model must include centrioles and some type of motile structure (flagellum or cilia). 4. At least half (50%)of the cell organelles/structures must be edible. 5. The cell model must be constructed on or in a sturdy container to prevent damage, leakage, and or spillage during the activity. Things to Remember *The container and all other food items must be brought into room 113 before school and placed in a bag that is labeled with your name and class period. **The cell model will be scored using the scoring rubric designed by Mrs. Mohan. ***You and your group will be asked questions concerning the structures/organelles and what they function to do in the cell. Name _________________ Date ____________ Period ______ # _____ Cell Group # _______ Period _______ Check the cell type constructed and write down the food item used for each organelle listed below. Plant Cell Animal Cell Cell Membrane Cell Membrane Nucleus Nucleus Nuclear Membrane Nucleolus Nuclear Membrane Nucleolus ` Mitochondria Mitochondria Gogi bodies Golgi bodies Smooth ER Smooth ER Rough ER Rough ER Ribosomes Ribosomes Cytoplasm (Cytosol) Chloroplasts Cytoplasm (Cytosol) Centrioles Large Central Vacuole Cell Wall Lysosome (small vacuole) Flagellum (Flagella) Name _________________ Date ____________ Period ______ # _____ Edible Cell Lab Scoring Rubric _______ The group has a model/drawing of the cell prior to constructing the edible cell. (5 points) _______ The cell type is identified on the lab report and recognizable by looking at the constructed cell. (5 points) _______ The cell is an accurate representation of an animal or plant cell because it has the proper structures and organelles for that cell type. The group is able to correctly identify the structures and organelles present in the cell and also give the function(s) of each by way of answering questions asked by Mrs. Mohan. (20 points) _______ The lab paper is correctly written up. (5 points) _______ The group uses actual food/substances that look like the cell’s structures and organelles. (10 points) _______ The cell is creative in that the substances chosen are different from other groups. (5 points) Group Grade ____________ Cell Group # _______ Period _______