spina bifida - Rural Rehab
advertisement

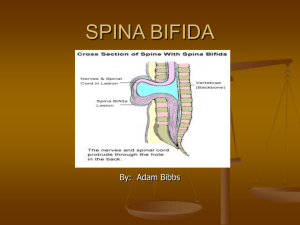
TREATMENT PROTOCOL FOR NEUROLOGIC CONDITION Condition: SPINA BIFIDA What is a spina bifida? Spina bifida: is defect that occurs in the vertebral column where neural tubes of the spinal cord fail to close over the centre of the tube of nerves, exposing the meninges and / or the spinal cord . As a result there are neurologic deficit to the lower limbs. VARIES FORMS OF SPINA BIFIDA Rachischisis: completely open spine with severe neorologic disability and death Myelocele: spinal cord protrudes Myeningocele : protruding sac contains meninges Myelomeningocele : both the spinal cord and the meninges CAUSES, INCIDENCE AND SCREENING There is neither single cause of spina bifida nor any known way to prevent it entirely. Scientists suspect genetic, nutritional, and environmental factors play a role. Research studies indicate that insufficient intake of folic acid a common B-vitamin in the mother’s diet is a key factor in causing spina bifida and other neural tube defects. Spina bifida is one of the most common birth defects, with an average worldwide incidence of 1-2 cases per 1000 births. PREGNANCY SCREENING AFP blood screening Fetal ultrasound Genetic counseling and genetic testing ( amniocentesis) / Trisomy 18 Symptoms Symptoms vary form person to person depending on the type of spina bifida and the level in which it occurs fluid filled sac at the back visible from the spine an abnormal tuft or clump of hair or a small dimple or birthmark on the skin at the back lower limb paralysis or weakness loss of sensation to lower limbs dislocated hips urinary and or bowel incontinence club foot hydrocephalus scoliosis poor eye-hand co-ordination learning difficulties contractures TREATMENT There is no cure for spina bifida. However dietary supplementation with folic acid (folate) has shown to help prevent spina bifida. The nerve tissue that is damaged or lost cannot be repaired or replaced, nor can function be restored to the damaged nerves. Treatment depends on the type and severity of the disorder. It requires a multi-disciplinary approach. Generally, children with the mild form need no treatment, although some may require surgery as they grow (to close the defect) or for a shunt incase of hydrocephalus. Club foot can be corrected. PHYSIOTHERAPY TREATMENT 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) 6) 7) 8) 9) 10) 11) Assessment and/or Identification of all impairment associated with spina bifida Assisting child to gain independency Exercises for strength, balance and muscle control Provision of assistive devices to where they needed Bowel and bladder management Helping Prevent and correction of contractures at childhood development Referring for Surgery and Orthopedic correction Prevention of pressure sores Prevention of secondary complications as a result of spina bifida Regular checking of the skin and carefully positioning of lower limbs to minimize injuries due to loss of sensation.