EXP6_TimerCounter_Degree 144KB Oct 18 2015 06:19:27 PM
advertisement

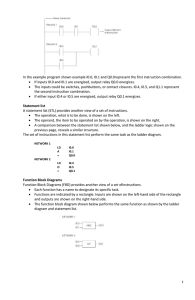
Electrical and Electronic Engineering Department BAPL2004 Programmable Logic Controllers PLC Laboratory 6 Timer and Counter Name: Due Date: Submission Date: Lecturer: 27 Oct 2015 Tan Teck Siang 1 OBJECTIVES 1. To learn the basic of timer and counter. 2. To design simple timer and counter ladder diagram EQUIPMENT AND SUPPLIES 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Mitsubishi FX1S-30MR PLC PC Toggle Switches PC with Mitsubishi MELSEC Programmer 3HP Air Compressor Pneumatic Cylinder with reed switches Pneumatic valves INTRODUCTION Timer Mitsubishi PLC’s offers several time base Timer as shown below: Timers by default are non-retentive. That means that they do not hold their value if the input circuit opens. Timers T0~T199 are 100 millisecond timers, T200~T245 are 10 millisecond timers, for this CPU. The K value is a multiplier. K123 means 123 x 100 milliseconds = 12.3 seconds. After the timer reaches 123, the T0 contact will close. 2 Counter Counter Presets Presets are the number of times the rung driving the counter has to go through a FALSE to TRUE state transition before turning on. 16 bit counters have a range of 1 to 32,767. Counter presets can be either a K constant, or a variable, such as a data or file register. Having a D device as the preset allows an operator to make changes to the counter preset from an HMI. The accumulated value of the timer never goes above the preset value. Once the counter coil has turned on, it will remain on until reset. Even the use of the Decrement instruction to reduce the count will not deactivate the counter coil. Counting direction 16 bit counters only count up. Counter Reset The accumulated value of a counter returns to 0 when the RST C# instruction is activated. Counter Example: Counter X000 K3 |-------| |-------------------------- (C000) --------| When X000 is cycled ON and OFF, the counter C000 will be incremented by 1. C000 will be turned ON when it counts to 3. 3 Part 1 Basic Timer Ladder Diagram Program the PLC with the ladder diagram below and record down your observation. X000 T000 |-------| |--------|/| ------------------ (Y000) --------| Y000 |-------| |----Y000 |-------| |---------------------- (T000 K100) --------| Observation: Part 2 Basic Counter ladder diagram Program the PLC with the ladder diagram below and record down your observation. X000 K3 |-------| |-------------------------- (C000) --------| C000 |-------| |-------------------------- (Y000) --------| X001 |-------| |-------------------- [RST C000] --------| Observation: Part 2 Solving Problem Using Timer and Counter. Program and verify using the PLC for the process as described below. Operation: (a) When the user presses the push button X0, the cylinder extends after waiting for 3 seconds. 4 (b) The cylinder extends after the user press the push button X0 three times, but it will not extend if the user pressed three more times. (c) When the user presses the push button X0 two times, the cylinder extends after 5 seconds delay. If the user pressed the push button X1 before 5 seconds timeout, the cylinder will cancel the extension stroke. (d) If the user pressed X0 for the first time, the cylinder extends. If the user pressed X0 for the second time, the cylinder will retracts. (e) Continue from the previous step (d). If the user pressed X0 for more than 5 times, the cylinder will delay 2 seconds before extension or retraction. 5