CCNA 2/Mod 7: Distance Vector Routing
advertisement
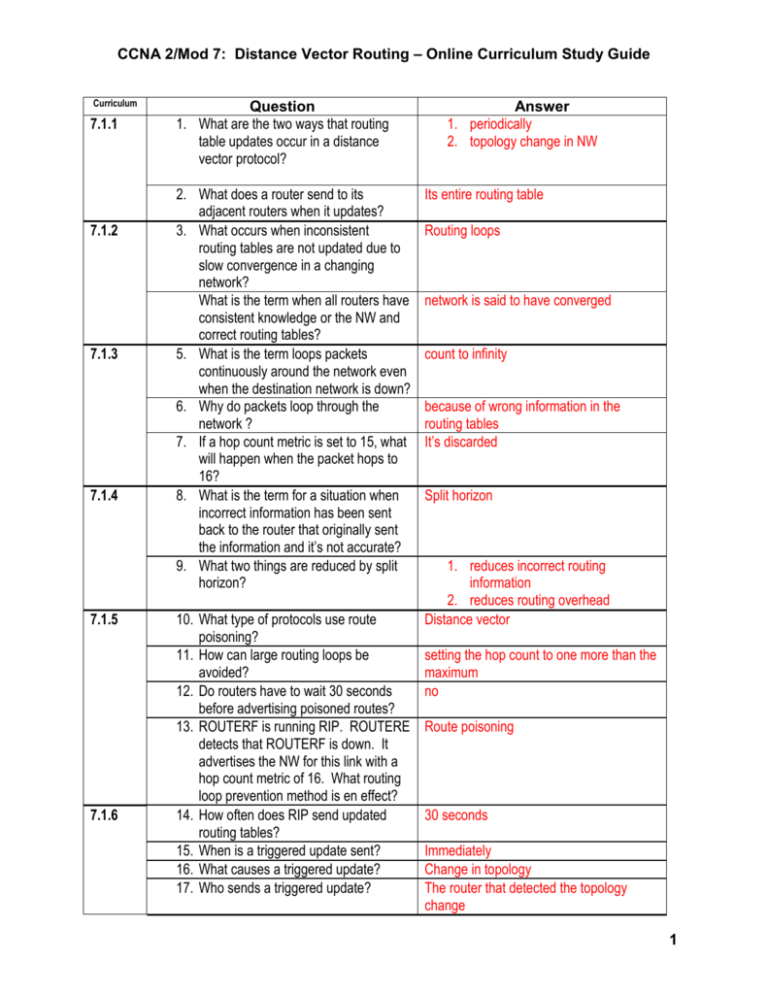
CCNA 2/Mod 7: Distance Vector Routing – Online Curriculum Study Guide Curriculum 7.1.1 7.1.2 7.1.3 7.1.4 7.1.5 7.1.6 Question 1. What are the two ways that routing table updates occur in a distance vector protocol? 2. What does a router send to its adjacent routers when it updates? 3. What occurs when inconsistent routing tables are not updated due to slow convergence in a changing network? 4. What is the term when all routers have consistent knowledge or the NW and correct routing tables? 5. What is the term loops packets continuously around the network even when the destination network is down? 6. Why do packets loop through the network ? 7. If a hop count metric is set to 15, what will happen when the packet hops to 16? 8. What is the term for a situation when incorrect information has been sent back to the router that originally sent the information and it’s not accurate? 9. What two things are reduced by split horizon? 10. What type of protocols use route poisoning? 11. How can large routing loops be avoided? 12. Do routers have to wait 30 seconds before advertising poisoned routes? 13. ROUTERF is running RIP. ROUTERE detects that ROUTERF is down. It advertises the NW for this link with a hop count metric of 16. What routing loop prevention method is en effect? 14. How often does RIP send updated routing tables? 15. When is a triggered update sent? 16. What causes a triggered update? 17. Who sends a triggered update? Answer 1. periodically 2. topology change in NW Its entire routing table Routing loops network is said to have converged count to infinity because of wrong information in the routing tables It’s discarded Split horizon 1. reduces incorrect routing information 2. reduces routing overhead Distance vector setting the hop count to one more than the maximum no Route poisoning 30 seconds Immediately Change in topology The router that detected the topology change 1 7.1.7 7.2.1 7.2.2 7.2.3 7.2.4 18. When does a distance vector routing protocol set a hold-down timer on a route? 19. What does a router do when it receives an update from a neighbor router with a better metric than it had originally recorded? 20. Why is an update with a poorer metric ignored? 21. Which version of RIP is classless? 22. Which version of RIP supports VLSM? 23. What is the maximum number of hops in a path? 24. What happens when the hop count is incremented +1 every hop and reaches 16? 25. What two commands are required to enable RIP on an interface? 26. What mode must you be in to set these two commands? 27. What will happen to packets when the no ip classless command is disabled? 28. What will happen to packets when the no ip classless command is disabled AND there is a default route defined? 29. What is the term to indicate that all the routers in the internetwork have the same routing information? 30. What causes routing loops and counting to infinity in RIP routers? 31. What do holddown timers do to convergence? 32. What is the default holddown time for RIP? 33. What would you do to decrease the network’s convergence time? 34. If you have 4 routers and updates are send every 50 seconds, what would the longest loop be? 35. What is RIP’s update interval default time? 36. What will this command do to a router? When it’s marked as inaccessible The router marks the NW as accessible and removes the holddown timer It allows more time for the knowledge of a disruptive change to propagate through the entire NW V2 V2 15 it is considered to be infinity and the network Router RIP command Networks (attached) Global Any packets received that are destined for a subnet that numerically falls within the router’s SN addressing scheme will be discarded Packets discarded Convergence Inconsistencies due to routing update messages with out of date routes being propagated around the internetwork Increase it 180 seconds Change it LOWER than 180 4 x 50 = 200 seconds 30 seconds Decrease convergence time GAD(config-router)#update-timer 15 2 37. What will this command do? GAD(config-interface)#ip rip send version 2 7.2.5 38. How are RIP routes indicated when you key the show ip route Configures an interface to send version 2 packets With an “R” command? 39. The following line was shown in the output of the show ip route command. What is the administrative distance of the routing protocol? 120 or RIP 192.168.3.0/24 (120/1) via 192.168.2.2, 00:00:30, Serial 0/0 7.2.6 7.2.7 7.2.8 7.2.9 40. What are the three most common RIP configuration errors? 41. What command verifies that routing updates are being sent and received? 42. What affect do route filters have on link state protocols? 43. When you use the passive interface command, you prevent routers from sending routing updates through an interface. What type of routes are you preventing other systems on the network from learning? 44. What is the maximum paths RIP can load balance over? 45. What is the term used when routers “take turn” load balancing? 46. If using RIP, which path will be given preference – a 56Kbps or a 155 Mbps? 1. an incorrect network statement 2. discontiguous subnets 3. split horizon Debug ip rip None dynamic 6 Round robin Neither --- RIP’s metric is hop – not speed 47. When a router learns multiple routes to a specific network which route is installed in the routing table? , the route with the lowest administrative distance 48. How many default static routes are installed when load balancing? 49. What are the 2 methods of load balancing Cisco IOS offers? 50. What is IGRP’s default administrative distance? 51. What is RIP’s default administrative distance? 52. Why would a static route be chosen over a RIP route? 6 1. per packet 2. per destination 100 120 Lower AD Static = 1 RIP = 120 3 7.2.10 7.3.1 7.3.2 7.3.3 7.3.4 7.3.5 7.3.6 7.3.7 7.3.8 53. How would an administrator configure a static route for use if a primary route failed? Configure the route with a metric greater 54. When an interface goes down, what happens to all static routes pointing out that interface? They are removed from the IP routing than the default value table. 55. What 2 functions do routers perform as routing information spreads throughout the network? 1. learn of failures 56. How often does IGRP send updates? 90 seconds 57. What are IGRP’s two default metrics? Bandwidth Delay MTU 58. What is the acronym for Maximum Transmission Unit? 59. Which routes within an AS do NOT include subnet information? 60. What routes support numbering outside the private network without renumbering inside? 61. What is used to prevent regular updates from inappropriately reinstating a route that may not be up? 62. What is used to prevent large routing loops? 63. If IGRP updates every 90 seconds, by default, how long will a router wait before declaring a route invalid? (invalid timer) 64. How long would this same route be in holddown? 65. What is the command to configure IGRP? No questions – it’s your lucky day! 66. What command is used to verify that IGRP has been configured properly? 67. How are IGRP routes displayed on the output? 68. What are the 3 most common IGRP configuration errors? 2. ID new destinations System Interior routes Holddowns Poison reverse updates 3x update period or 3 x 90 = 270 280 sec ROUTER(config)# show ip route I 1. mistyped network statement 2. discontiguous subnets 3. incorrect AS 4