US History and Government Overview
advertisement

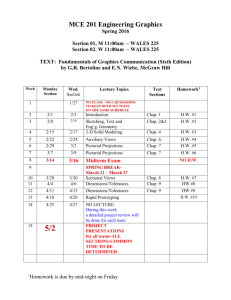
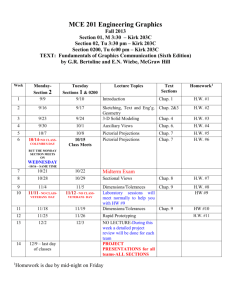
United States History and Government Grade: 11th Grade Credit: One Pre-Requisite: Successful Completion of Global II Course Description A chronological survey of American History with efforts to include (equitably) “voices” and perspectives of people within U.S. society that have been traditionally ignored, downplayed or omitted from the curriculum, i.e., women, Native, African, Hispanic and Asian Americans. Final Assessment New York State Regents Exam in United States History Format: 50 Multiple Choice Questions Thematic Essay Document Based Essay Course Textbook Pathways to Present 2007 Prentice Hall ISBN: Textbook Website http://www.phschool.com/ United States History- Pacing Chart Month Unit September 1. Three Worlds Meet (beginnings- 1600) 2. Colonial America October Week 2 (1492-1753) 2 3. Revolution and Constitution (1753- 2 Pathways to Present 2007 Chap 1The Atlantic World Chap 2 European Colonization Chap 3 Growth of American Colonies Chap 4 Road to Independence Chap 5 Constitution 1800) 4. An Emerging New Nation (17831855) November 2 5. Civil War and Reconstruction (1846-1877) (1850-1920) December Chap 6 Origins of American Politics Chap 7 Life in New Nation Chap 8 The Growth of National Economy Chap 9 Religion and Reform 3 Chap 10 The Coming of the Civil War Chap 11 The Civil War Chap 12 Reconstruction 5 Chap 13 Expansion of American Industry Chap 14 Looking to the West Chap 15 Politics Immigration +Urban 6. Expansion: Rewards and Costs Brief Review in US History Chap Chap Life 16 Life at the turn of 20th Century 18 Progressive Era African American History Chap 1 Africa Chap 2 Middle Passage Unit 1Unit 2Sec 1 Unit 2Sec 2 Unit 2Sec 2 Unit 3Sec 1 Unit 3Sec 2 Unit 3Sec 3 Unit 4Sec 1 Chap 3 Black People in Colonial North America Chap 4 African Americans and the Struggle for Independence Chap 5 A. A. in the New Nation Chap 6 Life in the Cotton Kingdom Chap 7 Free Black People in Chap Chap Chap Chap Chap Chap Chap Chap Chap Antebellum America 8 Opposition to Slavery 9 Let Your Motto Be Resistance 10 The United States Disunites over Slavery 11 A. A. and the Civil War 12 The Promise Reconstruction 13 The Failure of Reconstruction 14 A.A. in the South in the Late 19th Century 15 Black Southerners Challenge White Supremacy 16 African Americans in the Early 20th Century January 7. Becoming A World Power (1890- 2 Chap 17 Becoming a World Power Chap 19 World War I Era 1920) Review Unit 4Sec 2 1 MIDTERM February 8. Boom Times to Hard Times (19201941) 6 March 9. Hot and Cold War (1931-1960) 4 Chap 20 Postwar Social Change Chap 21 Politics and Prosperity Chap 22 Crash and Depression Chap 23 The New Deal Chap 24 and 25 World War II Chap 26 Cold War Chap 27 Postwar Years at Home April 10. A Period of Turmoil and Change (1950-1975) 4 11. Continuity and Change (1969-present) 1 May June 12. REVIEW Chap 28 Civil Rights Movement Chap 29 Kennedy and Johnson Years Chap 30 The Era of Activism Chap 31 Vietnam War Chap 32 Nixon, Ford and Carter Chap 33 The Conservative Revolution Chap 34 Entering the New Era Unit 5Sec 1 Unit 5Sec 2 Unit 6Sec 1 + 2 Unit 7Sec 1 Unit 7Sec 2 Unit 7Sec 3 Unit 7Sec 4 Unit 7Sec 5 Chap 17 A.A. and the 1920’s Chap 18 Black Protest, The Great Depression and the New Deal Chap 19 Culture and Society in the 1930’s and 1940’s Chap 20 The World War II Era and the Seeds of the Revolution Chap 21 Freedom Movement Chap 22 The Struggle Continues Chap 23 Black Politics Chap 24 A.A. in the New Millennium UNIT 1 - Three Worlds Meet (beginnings- 1600) (Recommended time – 2 weeks) RESOURCESPathways to Present 2007 Chap 1- The Atlantic World Chap 2 - European Colonization (1492- 1754) African-American History Prentice Hall 2006 Chap 1- Africa Chap 2- Middle Passage TOPICSA. Africa 1. Birthplace of Humanity (AAH7) 2. Ancient Civilizations (AAH9-13) a. Egypt, Kush, Meroe, Axum 3. West African Civilizations (AAH14-23) (PP 19-21) a. Ghana, Mali, Songhai, Senegambia, Benin 4. West African Society and Culture (AAH24-28) (PP 17-18) B. North America 1. Settlement of Americas (PP 4-5) 2. North American Life (PP 5-10) C. Europe 1. Greeks and Romans 2. Early Middle Ages (PP 10-11) 3. Late Middle Ages (PP 11-13) 4. The Renaissance (PP 13-16) D. Three Worlds Collide 1. European Exploration and Colonization a. Africa (AAH37-44) (PP 17) b. North and South America (PP 22-28) People, Events, Documents and Vocabulary For the Regents North America Iroquois Confederacy Europe Greece-Democracy Roman Republic Magna Carta (1215) Petition of Right (1628) English Bill of Rights (1689) John Locke Baron De Montesquieu Jean-Jacques Rousseau Voltaire UNIT 2 – Colonial America (1492-1754) (Recommended time – 2 week) RESOURCESPathways to Present 2007 Chap 2 - European Colonization (1492- 1754) Chap 3 – Growth of American Colonies (1689-1754) Brief Review in United States History and Government Unit 1- Introduction- Geography and the Development of the US African-American History Prentice Hall 2006 Chap 2- Middle Passage Chap 3- Black People in Colonial North America (1526-1763) ExamGen Chapter and Topics Chap 1 US Geography and Demographics (59 questions) TOPICS- A. The Physical Setting B. European Colonization of the Americas(1492-1752) 1. Spanish Explorers (PP 36-41) 2. Jamestown (PP 42-48) 3. New England Colonies (PP 49-57) 4. Middle and Southern Colonies (PP 59-63) C. Middle Passage 1. Slave Trade (AAH37-44) 2. Capture of Africans (AAH45-47) 3. Middle Passage (AAH47-57) 4. Landing and Sale in West Indies (AAH59-62) 5. Africans Arrive in Chesapeake (AAH75-79) D. Growth of Colonies (1689-1754) 1. An Empire and Its Colonies (PP 70-75) 2. Life in Colonial America (PP 77-82) 3. African Americans in the Colonies (PP 83-88) a. Africans Arrive in the Chesapeake (AAH 75-80) b. Plantation Slavery 1700-1750 (AAH 81-87) c. Origins of African-American Culture (AAH 88-94) d. Slavery in Colonial America (AAH 95-102) 4. Emerging Tensions (PP 89-93) People, Events, Documents and Vocabulary For the Regents The Physical Setting Great Plains Central Plains Mississippi River Appalachian Mountains Rocky Mountains Great Lakes European Colonization of the Americas (1492-1752) New England Middle Colonies Southern Colonies House of Burgesses Indentured servant Mayflower Compact Middle Passage Triangular Trade Growth of Colonies (1689-1754) John Peter Zenger (1735) UNIT 3 – Revolution and Constitution (1753-1800) (Recommended time – 2 weeks) RESOURCESPathways to Present 2007 Chap 4 Road to Independence (1753-1783) Chap 5 Constitution (1776-1800) Brief Review in United States History and Government Unit 2 Constitutional Foundations - Section 1- The Constitution African-American History Prentice Hall 2006 Chap 4- African Americans and the Struggle for Independence (1763-1783) ExamGen Chapter and Topics Chap 2: United States Constitution (616 questions) TOPICS- A. The Road to Independence (1753-1783) 1. The French and Indian War (PP104-108) 2. Issues Behind the Revolution (PP 109-116) 3. Ideas Behind the Revolution (PP 118-122) a. The Declaration of Independence and AA (AAH 115-118) b. Black Enlightenment (AAH 119-122) 4. Fighting for Independence (PP 127-132) a. African Americans in the War for Independence (AAH 123-126) 5. Winning Independence (PP 133-137) a. Revolution and Emancipation (AAH 127-132) B. The Constitution of the United States (1776-1800) 1. Government by the States (PP 144-149) 2. The Constitutional Convention (PP 150-157) 3. Ratifying the Constitution (PP 158-163) People, Events, Documents and Vocabulary For the Regents The Road to Independence (1753-1776) Salutary Neglect Albany Plan Proclamation of 1763 mercantilism Stamp Act (1765) First Continental Congress (1774) Second Continental Congress (1775) Common Sense (1776) Declaration of Independence (1776) The Constitution of the United States (1776-1800) Articles of Confederation (17811789) Treaty of Paris (1783) Land Ordinance (1785) Northwest Ordinance Constitutional Convention (1787) Great Compromise 3/5 Compromise Federalists Anti-Federalists Popular sovereignty Limited government Separation of powers Checks and Balances Elastic clause Amendment Process Federalism Delegated powers Implied powers Denied powers Concurrent powers Reserved powers Judicial Review Bill of Rights Federal Government State Government Electoral College Impeachment UNIT 4 – Emerging New Nation (1783-1855) (Recommended time – 2 weeks) RESOURCESPathways to Present 2007 Chap 6 Origins of American Politics (1789-1820) Chap 7 Life in New Nation (1783-1850) Chap 8 The Growth of National Economy (1790-1850) Chap 9 Religion and Reform (1815-1855) Brief Review in United States History and Government Unit 2 Constitutional Foundations Sec. 2- The Constitution Tested African-American History Prentice Hall 2006 Chap 5- African Americans in the New Nation (1783-1820) Chap 6- Life in the Cotton Kingdom Chap 7- Free Black People in Antebellum America (1820-1861) Chap 8- Opposition to Slavery (1800-1833) Chap 9- Let Your Motto Be Resistance (1833-1850) TOPICS A. The Origins of American Politics (1789-1820) 1. New Government (PP 165-169) 2. Liberty versus Order in 1790’s (PP 200-206) a. Forces for Freedom (AAH 141-148) b. Forces for Slavery (AAH 149-153) 3. The Election of 1800 (PP 207-212) 4. The Jefferson Administration (PP 213-218) 5. Native American Resistance (PP 220-223) 6. War of 1812 (PP 224-229) B. An Emerging Nation (1783-1855) 1. Culture, Social, and Religious Life (PP 240-248) a. Emergence of Free Black Communities (AAH 154-159) b. Black Leaders and Choices (AAH 160-164) 2. Trails West (PP 249-256) 3. Great Plain and the Southwest (PP 258-263) C. Growth of a National Economy (1790-1850) 1. Inventions and Innovations (PP 272-279) 2. The Northern Section (PP 280-284) a. Limits to Freedom (AAH 221-226) b. Black Communities in Urban North (AAH 227) c. African-American Institutions (AAH 235-239) d. Free African Americans (AAH 240-246) 3. The Southern Section (PP 285-289) a. Expansion of Slavery (AAH 181-185) b. Slave Labor in Agriculture (AAH 186-189) c..Other Types of Slave Labor (AAH 190-197) d. Slave Life (AAH 198-204) e. Socialization of Slaves (AAH 205-208) 4. The Growth of Nationalism (PP 290-295) 5. The Age of Jackson (PP 297-303) D. Religion and Reform (1815-1855) 1. Reforming Society (PP 310-316) 2 The Antislavery Movement (PP 318-325) a. Abolitionism Begins in America (AAH 259-262) b. Colonization (AAH 263-266) c. Black Abolitionists (AAH 267-274) d. A Rising Tide of Violence (AAH 283-285) e. The Response of Antislavery Movement (AAH 286-290) f. Black Community Institutions (AAH 291-292) g. Changing abolitionist movement (AAH 293-299) h. Resistance and Nationalism (AAH 300-304) 3. The Movement for Women’s Rights (PP326-331) 4. Growing Divisions (PP 332-335) People, Events, Documents and Vocabulary For the Regents The Origins of American Politics (1789-1820) Proclamation of Neutrality Washington’s Farewell Address Hamilton’s Financial Plan National Bank Whiskey Rebellion Alien and Sedition Acts Federalist Party vs. DemocraticGeorge Washington Thomas Jefferson Judicial Review Marbury v Madison An Emerging Nation (1783-1855) Tariff of 1828 Indian removal Act Trail of Tears War of 1812 Monroe Doctrine American System Tariff of Abominations Force Bill Bank War Manifest Destiny Louisiana Purchase Growth of a National Economy (1790-1850) “King Cotton” Spoils system Religion and Reform (1815-1855) Abolition Underground railroad Seneca Falls Convention Declaration of Sentiments UNIT 5 – Civil War and Reconstruction (1846-1877) (Recommended time – 3 weeks) RESOURCESPathways to Present 2007 Chap 10 The Coming of the Civil War (1846-1861) Chap 11 The Civil War (1861-1865) Chap 12 Reconstruction (1865-1877) Brief Review in United States History and Government Unit 2 Constitutional Foundations Sec 2- The Constitution Tested Unit 3 Industrialization Sec 1- The Reconstructed Nation African-American History Prentice Hall 2006 Chap 10- The United States Disunites over Slavery (1846-1861) Chap 11- African Americans and the Civil War (1861-1865) Chap 12- The Promise of Reconstruction (1865-1868) Chap 13- The Failure of Reconstruction (1868-1877) ExamGen Chapter and Topics Chap 3- The Reconstruction Era (48 questions) TOPICS- A. The Coming of the Civil War (1846-1861) 1. Two Nations (PP 346-350) a. Uncle Toms Cabin (AAH 324) 2. New Political Parties (PP 355-361) a. Fugitive Slave Laws (AAH 316-322) b. Rochester Convention (AAH 323) c. Kansas-Nebraska Act (AAH 324-327) 3. The System Fails (PP 363-368) a. Dred Scott Decision (AAH 327-329) b. Lincoln-Douglas Debates (AAH331-332) c. John Brown’s Raid (AAH 332-335) 4. A Nation Divided Against Itself (PP 369-373) B. The U.S. Civil War (1861-1865) 1. 2. 3. 4. From Bull Run to Antietam (PP 380-389) Life Behind the Lines (PP 390-400) a. Lincoln and Emancipation (AAH 354-361) b. Black Men Fight for the Union (AAH 362-375) c. Opposition to Black People (AAH 376- 382) The Tide of the War Turns (PP 402-409) Devastation and New Freedom (PP 410-417) C. Reconstruction (1865-1877) 1. 2. 3. Presidential Reconstruction (PP 424-429) Congressional Reconstruction (PP 430-435) a. The End of Slavery (AAH 391-399) b. Life after Slavery (AAH 400-406) Birth of the “New South” (PP 436-440) a.. 4. The Crusades for Political and Civil Rights (AAH 407-411) The End of Reconstruction (PP 442-445)(AAH 426- 448) People, Events, Documents and Vocabulary The Coming of the Civil War (1846-1861) Expansion of Slavery: Missouri Compromise Compromise of 1850 Kansas-Nebraska Act Dred Scott Case Lincoln-Douglas Debates John Brown’s Raid Bloody Kansas Harper’s Ferry Whig Party The U.S. Civil War (1861-1865) Secession Suspension of Habeas Corpus Gettysburg Address Emancipation Proclamation Reconstruction (1865-1877) Lincoln’s Plan Radical Republican Plan Tenure of Office Act Andrew Johnson Scalawags Carpetbaggers Ulysses S Grant 13th, 14th, 15th Amendments Election of 1876 Compromise of 1877 Rutherford Hayes Black Codes Ku Klux Klan Disenfranchisement Literacy Test; Poll Tax; Grandfather Clause Jim Crow Laws Freedmen Bureau UNIT 6 – Expansion:Rewards and Costs (1850-1920) (Recommended time – 5 weeks) RESOURCESPathways to Present 2007 Chap 13 The Expansion of American Industry(1850-1900) Chap 14 Looking to the West (1860-1900) Chap 15 Politics Immigration and Urban Life (1870-1915) Chap 16 Life at the turn of 20th Century (1870-1915) Chap 18 Progressive Era (1890-1920) Brief Review in United States History and Government Unit 3- Section 2 and 3 Unit 4- Section 1 African-American History Prentice Hall 2006 Chap 14- A. A. in the South in the Late 19th Century (1875-1900) Chap 15- Black Southerners Challenge White Supremacy (1867-1917) Chap 16- African Americans in the Early 20th Century (1895-1928) ExamGen Chapter and Topics Chap 4- Age of Corporations (212 questions) Chap 5- Progressive Movement (83 questions) Topic A- Pressures for reform Topic B- Progressivism and government action TOPICS- A. The rise of U.S. business and labor (1865-1920) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. A Technological Revolution (PP 456-465) Growth of Big Business (PP 467-472) Black Businesspeople and Entrepreneurs (AAH 521-527) Industrialization and Workers (PP 473-476) The Great Strikes (PP 477-483) B. Looking West (1860-1900) 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. C. Politics, Immigration and Urban Life (1870-1915) 1. 2. 3. 4. D. Moving West (PP 488-490) Conflict with Native Americans (PP 491-497) Mining, Ranching and Farming (PP 498 -506) Migration (AAH 481-487) Populism (PP 507-512) Politics in Gilded Age (PP 520-526) (AAH 461-466) Immigration (PP 527-533) Challenges of the City (PP 534-539) Ideas of Reform (PP 541-545) Life at the Turn of the Century (1870-1915) 1. Expansion of Education (PP 552-557) a. Educating African Americans (AAH 499-504) 2. New Forms of Entertainment (PP 559-563) a. Music and Sports (AAH 528-532) 3. The World of Jim Crow (PP 564-568) a. Disfranchisement (AAH 467-469) b. Segregation (AAH 470-475) c. Violence (AAH 476-480) d. African Americans and the Southern Courts (AAH 488-490) 4. The Changing Roles of Women (PP 569-573) 5. Church and Religion (AAH 505-510) E. The Progressive Reform Era (1890-1920) 1. Origins of Progressivism (PP 614-619) 2. Progressive Legislation (PP 621-627) 3. 4. 3. 6. 4. Race and Social Change (AAH 541-549) New Black Organizations (AAH 550-560) Progressivism Under Taft and Wilson (PP 628-634) Racial Violence (AAH 567-574) Suffrage at Last (PP635-639) People, Events, Documents and Vocabulary For the Regents The rise of U.S. business and labor (1865-1920) Entrepreneurs Corporations Monopoly Conglomerate Merger Trust Andrew Carnegie John D Rockefeller J. Pierpont Morgan Henry Ford Assembly line Laissez-faire Horatio Alger Adam Smith Wealth of a Nation(1776) Charles Darwin Social Darwinism Robber Baron Philanthropist Munn v Illinois (1877) Wabash, St. Louis & Pacific Railroad v Illinois (1886) Interstate Commerce Act (1886) Sherman anti-trust act (1890) US v EC Knight Company (1895) Labor unions Collective bargaining Knights of Labor Haymarket Riot (1886) American Federation of Labor Samuel Gompers Great Railway Strike (1877) Homestead Strike (1892) Pullman Strike (1894) Lawrence Textile Strike (1912) Looking West (1860-1900) Transcontinental Railroad Homestead Act (1862) Indian Wars Dawes Act (1887) The grange Populist Party Politics, Immigration and Urban Life (1870-1915) Tenements Political machines Nativism Melting pot theory Assimilation Pluralism Know-nothing party Chinese exclusion Act (1882) Gentleman’s Agreement (1907) Life at the Turn of the Century (1870-1915) The Progressive Reform Era (1890-1920) Jane Addams Settlement Houses Upton Sinclair The Jungle (1906) Jeannette Rankin Carrie Chapman Catt Alice Paul Booker T Washington Web Dubois Marcus Garvey Ida b Wells-Barnett Muckrakers Jacob Riis- How the Other Half Lives (1890) Lincoln Steffens- Shame of the Cities (1906) Temperance movement Susan b Anthony Elizabeth Cady Stanton National American Women’s Suffrage Association Plessy v Ferguson (1896) NAACP Secret ballot Initiative Referendum Recall Direct primary Hepburn Act (1906) Pure food and drug act (1906) Meat inspection act (1906) 16th amendment (1913) 17th amendment (1913) National Park service (1916) 18th amendment (1919) Employers Liability Act (1906) Lochner v New York (1905) Muller v Oregon (1908) Standard Oil of New Jersey v United States (1911) Federal reserve system (1913) Clayton Antitrust Act (1914) UNIT 7 – Becoming a World Power (1890-1920) (Recommended time – 2 weeks) RESOURCESPathways to Present 2007 Chap 17 Becoming a World Power (1890-1915) Chap 19 World War I Era (1914-1920) Brief Review in United States History and Government Unit 4- Section 2 Unit 5- Section 1 African-American History Prentice Hall 2006 Chap 15- Black Southerners Challenge White Supremacy (1867-1917) Chap 16- African Americans in the Early 20th Century (1895-1928) ExamGen Chapter and Topics Chap 5- The Progressive Movement (101 questions) Topic C- Expansion of US power overseas Topic D- WWI and US involvement TOPICS- A. Becoming a World Power (1890-1915) 1. The Pressure to Expand (PP 584-588) 2. Spanish-American War (PP 589-596) a. Black Troops (AAH 511-520) 3. A New Foreign Policy (PP 598-603) 4. Debating America’s New Role (PP 604-607) B. The World War I Era (1914-1920) 1. The Road to War (PP 646-651) 2. The United States Declares War (PP 653-656) a. Politics and the Military (AAH 561-566) 3. Americans on the European Front (PP 657-663) 4. Americans on the Home Front (PP 664-668) 5. Global Peacemaker (PP 669-673) People, Events, Documents and Vocabulary For the Regents Becoming a World Power (1890-1915) Social Darwinism Missionary spirit Open door policy Boxer rebellion Jingoism Yellow journalism William Hearst Joseph Pulitzer De lome letter Sinking of the Maine Teller amendment Imperialism Foraker act (1900) Platt Amendment (1902) Roosevelt corollary Big stick policy Dollar diplomacy Good neighbor policy Panama canal The World War I Era (1914-1920) Causes of war Central powers Allies Propaganda German submarine warfare Lusitania (1915) Zimmerman note Selective service act (1917) Espionage and sedition act (1917 + 1918) Schenck v United States (1918) Red Scare (1918-1920) Fourteen points (1918) Treaty of Versailles (1919) League of Nations reparations UNIT 8 – Boom Times to Hard Times (1920-1941) (Recommended time – 6 weeks) RESOURCESPathways to Present 2007 Chap 20 Postwar Social Change (1920-1929) Chap 21 Politics and Prosperity (1920-1929) Chap 22 Crash and Depression (1929-1933) Chap 23 The New Deal (1933-1941) Brief Review in United States History and Government Unit 5- Section 1 + 2 African-American History Prentice Hall 2006 Chap 17- African Americans and the 1920’s (1915-1928) Chap 18- The Great Depression and the New Deal (1929-1941) Chap 19- Culture and Society in the 1930’s and 1940’s (1930- 1949) ExamGen Chapter and Topics Chap 6- Roaring 20’s & Depression (143 questions) TOPICS- A. Postwar Social Change (1920-1929) 1. Society in 1920’s (PP 684-690) a. The Great Migration (AAH 575-582) 2. Mass Media and the Jazz Age (PP 691-697) a. The Harlem Renaissance (AAH 606-615) b. Sports (AAH 617-618) 3. Cultural Conflicts (PP 699-705) a. Fighting Racism (AAH 591-593) b. Black Organizations of the 1920s (AAH 594-601) c. Uniting Black Workers (AAH 602-605) B. Politics and Prosperity (1920-1929) 1. A Republican Decade (PP 712-721) 2. A Business Boom (PP 723-729) 3. The Economy in the Late 1920’s (PP 730-733) C. Crash and Depression (1929-1933) 1. The Stock Market Crash (PP 740-744) 2. Social Effects of the Depression (PP 745-750) a. Blacks during the Great Depression (AAH 631-637) b. Black Protest (AAH 638-643) 3. Surviving the Great Depression (PP 752-755) a. Black Culture (AAH 671-675) b. Popular Culture for the Masses (AAH 676-680) c. The Black Chicago Renaissance (AAH 681-687) d. Black Art and Literature (AAH 688-692) e. African Americans in Sports (AAH 693-695) f. Black Religious Culture (AAH 696-698) 4. The Election of 1932 (PP 756-761) D. The New Deal (1933-1941) 1. Forging a New Deal (PP 768-776) a. African Americans and the New Deal (AAH 644-656) 2. The New Deal’s Critics (PP 777-783) 3. Last Days of the New Deal (PP 785-791) People, Events, Documents and Vocabulary For the Regents Postwar Social Change (1920-1929) Great migration Return to normalcy Teapot dome scandal Harlem renaissance Flappers Jazz age Kkk Sacco and Vanzetti Prohibition Scopes monkey trial Quotas Politics and Prosperity (1920-1929) Crash and Depression (1929-1933) Causes of depression Bonus army Hoovervilles Dust bowl The New Deal (1933-1941) Relief, Recovery and Reform UNIT 9 – Hot and Cold War (1931-1960) (Recommended time – 4 weeks) RESOURCESPathways to Present 2007 Chap 24 and 25 World War II (1931-1945) Chap 26 Cold War (1945-1960) Chap 27 Postwar Years at Home (1945-1960) Brief Review in United States History and Government Unit 6- Section 1 + 2 Unit 7- Section 1 African-American History Prentice Hall 2006 Chap 20- The World War II Era and the Seeds of the Revolution (1936-1948) ExamGen Chapter and Topics Chap 7- America’s move from isolation to world leader (153 questions) TOPICS- A. Road to War (1931-1941) 1. 2. 3. 4. The Rise of Dictators (PP 800-806) Europe Goes to War (PP 807-811) Japan Builds an Empire (PP 813-816) From Isolationism to War (PP 817-821) a. On the Eve of War (AAH 707-711) B. Americans at War (1941-1945) 1. Mobilization (PP 826-831) a. Race and the US Armed Forces (AAH712-716) b. The Beginning of Military Desegregation (AAH 717-722) c. Black People on the Home Front (AAH 723-728) 2. Retaking Europe (PP 832-840) 3. The Holocaust (PP 841-845) 4. The War in the Pacific (PP 846-853) 5. The Social Impact of the War (PP 855-861) C. The Cold War (1945-1960) 1. 2. 3. 4. Origins of the Cold War (PP 868-874) The Cold War Heats Up (PP 876-883) The Korean War (PP 884-888) The Continuing Cold War (PP 889-893) D. Postwar Years at Home (1945-1960) 1. The Postwar Economy (PP 900-906) 2. Mood of the 1950’s (PP 907-911) 3. Domestic Politics and Policy (PP 912-918) a. The Transition to Peace (AAH 729-734) People, Events, Documents and Vocabulary For the Regents Road to War (1931-1941) Isolationism Neutrality Totalitarianism Adolph Hitler Benito Mussolini Joseph Stalin Fascism 1938 Munich Agreement Appeasement Lend-Lease Act Americans at War (1941-1945) Pearl Harbor Allies Winston Churchill Harry S Truman Dwight Eisenhower Douglas MacArthur Charles de Gaulle Axis Powers Emperor Hirohito Atlantic Charter Meeting (1941) Casablanca (1943) Cairo (1943) Tehran Conference (1943) Yalta (1945) Potsdam (1945) Manhattan Project Hiroshima Nagasaki Holocaust Nuremberg Trials Rosie the Riveter Wartime Relocation Authority Korematsu v United States 1944 Servicemen’s Readjustment Act Employment Act of 1946 Taft-Hartley Act The Cold War (1945-1960) United Nations Universal Declaration of Human Rights Containment Iron curtain Truman Doctrine Marshall Plan Berlin Blockade Berlin airlift NATO Warsaw Pact Korean War 38th parallel Sputnik Domino Theory Eisenhower Doctrine U-2 incident Postwar Years at Home (1945-1960) HAUC McCarthyism Growth of suburbs Jackie Robinson Warren Court Brown v Board of Education 1954 Little Rock Civil Rights Movement Montgomery bus boycott Freedom rides James Meredith March on Washington (1963) UNIT 10 – A Period of Turmoil and Change (19501975) (Recommended time – 4 weeks) RESOURCES- Pathways to Present 2007 Chap 28 Civil Rights Movement (1950-1968) Chap 29 Kennedy and Johnson Years (1961-1969) Chap 30 The Era of Activism (1960-1975) Chap 31 Vietnam War (1954-1975) Brief Review in United States History and Government Unit 7- Section 2 + 3 African-American History Prentice Hall 2006 Chap 21- Freedom Movement (1954-1965) Chap 22- The Struggle Continues (1965-1980) ExamGen Chapter and Topics Chap 8- 1950- 1981 (236 questions) TOPICS- A. The Civil Rights Movement (1950-1968) 1. Demands for Civil Rights (PP 930-935) a. The 1950’s (AAH 747-755) b. The Montgomery Bus Boycott ( AAH 756-761) 2. Leaders and Strategies (PP 936- 940) a. Martin Luther King (AAH 814-816) 3. The Struggle Intensifies (PP 941-946) a. No Easy Road to Freedom (AAH 762-767) 4. The Political Response (PP 948-953) a. The Movement at High Tide (AAH 768-778) b. A Hard Victory (AAH 778-784) 5. The Movement Takes a New Turn (PP 954-959) a. Racial Integration (AAH 793-802) B. The Kennedy and Johnson Years (1961-1969) 1. The New Frontier (PP 968-973) 2. The Great Society (PP 975-981) a. The Great Society (AAH 803-813) 3. Foreign Policy in early 1960’s (PP 983-991) C. An Era of Activism (1960-1975) 1. The Women’s Movement (PP 996-1001) 2. Ethnic Minorities Seek Equality (PP 1003-1008) a. The Black Arts Movement (AAH 817-824) 3. Counterculture (PP 1009-1012) 4. Environmental and Consumer Movement (PP 1013-1017) D. The Vietnam War (1954-1975) 1. The War Unfolds (PP 1024-1029) 2. Fighting the War (PP1030-1036) 3. Political Divisions (PP 1037-1043) 4. The End of the War (PP 1044-1049) People, Events, Documents and Vocabulary For the Regents The Civil Rights Movement (1950-1968) Civil disobedience James Meredith Medgar Evers Civil Rights Act (1964) Voting Rights Act (1965) Martin Luther King Jr. Malcolm X The Kennedy and Johnson Years (1961-1969) New Frontier Great Society Space program Peace corps VISTA program Office of Economic Opportunity (1964) The Elementary and Secondary Education Act (1965) Medicare Department of Housing and Urban Development Bay of Pigs Cuban Missile Crisis Berlin Wall An Era of Activism (1960-1975) Betty Frieden- The Feminine Mystique (1963) Title VII- of Civil Rights Act NOW Equal Rights Ammendment Title IX of the Educational Amendments Act Roe v Wade (1973) Affirmative action Feminism Sexism Glass ceiling Regents of the University of California v Bakke (1979) Cesar Chavez United Farm Workers American Indian Movement Ralph Nader The Vietnam War (1954-1975) Gulf of Tonkin Resolution (1964) Hawks and Doves Students for Democratic Society Vietnamization War Powers Act UNIT 11 – Continuity and Change (1960-present) (Recommended time – 1 weeks) RESOURCESPathways to Present 2007 Chap 32 Nixon, Ford and Carter (1969-1981) Chap 33 The Conservative Revolution (1980-1992) Chap 34 Entering the New Era (1992- present) Brief Review in United States History and Government Unit 7- Section 4 + 5 African-American History Prentice Hall 2006 Chap 23- Black Politics (1980-2004) Chap 24- African Americans in the New Millennium ExamGen Chapter and Topics Chap 9- 1981-Present (195 questions) TOPICS- A. Nixon, Ford and Carter (1969-1981) 1. Nixon’s Domestic Policy (PP 1058-1063) a. Politics (AAH 825-829) 2. Nixon’s Foreign Policy (PP 1064-1069) 3. Watergate Scandal (PP 1070-1076) 4. The Ford Administration (PP 1078-1082) 5. The Carter Administration (PP 1083-1089) a. Black Elected Officials (AAH 830-836) B. The Conservative Revolution (1980-1992) 1. Roots of New Conservatism (PP 1096-1100) a. The Conservative Reaction (AAH 845-849) 2. Reagan Revolution (PP 1102-1107) 3. Reagan’s Second Term (PP 1108-1113) 4. George HW Bush Presidency (PP 1114-1119) C. Entering a New Era (1992-Present) 1. Politics in Recent Years (PP 1126-1131) a. Civil Rights (AAH 850-855) b. Jesse Jackson and the Rainbow Coalition (AAH 856-858) c. Policing the Black Community (AAH 859-862) d. The Clinton Years (AAH 863-865) e. The Bush Years (AAH 868-876) 2. The United States in a New World (PP 1133-1141) 3. Americans in the New Millennium (PP 1142-1149) a. Progress and Poverty (AAH 885-892) b. Art and Culture (AAH 893-901) c. Religion (AAH 902-908) d. Black Identity (AAH 909-914) People, Events, Documents and Vocabulary For the Regents Nixon, Ford and Carter (1969-1981) Détente OSHA Clean Air Act (1970) Drug Enforcement Agency (1973) New federalism Watergate Amnesty Plan Inflation OPEC Stagflation Camp David Accords Hostage Crisis The Conservative Revolution (1980-1992) Supply-side economics Star Wars Farm Aid Iran Contra Affair Savings and Loan Scandal End of Cold War Persian Gulf War Entering a New Era (1992-Present) Health Care Reform Welfare Reform N.A.F.T.A. New World Order: Somalia; Bosnia; Kosovo Clinton v. Jones Clinton’s Impeachment Trial New York State Core Curriculum can be found at http://www.emsc.nysed.gov/ciai/socst/pub/sscore2.pdf The following concepts and themes in United States history are also emphasized in this curriculum: Change Citizenship Civic Values Constitutional Principles Culture and Intellectual Life Diversity Economic Systems Environment Factors of Production Foreign Policy Government Human Systems Immigration and Migration Individuals, Groups, Institutions Interdependence Physical Systems Places and Regions Reform Movements Presidential Decisions and Actions Science and Technology Since this curriculum emphasizes government and basic constitutional principles, students should understand the importance of key United States Supreme Court decisions. The following Supreme Court decisions have had significant impact on our nation’s history: Marbury v. Madison (1803) McCulloch v. Maryland (1819) Gibbons v. Ogden (1824) Worcester v. Georgia (1832) Dred Scot v. Sanford (1857) Civil Rights Cases (1883) Wabash, St. Louis & Pacific R.R. v. Illinois ( 1 8 8 6 ) United States v. E.C. Knight Co. (1895) In Re Debs (1895) Plessy v. Ferguson (1896) Northern Securities Co. v. United States (1904) Lochner v. New York (1905) Muller v. Oregon (1908) Schenck v. United States (1919) Schechter Poultry Corporation v. United States (1935) Korematsu v. United States (1944) Brown v. Board of Education of Topeka (1954) Watkins v. United States (1957) Mapp v. Ohio (1961) Baker v. Carr (1962) Engle v. Vitale (1962) Gideon v. Wainwright (1963) Heart of Atlanta Motel v. United States (1964) Miranda v. Arizona (1966) Tinker v. Des Moines (1969) New York Times v. United States (1971) Roe v. Wade (1973) United States v. Nixon (1974) New Jersey v. TLO (1985) Cruzan v. Director, Missouri Department of Health (1990) Planned Parenthood of Southeastern Pennsylvania, et. al. v. Casey (1992) Vernonia School District v. Acton (1995)