Place Value UDL Lesson Plan
advertisement

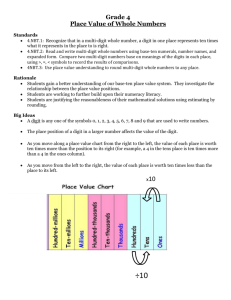
Rowan IMPACT Project District ____Pennsauken Gail Stallings Unit Overview Template Content Area: Math Unit Title: Numeration Target Course/Grade Level: 5, Inclusion Unit Summary This unit, Numeration, represents one of two Number and Operations in Base Ten standards in the 2009 Common Core and one of two (Numeration) units in envision MATH, Grade 5. Numeration focuses on base ten place value concepts in whole numbers and decimals, and provides the foundation for Unit 9 (Fractions and Decimals). This class of inclusion students has a wide range of abilities (and needs) in this topic. In this unit, students will review and expand on previous knowledge and experience (with whole number place value concepts), learning to work with larger numbers (billions.) They will find examples of very large numbers in the real world and situations that create the need to compare numbers. They will explore place value concepts and relationships by problem solving and working with manipulatives, place value charts and templates, calculators, digital representations, and print, working individually, in pairs and groups. Students will extend their knowledge of how to read, write, compare, order and round whole numbers to numerals through the billions. They will recognize that in a multi-digit number, a digit in one place represents 10 times as much as it represents in the place to its right and 1/10 of what it represents in the place to its left (to 1,000,000,000). Following their work with whole numbers, students will review and expand on previous knowledge and experience (with decimal place value concepts), learning to work with decimals to the thousandths. They will read, write, compare and order decimals. The final topic will call on students to observe and explain patterns in whole numbers and decimals. Primary interdisciplinary connections: Social Studies, Science, Language Arts 21st century themes: Communication and Collaboration, Life and Career Skills, Financial, Economic, Business, and Entrepreneurial Literacy Unit Rationale: Understanding numeration and how our number system works is the foundation for all math that follows, including everyday math (life skills.) Rowan IMPACT Project Learning Targets Standards: 4.NBT 5.NBT NUMBER AND OPERATIONS IN BASE TEN NUMBER AND OPERATIONS IN BASE TEN Content Statements: Generalize place value understanding for multi-digit numbers. (4) Understand the Place Value System (5) CPI # 4.NBT.1 Cumulative Progress Indicator (CPI): The student will: Recognize that in a multi-digit whole number, a digit in one place represents ten times what it represents in the place to its right. For example, recognize that 700/70 = 10 by applying concepts of place value and division (to 1,000,000). 5.NBT.1 Recognize that in a multi-digit number, a digit in one place represents 10 times as much as it represents in the place to its right and 1/10 of what it represents in the place to its left (to 1,000,000,000) 4.NBT.2 Read and write multi-digit whole numbers using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form (through billions). 4.NBT.3 5.NBT.2 Use Place Value understanding to round multi-digit whole numbers to any place. Explain patterns in the number of zeros of the product when multiplying a number by powers of 10. Compare and Order (whole) Numbers 1-2 5.NBT.3.a. Read and write decimals to thousandths using base-ten numerals, number names, and expanded form, eg., 347.392= 3 x 100 + 4 x 10 +7 x 1 + 3 x (1/10) + 9 x (1/100) + 2 x (1/1,000). 5.NBT.3.b. Compare two decimals to the thousandths based on meanings of the digits in each place, using >, =, and < symbols to record the results of comparisons. 5.NBY.4 Use place value understanding to round decimals to any place. 5.NBT.2 Explain patterns in the placement of the decimal point when the decimal is multiplied or divided by powers of 10. Unit Essential Questions How can we read, write and compare large numbers (through billions)? How can we read, write and compare decimals (through hundredths)? What is the relationship among the various place values? Unit Enduring Understandings Our number system is based on groups of ten. Whenever we get 10 in one place value, we move to the next greater place value. (A digit in in one place represents 10 times as much as it represents in the place to its right and 1/10 of what it represents in the place to its left.) Numbers can be used to tell how many. Place value can be used to compare and order whole numbers and decimals. Unit Learning Targets Students will ... Demonstrate and understanding of place value concepts (including value, order, place, magnitude and relationships to other numbers/digits.) Rowan IMPACT Project Read and write whole numbers to the billions, and decimals to the thousandths. Compare, order and round whole numbers and decimals. Explain the relationship between a digit in one place and the digit to its right or left. Evidence of Learning UNIT Summative Assessment (last day) (after 6-9 days) Topic 1 Test (Page 18,19) This is a diagnostic, multiple-choice test to assess students’ understanding of geometric concepts and skills presented in Topic 1. An Item Analysis for Diagnosis and Intervention is provided in the Teacher Edition. The Intervention System materials are provided in a separate box. Administer test questions in Senteo format (see below), five to a page. Alternative tests (for differentiation) – Free Response Test, Multiple Choice Test Equipment needed (for assessment): Computer w/SmartBoard/ Smart Response software and peripherals; Senteo Question Set (Unit Test questions); print copies of test questions (provide larger print,(or magnifying glasses); and space for those students who need it; provide sticky notes or small squares of paper for blocking); manipulatives; (Base ten blocks, play money, number tile sets, overlapping place value number sets, E-tools large digit cards (8x10), place-value charts, place value chart templates, graph paper cut into blocks of three communicators, markers, erasers,) Teacher Resources: enVisionMATH, Grade 5, TE, Topic 1 http://www.primaryresources.co.uk/maths/mathsB4.htm#1 http://www.ronblond.com/MathGlossary/ http://teacher.scholastic.com/maven/index.htm http://olc.spsd.sk.ca/de/math1-3/baseten1.htmlhttp://www.linkslearning.org/Kids/1_Math/2_Illustrated_Lessons/3_Place_Value/index.html http://www.watchknow.org/Category.aspx?CategoryID=2214 http://teachingtoday.glencoe.com/videos/view/place-value http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y-rLi2HKwkI&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XFX-YFU-Ofk&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2BFu6fib9sA&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q9C5dwv5oFw&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q9C5dwv5oFw&feature=related “Bully” as numbers 5 – 9 for rounding Illuminations.com Envisions Number Devil (book, CD) Unit Formative Assessments Independent Work Create own place-value chart Quick Checks Games and Activities Observation Projects Homework Group work Bell work Quizzes Exit cards Rowan IMPACT Project Lesson Plans Lesson Timeframe Lesson 1 1-2 days (80 min/day) Place Value Lesson 2 1 day Comparing and Ordering Whole Numbers Lesson 3 1-2 days Decimal Place Value Lesson 4 1 day Comparing and Ordering Decimals Lesson 5 1 days Look for a Pattern Teacher Notes: Accommodations/adaptations: Writing large numbers: build up from known place values; always write from ones, one period at a time; Use BTB/money to demonstrate magnitude, patterns, values and rounding Show students overall structure and patterns; make sure students are able to create their own chart with their own symbols when they need it Use lined or grid paper When rounding, write new digits above original digits (use manipulatives such as money) Do all the steps Be able to copy rounding rule (or big enough to “bully” rounded digit?) Block all but two focus numbers; (think in tens) Copy digits in greater place values, put in zeros, decide about remaining digit Standard to expanded – deconstruct in layers below Expanded to standard – stack and construct as column problem Written to standard – construct over respective words Standard to written – break down ( list in periods) – write numerals next to numbers Value – relate to expanded form Use standard/expanded foldables/overlapping numbers Bank checks to reinforce standard/word form Bank questions to reinforce other place-value concepts Emphasize word problems, practical applications Videos (music) Blank place value charts Decimals show fraction/decimal/name/abbreviation Demo concept with decimal squares Show rainbow pattern Have student write and read fraction for decimal Place value Puzzler Virtual manipulatives Place value game Experiment with adding and subtracting large numbers to see how to get greatest and smallest sums and differences Dictate period by period, allowing students time to record one period before moving on to the next. Use number tiles, or graph squares cut in sets of three.) Rowan IMPACT Project Curriculum Development Resources enVisionMATH, Grade 5, TE, Topic 1 Click the links below to access additional resources used to design this unit: http://www.primaryresources.co.uk/maths/mathsB4.htm#1 http://www.ronblond.com/MathGlossary/ http://teacher.scholastic.com/maven/index.htm http://olc.spsd.sk.ca/de/math1-3/baseten1.htmlhttp://www.linkslearning.org/Kids/1_Math/2_Illustrated_Lessons/3_Place_Value/index.html http://www.watchknow.org/Category.aspx?CategoryID=2214 http://teachingtoday.glencoe.com/videos/view/place-value http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y-rLi2HKwkI&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XFX-YFU-Ofk&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2BFu6fib9sA&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q9C5dwv5oFw&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q9C5dwv5oFw&feature=related “Bully” as numbers 5 – 9 for rounding, Illuminations.com Number Devil (book, CD), E-tools Unit Authors: Gail Stallings Date: 12/12/2010 Rowan IMPACT Project Lesson Plan Content Area: Math Grade: 5 Lesson Title: Numeration: Place Value Timeframe: 1-2 days (80 min/day) Lesson Components 21st Century Themes x Global Awareness: Other monetary/counting systems x Civic Literacy Financial, Economic, Business, and Entrepreneurial Literacy: accounting, US monetary system Health Literacy 21st Century Skills x Creativity and Innovation Create personal place value charts/tools x Media Literacy Recognizing and responding to math in various media (life) x Critical Thinking and Problem Solving Looking for patterns, organizing information x Communication & Collaboration: Group work x Information Literacy Reading and interpreting symbols ICT Literacy x Life and Career Skills: Money skills, check writing, organizing Interdisciplinary Connections: Social Studies, Science, Language Arts Integration of Technology: Interactive SmartBoard, DocuCam, software, SmartResponse System Equipment & materials needed: laptop, internet access, Smartboard, SmartResponse System, Docu-Cam, E-tools Interactive Recording Sheet 1, worksheets Base ten blocks, play money, number tile sets, overlapping place value number sets, 8x10 digit cards place-value charts, place value chart templates, graph paper cut into blocks of three communicators, markers, erasers, Goals/Objectives/CPIs Students will: Read and write whole numbers to the billions. Recognize that in a multi-digit number, a digit in one place represents 10 times as much as it represents in the place to its right and 1/10 of what it represents in the place to its left. Learning Activities/Instructional Strategies 1. Engagement: Rowan IMPACT Project 2. 3. 4. 5. Set the Purpose. You know how to read and write numbers to one million. Toda you will learn how to read and write numbers greater than one million. Connect: Can you describe a situation in which you have seen or heard a very large number? Exploration – Smartboard Lesson Pose the Problem: Review place value through millions. Give students a copy of Interactive Learning Recording Sheet 1. Also, write/show a place-value chart on the Smartboard*. (Tell) How many millions does it take to make one billion? (1,000) Have students work together to solve. Tell students to compare ones to one thousand and one thousand and one million to help. Explanation: Instruct in Small Steps Explain/demonstrate: A period is a group of three digits, separated by commas, starting on the right. Write 1,246,065,702 on the Smartboard. Let’s fill the place-value chart with the digits from the number I wrote on the chalkboard. Have students tell you where to (locate) write each digit using commas to separate each set of 3 digits in a period, or move the numbers on the Smartboard, themselves. Emphasize: The place of a digit in a number tells you its value. Now let’s read the number together. [one billion, two hundred forty-six million, sixty-five thousand, seven hundred two.] Make sure students can create their own place-value chart. Small-Group Interaction: On the Recording Sheet, write a 10-digit number and a 12-digit number. Discuss with your partner(s) how to read each number, use the place-value chart to help you. Write each number in word form below the chart. Have 2 or 3 groups write their numbers on the Smartboard (or show their work on communicators/DocuCam) and explain how to read them. Elaboration: Extend Rearrange the digits in 4,605,800,000 to make the greatest number possible. (8,654,000,000); (For a “brain break”, have 10 students each take a 8x10 number and stand in a line; then tell them to arrange themselves to create the largest/smallest number possible.) Visual Learning Bridge: In this lesson you will learn to read and write the standard, expanded, and word forms of whole numbers through billions. Guided Practice: Problems #1-5 (Remind students to use their place-value charts.) Evaluation: Independent Practice: #6-18 even numbers; Problem Solving - Pick 4 Create your own place value chart to help you when you need it. Create your own problem like Exercise 22. Exchange problems with your partner and check answers. Formative Assessment Tasks Recording Sheet 1 Activity Create personal place-value chart Create a problem like #22. Quick Check Group work Independent work Rowan IMPACT Project Universal Design for Learning Options for Unit Multiple Means of Representation 1. Perception : Readability, Readability™ is a tool that removes the visual clutter on web pages making reading on the Web easier. 2. Language and Symbols : Shahi This site is a visual dictionary that provides definitions as well as (multiple) images from the Internet 3. Comprehension TeacherVision: Activating Background Knowledge, TeacherVision is a comprehensive, subscription-based resource website for teachers. This article explains Activating Background Knowledge and links it to specific resources and materials in the website. Multiple Means of Action and Expression 1. Physical activity: No Keys Virtual Keyboard, No-Keys is a computer software program that displays an on-screen keyboard. Students can "type" on the keyboard using a mouse, trackball, or even a scan option. The program can be used with touch screen keyboards. 2. Expressive skills and fluency: Glogster, Offers an alternate way for students (especially girls) to express themselves and demonstrate their knowledge and skills through words, photos, videos, graphics, and music. 3. Executive functions: Goal Setting w/s (worksheetplace.com) This site offers free worksheets, templates and organizers on a wide variety of subjects and topics including this one--- for goal setting. Multiple Means of Engagement 1. Recruiting interest: Tic-Tac-Toe (vimeo.com) this is a subscriber-based site which offers videos on a variety of topics. This activity allows for differences in learning styles and ability levels. “. (Scavenger Hunt), 2. Sustaining effort and persistence: Cooperative Arithmetic (edutopia.org) This website, ( A project of the George Lucas Educational Foundation, provides a wide range of resources fro teachers in a variety of formats. The following articles from spdbayarea.org, are especially helpful for teachers of students with LD: Sensory Processing Disorder: Tips for Teachers, Sensory Integration Dysfunction, Classroom Distractions: How can w avoid them? 3. Self-regulation: Coping Skills for Kids: Brain Works Project This site provides information and activities (for students, parents and educators) designed to strengthen emotional resilience and self-acceptance in teenagers to develop and promote emotional health. Knowing How You Learn (edutopia.org), video- “students learn how their brains work and how to accommodate their learning styles” and that there is no one "right" way to learn Teacher Resources: http://www.primaryresources.co.uk/maths/mathsB4.htm#1 http://www.ronblond.com/MathGlossary/ http://teacher.scholastic.com/maven/index.htm http://olc.spsd.sk.ca/de/math1-3/baseten1.htmlhttp://www.linkslearning.org/Kids/1_Math/2_Illustrated_Lessons/3_Place_Value/index.html http://www.watchknow.org/Category.aspx?CategoryID=2214 http://teachingtoday.glencoe.com/videos/view/place-value http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=y-rLi2HKwkI&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=XFX-YFU-Ofk&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=2BFu6fib9sA&feature=related http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q9C5dwv5oFw&feature=related Rowan IMPACT Project http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q9C5dwv5oFw&feature=related “Bully” as numbers 5 – 9 for rounding Illuminations Envisions Number Devil (book, CD) Universal Design for Learning Options Lesson Multiple Means of Representation 1. Perception: Math Type MathType is a software program (for purchase) for creating mathematical notation for word processing, web pages, desktop publishing, etc.. 2. Language and Symbols: Math Glossary (ronblond.com), is comprehensive visual glossary organized by grade, topic and an alphabetical index. It offers definitions, diagrams, pictures and real world examples. 3. Comprehension: CueCard (download.cnet.com) (CueCard is a program that allows you to generated your own flash cards (including printing, pictures and sounds) and then it automatically focuses on the cards you need more practice with. Multiple Means of Action and Expression 1. Physical activity: No Keys Virtual Keyboard, No-Keys is a computer software program that displays an on-screen keyboard. Students can "type" on the keyboard using a mouse, trackball, or even a scan option. The program can be used with touch screen keyboards 2. Expressive skills and fluency: ToonDoo This is a cartoon creation website. Cartooning offers another way for students to show what they know. 3. Executive functions: Goal Setting w/s (worksheetplace.com) This site offers free worksheets, templates and organizers on a wide variety of subjects and topics including this one--- for goal setting. Multiple Means of Engagement 1. Recruiting interest: Tic-Tac-Toe, (vimeo.com) this is a subscriber-based site which offers videos on a variety of topics. This activity allows for differences in learning styles and ability levels. “ . (Scavenger Hunt), 2. Sustaining effort and persistence: Cooperative Arithmetic, (edutopia.org) This website, ( A project of the George Lucas Educational Foundation, provides a wide range of resources fro teachers in a variety of formats. The following articles from spdbayarea.org, are especially helpful for teachers of students with LD: Sensory Processing Disorder: Tips for Teachers, Sensory Integration Dysfunction, Classroom Distractions: How can w avoid them? 3. Self-regulation: , Knowing How You Learn Knowing How You Learn (edutopia.org), video“students learn how their brains work and how to accommodate their learning styles” and that there is no one "right" way to learn Rowan IMPACT Project LESSON REFLECTION Reflect on the lesson you have developed and rate the degree to which lessons Strongly, Moderately or Weakly meet the criteria below. Lesson Activities: Strongly Moderately Weakly Are challenging and require higher order thinking and problem solving skills x Allow for student choice x Provide scaffolding for acquiring targeted knowledge/skills x Integrate global perspectives x Integrate 21st century skills x Provide opportunities for interdisciplinary connection and transfer of knowledge and skills x Foster student use of technology as a tool to develop critical thinking, creativity and innovation skills x Are varied to address different student learning styles and preferences x Are differentiated based on student needs x Are student-centered with teacher acting as a facilitator and x co-learner during the teaching and learning process Provide means for students to demonstrate knowledge and x skills and progress in meeting learning goals and objectives Provide opportunities for student reflection and selfassessment x Provide data to inform and adjust instruction to better meet the varying needs of learners x