chapter 16-1
advertisement

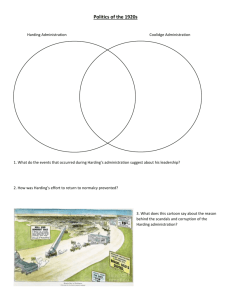
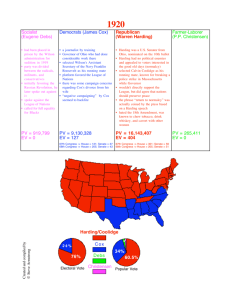
CHAPTER 16 THE DECADE OF NORMALCY 1920-1928 FOCUS - The decade that followed WWI differed considerably from the Progressive years that came before it. Voters turned to conservative leaders who promised to turn the country away from European affairs and inward to “normalcy”. For many Americans this shift meant preserving the values of rural America and enjoying prosperity. For others it meant a fascination with a dazzling new assortment of consumer goods, entertainment, and changing fashion. CHAPTER 16-1 THE HARDING YEARS - New problems for the US after WWI o Businesses lost profitable military contracts o 4 million demobilized men and women from the military o 1920-21 Unemployment soared Prices soared Strikes increased US Steel Boston Police Strike THE ELECTION OF 1920 - Republican nominations o Sought by many o Warren G. Harding Portrait Warren G Harding Ohio businessman Running mate – Calvin Coolidge Democratic nominations o Ohio Governor James M. Cox Loyal Wilson supporter Running mate – FDR Distant cousin of Teddy Assistant Sec of Navy - Campaign strategy o Campaign for the League of Nations - Republicans divided on issue of the League o Harding favored “a society of free nations” o Left uncertain whether Harding supported the “League” or not Harding wins support from both those for and against the “League” - Overwhelming republican victory o Harding wins every northern and western state Also carried Tenn Broke the “Solid South” of the Democrats - Campaigned on the slogan of a “return to normalcy” o A return to the “good old days” before WWI POSTWAR FOREIGN POLICY - Post election - Harding announced he would not lead the US into the “League” - US did however participate in many “League” conferences War Debt - International problem - Allies owed $10.3 billion to US for food and war materials - Debtors had difficulty meeting payments o Argued that US high tariff limited what they could sell to US thus slowing their economic recovery o They argued that the US lost less men thus should shoulder more of the cost of the war o US argues that the Allies had gained territory and reparations while US had claimed no reward o US says canceling the debt would destroy faith in international agreements - US makes agreements with 17 of 20 debtor countries o Reduce debt 30 – 80 per cent o Most of Allies money was that which came from German reparations Germany had to get loans from private banks Most banks were from the US Washington Conference - 8 nation conference in held in DC – November 1921 – February 1922 - US, GB, Japan all experiencing costly naval buildups - Friction in East Asia o Mainly over commercial rights in China o Also over suspicions of Japanese intentions Post WWI Japan acquired all of Germany’s Pacific islands north of the equator Japan acquired Chinese port of Kiaochow Japan treated the rest of the province of Shantung as its own. - Three important treaties come from this conference The Four-Power Treaty - Signed by US, GB, France and Japan o Agreement to respect each other’s Pacific holdings o In case of a disagreement or threat from another nation the signers would to confer “ fully and frankly” The Five-Power Treaty - Signed by 5 naval powers - US, GB, Japan, France and Italy - Agreement to freeze navies at 1921 levels o Avoid financial strain of further buildup - Agreed to halt building warships for 10 years o Some ships under construction scrapped - US and GB agree to not build naval fortifications in western Pacific o Gave Japan control of nearby waters in exchange for inferior naval strength The Nine-Power Treaty - US, GB, France, Japan, Italy, Belgium, China, Netherlands, and Portugal - Put in Jon Hay’s “Open Door” policy toward China into a treaty o Signers agree to preserve equal commercial rights in China o Refrain from taking advantage of conditions in China to seek special rights or privileges - Immediate results of Washington conference encouraging o Failed to reach agreement limiting military forces on land o Notable shortcomings 5 Power Treaty Nations could still build smaller naval vessels o Submarines o Destroyers - 4 Power Treaty o did not commit signers to active military defense of their allies o Would have been unacceptable to the US - 9 Power Treaty o Made no provision for enforcement of the Open Door policy BUSINESS NORMALCY - Harding’s actions on domestic problems made it apparent that normalcy meant government retreat from regulation of business o It did aid business by Levying protective tariffs Promoting foreign trade Breaking strikes - Other policies were “laissez-faire” o Little effort in antitrust law enforcement o Businesses allowed to merge o ICC and FTC largely unsympathetic to policies restricting private enterprise Fordney-McCumber Tariff - 1922 - Raised import duties to high levels - Authorized the president to raise duties 50% or higher - Protected ag and other young industries o Rayon, china, optical glass, chemical patents Seized from Germany during the war Creating the Bureau of the Budget - Created in 1921 within the Treasury Dept - WWI raised national debt from $10/person to $200/person o U.S. National Debt Clock - Harding and Coolidge attempt to lower it by making government more fiscally responsible - Efforts to induce saving - Coolidge emphatic about the issue o Attention paid to minor details Lead pencils Typewriter ribbons - Military expenditures were also greatly reduced Change in Taxation - 1921 – 1932 - Andrew Mellon – Sec of Treas o Believed that heavy taxes on excess profits “penalized success” and discouraged investment in productive enterprise o Congress abolishes wartime excise and excess profits taxes Reduces income taxes by 2/3 - Nation’s prosperity reduced the national debt by $8 billion between 1921 and 1929 LABOR AND LABOR UNIONS - 1921 – 1928 - Annual salary rose o $1,277 to $1,384 - New manufacturing caused technological unemployment o Jobs lost when occupations become obsolete o People usually find jobs elsewhere Transition sometimes difficult Often forced to leave home to find a job Frequently lost benefits from old job Example Introduction of jukeboxes and sound films o Widespread unemployment among musicians - Many workers could not stand the monotony and nervous tension of working at a speed set by a machine. Union Decline - “Prosperity decade” lowered union membership - AFL even had difficulty holding members - Employers promote open shop o Shop where workers do not have to join a union o Labeled the “American Plan” Closed to union members - Companies promote welfare capitalism o A system to make employees feel more a part of the business by enabling them to… o Buy shares of stock, o By instituting profit sharing o By providing such fringe benefits as medical care, retirement pensions and recreational facilities - Wages and conditions improved somewhat during the 1920s - Improvements in their standard of living - Weakness of unions - Striking seemed useless to many workers Strikebreaking - Herbert Hoover o Sec of commerce o Persuaded Harding to appeal to the leaders of the steel industry to abandon the 12-hour work day - Attorney General Harry Daugtherty helped brake railroad and coal strikes in 1922 o Obtains injunctions that prohibit every conceivable union activity Picketing Making public statements to the press Jeering at strikebreakers - 1919 o Indiana State guard and federal troops Protected strike breakers at US Steel - Supreme Court continually whittled away at the protections that unions thought they had secured by the Clayton Act of 1914 - Injunctions freely used to stop strikes and boycotts RESTSRICTING IMMIGRATION - PRE WWI o 1 million immigrants a year o 2/3 come from southern and eastern Europe o Congress passes laws to slow down immigration Required a literacy Excluded large number of immigrants Act had little effect - Immigrants congregate in NY and Chicago o Employment opportunities - Established immigrants resented new immigrants o Feared newcomers Most of whom were Catholic Feared they would overthrow Protestant values - Conservative labor unions angered by willingness of poor immigrants to work for very low wages - Even employers were turning against new immigrants - Fear new immigrants were radicals o Feared they would fight for communist revolution National Origins Act 1924 - Many after WWI have harsh feelings toward “hyphenatedAmericans” - Stimulated by o Anti-German hysteria o Red Scare o KKK - 1921 o Harding signs Emergency Quota Act Cut the number of immigrants admitted to 3 percent of the base year of 1910 per year - 1924 Nat Origins Act o Made restriction permanent policy o Would allow only 150,000 immigrants a year o Base year changed to 1920 o 85 percent of immigrants would be coming from GB, Ireland, Germany, Scandinavia Clearly demonstrates discrimination toward certain nationalities and races Some Asians and Africans restricted even more and even barred entirely Especially harmful to Japanese o Declared a national day of mourning and humiliation in Japan o Helped advance the cause of reactionary militarists in Japan Sacco and Vanzetti 1921 - 2 Italian Immigrants - Admitted anarchists - Accused of killing 2 men during a robbery in Mass - Convicted - Many think they do not receive a fair trial o Accuse the judge of being prejudice against foreigners - Executed in 1927 o Many unsuccessful attempts for a retrial o Quote from Vanzetti page 490 - People around the world criticized the decision - 1961 ballistics info did link Sacco’s gun to the murder victims SCANDALS AMONG HARDING’S ADVISORS - Harding personally honest - His friends “Ohio Gang” – poker playing partners o Used their ties to Harding and the attorney general Sold government appointments Sold pardons Sold immunity from prosecution Examples Charles Forbes o Director of Vets Bureau o Made illegal deals o Netted $100,000 in commissions o Info became public Attorney also involved committed suicide Jesse Smith also committed suicide A close friend of AG Daugherty o Also accused of corruption while in office - Worst scandal o Sec of Interior Albert Fall o Secretly leased government oil lands set aside for the navy o Known as the Teapot Dome scandal Fall receives $300,000 in the deal Later convicted and sent to prison - Harding o “I have no trouble with my enemies, it’s my friends that keep me awake at night” - Summer 1923 o Harding travels to Alaska o Becomes ill upon his return trip o His physician – US Surgeon General – diagnosed his illness as food poisoning Harding dies 2 days later of a massive heart attack Harding dies shortly before the news of the scandals is made known to the public. - 1920s History - Food Groceries and Toiletries in the 1920's VISUALIZING HISTORY PAGE 485 USING GRAPHS PAGE 486 SIDELIGHT: PRESIDENTIAL GAFFES PAGE 486 CURRICULUM CONNECTION PAGE 487 VISUALIZING HISTORY PAGE 487 DID YOU KNOW? PAGE 487 LINKING ACROSS TIME PAGE 488 GRAPH STUDY PAGE 488 HISTORY AND ART PAGE 489 LINKING ACROSS TIME PAGE 489 SIDELIGHT: RELIGION AND BUSINESS PAGE 489 SECTION 1 ASSESSMENT PAGE 490 HISTORY AND SCIENCE PAGE 491